Abstract
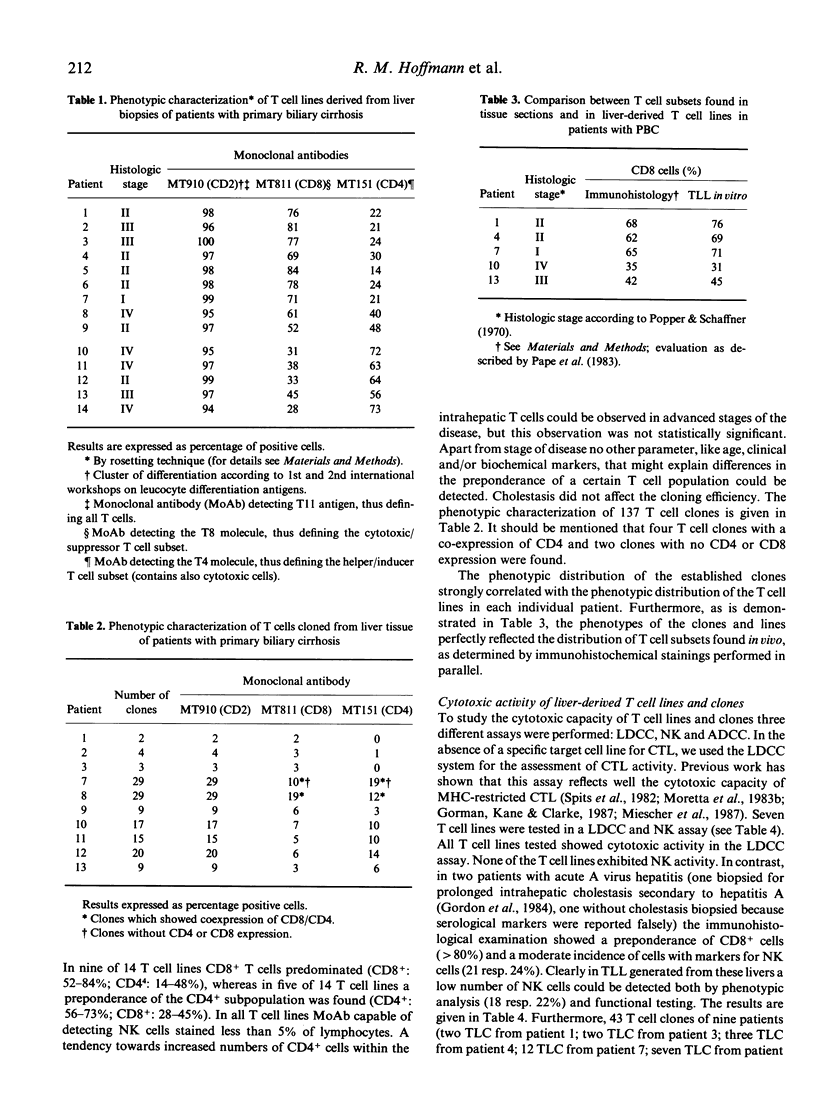
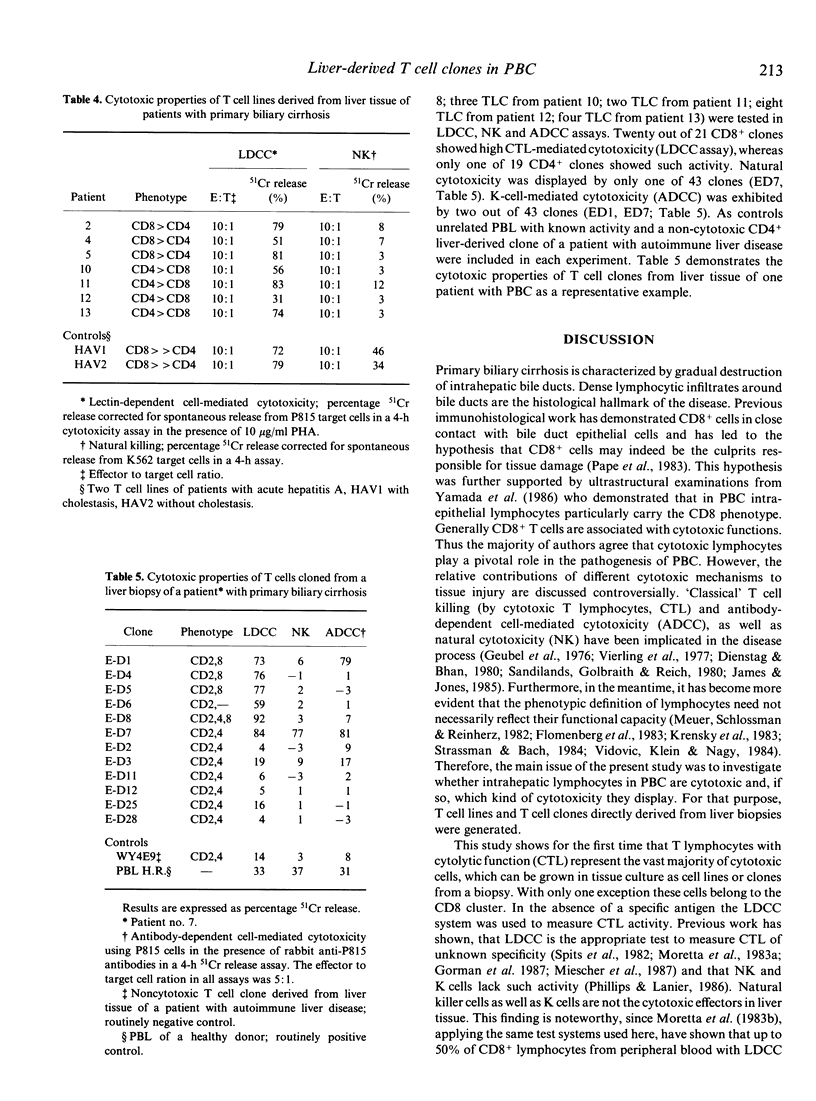
Lymphocyte infiltration in liver tissue is one important histological finding in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). So far, functional analyses of lymphocytes in PBC have focused on circulating lymphocytes, whereas lymphocytes at the involved site, the liver, have not been examined functionally. We have established interleukin 2 (IL-2)-dependent T lymphocyte lines (TLL) and clones (TLC) from liver biopsies of 14 patients with PBC. Phenotypic analysis using the monoclonal antibodies MT910 (CD2), MT811 (CD8), and MT151 (CD4) revealed that in nine of 14 TLL cytotoxic-suppressor T cells predominated (CD8+:52-84%; CD4+:14-48%), whereas in five of 14 TLL a preponderance of the CD4+ subpopulation was found (CD4+:56-73%; CD8+:28-45%). From 10 patients 137 TLC were generated which phenotypically correlated to the TLLs. We have tested the cytotoxic potential of seven TLL and 43 TLC in LDCC (lectin-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity), NK (natural killing) and ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity) assays. All TLL and all but one CD8+ TLC tested showed high activity in the LDCC assay, reflecting the cytolytic activity of cytotoxic T cells (CTL). CD4+ clones with LDCC activity were rarely found. NK activity and K cell activity could only be found in two clones. For the first time TLC and TLL from liver tissue of PBC patients could be generated. The high cytotoxic activity displayed by T cells derived from the liver indicates an important role for this immunological mechanism in the tissue damaging process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballardini G., Mirakian R., Bianchi F. B., Pisi E., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigens on bileduct epithelium in primary biliary cirrhosis: relevance to pathogenesis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1009–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Bhan A. K. Enhanced in vitro cell-mediated cytotoxicity in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: absence of specificity for virus-expressed antigen on target cell membranes. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2269–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Lysis of bystander target cells after triggering of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):1021–1024. