Abstract
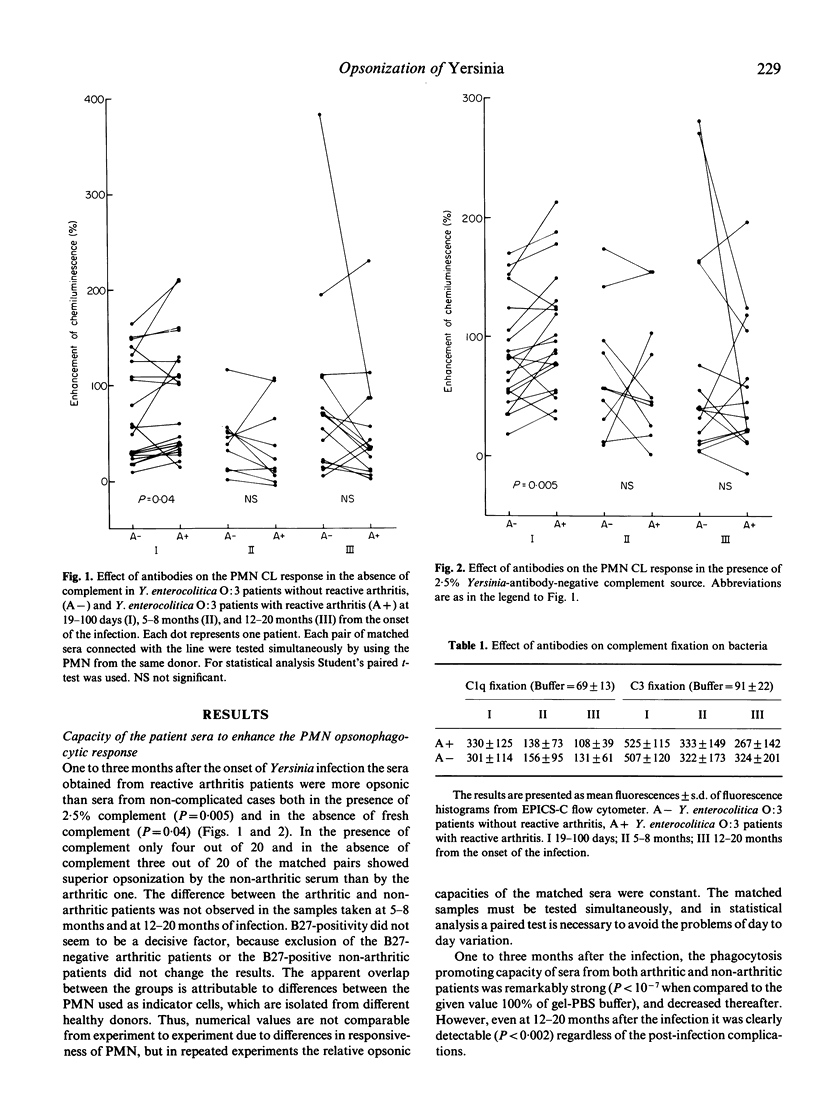
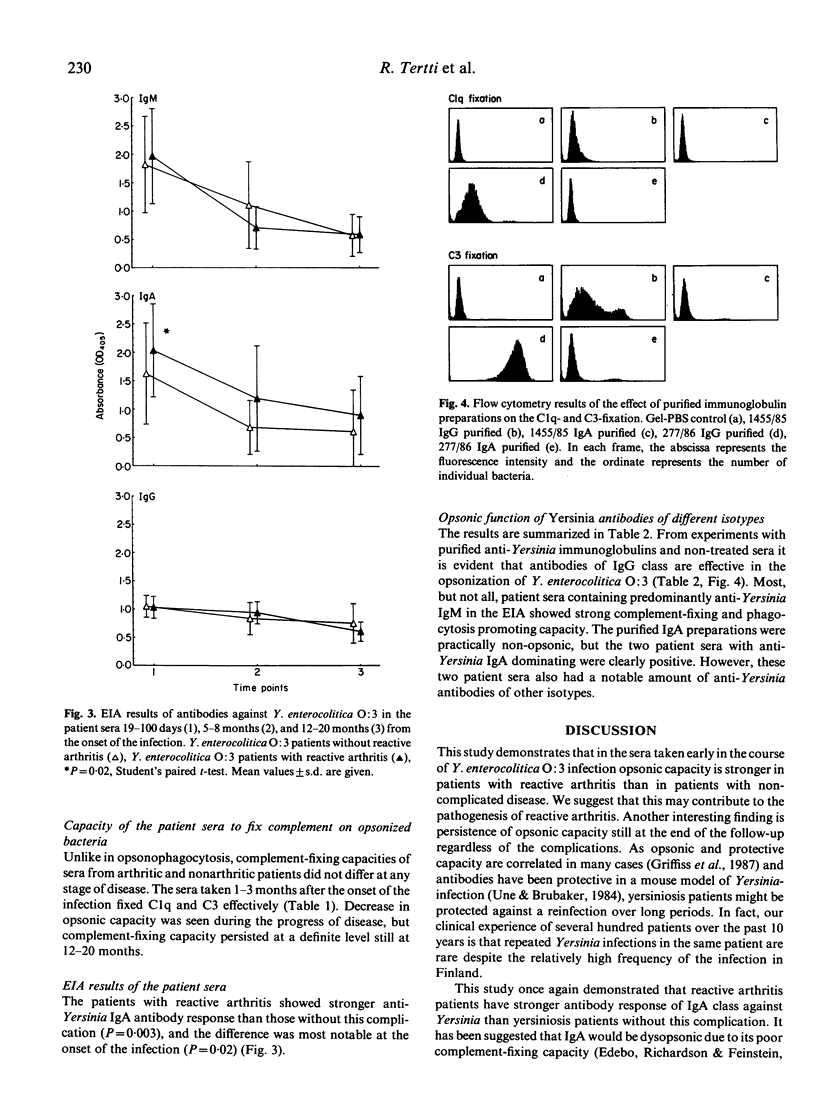
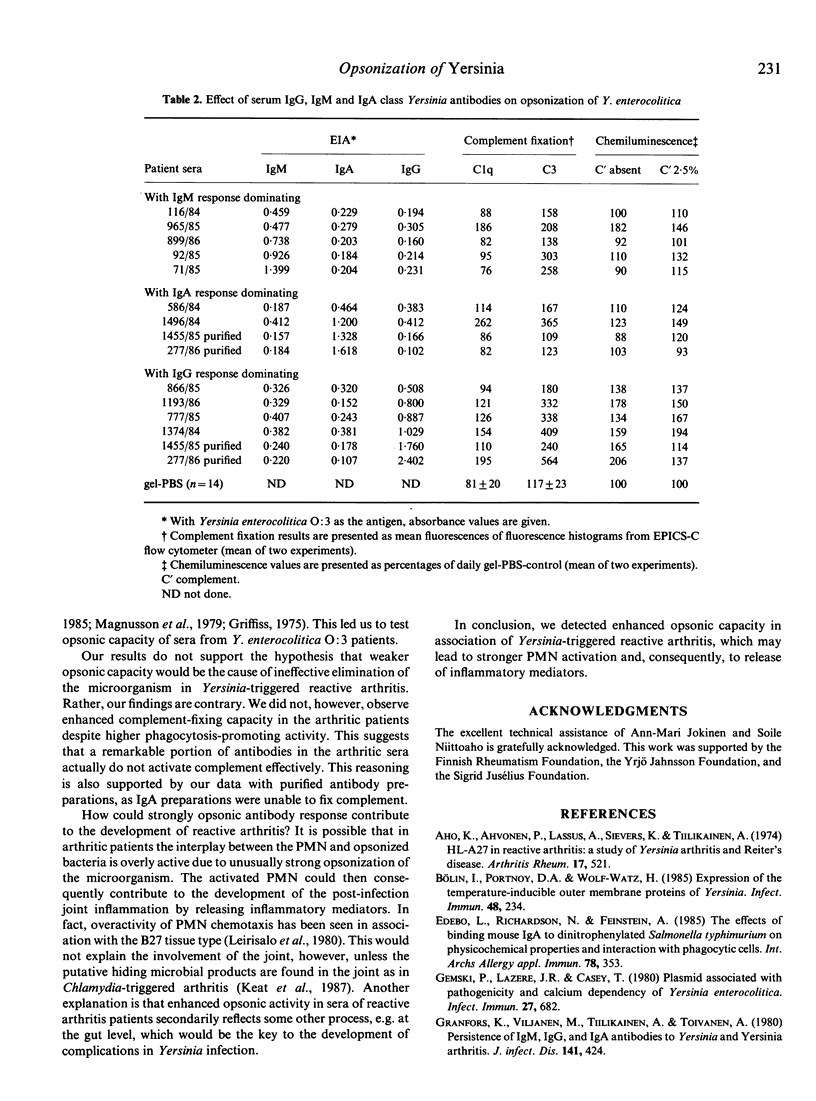
The opsonic capacity of 45 sera from patients with reactive arthritis after Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 infection and of 45 matched sera from yersiniosis patients without post-infection complications was studied at 1-3 months, 5-8 months and 12-20 months after the onset of the infection. Antibody-mediated opsonization of virulence-plasmid-containing Y. enterocolitica O:3 was studied by measuring complement-fixation on opsonized bacteria and opsonophagocytic function of the polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN). The PMN response against bacteria pre-opsonized by heat-inactivated sera was measured by using a chemiluminescence (CL) assay. The fixation of complement Clq and C3 on bacteria was determined by flow cytometry using fluorescein-conjugated Clq- and C3c-antisera. All the sera were strongly opsonic at the onset of the infection, and this capacity persisted in most of the patients still at the end of the follow-up. No difference was observed in complement-fixing capacity between the sera of the two groups, but the sera from arthritic patients showed stronger augmentation of PMN CL response at the early phase of the infection (P = 0.005 in the presence of complement, P = 0.04 in the absence of complement). These results suggest that enhanced opsonic capacity may play a role in the development of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis by leading to strong activation of the PMN and, consequently, to release of inflammatory mediators.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Ahvonen P., Lassus A., Sievers K., Tiilikainen A. HL-A 27 in reactive arthritis. A study of Yersinia arthritis and Reiter's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Sep-Oct;17(5):521–526. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edebo L., Richardson N., Feinstein A. The effects of binding mouse IgA to dinitrophenylated Salmonella typhimurium on physicochemical properties and interaction with phagocytic cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;78(4):353–357. doi: 10.1159/000233912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M. K., Toivanen A. Measurement of immunoglobulin M, immunoglobulin G, and immunoglobulin A antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: comparison of lipopolysaccharide and whole bacterium as antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.6-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M., Tiilikainen A., Toivanen A. Persistence of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies to Yersinia in yersinia arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):424–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Apicella M. A., Greenwood B., Mäkelä P. H. Vaccines against encapsulated bacteria: a global agenda. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):176–188. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal activity of meningococcal antisera. Blocking by IgA of lytic antibody in human convalescent sera. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keat A., Thomas B., Dixey J., Osborn M., Sonnex C., Taylor-Robinson D. Chlamydia trachomatis and reactive arthritis: the missing link. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):72–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91910-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Granfors K., Kekomäki R., Toivanen A. Circulating yersinia specific immune complexes after acute yersiniosis: a follow up study of patients with and without reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Feb;46(2):121–126. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Lehtonen O. P., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Avidity of anti-Yersinia antibodies in yersiniosis patients with and without Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Oct;30(10):1176–1181. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Pai C. H. Inhibition of human neutrophil chemiluminescence by plasmid-mediated outer membrane proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.145-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Stjernström I., Edebo L. Reduction of phagocytosis, surface hydrophobicity and charge of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MR10 by reaction with secretory IgA (SIgA). Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):439–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet M., Berche P., Mazigh D., Veron M. Protection against Yersinia infection induced by non-virulence-plasmid-encoded antigens. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Oct;20(2):225–231. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Bölin I., Heikkinen H., Piha S., Wolf-Watz H. Virulence plasmid-associated autoagglutination in Yersinia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1033-1036.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlberg T. H., Tertti R., Wolf-Watz H., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Antibody response in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis III infection: analysis of an outbreak. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):388–391. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Eerola E., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Pekkola-Heino K., Toivanen A. Role of antibodies in the opsonization of Yersinia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1295–1300. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1295-1300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Eerola E., Lehtonen O. P., Ståhlberg T. H., Viander M., Toivanen A. Virulence-plasmid is associated with the inhibition of opsonization in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):266–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Leino R., Ståhlberg T., Vuento R. Pathogenesis of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: immunological, microbiological and clinical aspects. Immunol Rev. 1985 Aug;86:47–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Vuento R., Granfors K. Association of persisting IgA response with yersinia triggered reactive arthritis: a study on 104 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Dec;46(12):898–901. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.12.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence and immunity in yersiniae. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento R., Leino R., Viander M., Toivanen A. In vitro lymphoproliferative response to Yersinia: depressed response in arthritic patients years after Yersinia infection. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1983 Jul-Sep;1(3):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