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Wagner H. Significance of T4 or T8 phenotype of human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clones. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;126:101–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71152-7_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg N., Naito K., Duffy E., Knowles R. W., Evans R. L., Dupont B. Allocytotoxic T cell clones: both Leu 2+3- and Leu 2-3+ T cells recognize class I histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Nov;13(11):905–911. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geubel A. P., Keller R. H., Summerskill W. H., Dickson E. R., Tomasi T. B., Shorter R. G. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition studied with autologous liver cells: observations in chronic active liver disease and the primary biliary cirrhosis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S. C., Reddy K. R., Schiff L., Schiff E. R. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):635–637. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman K. C., Kane K. P., Clark W. R. Target cell recognition structures in LDCC and ODCC. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1014–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Hercend T., Beveridge R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of an antigen expressed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2947–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann R. M., Pape G. R., Rieber P., Eisenburg J., Döhrmann J., Zachoval R., Paumgartner G., Riethmüller G. Cytolytic T cell clones derived from liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1635–1638. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Hoofnagle J. H., Strober W., Jones E. A. NIH conference: Primary biliary cirrhosis: a model autoimmune disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):500–512. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Jones E. A. Abnormal natural killer cytotoxicity in primary biliary cirrhosis: evidence for a functional deficiency of cytolytic effector cells. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90758-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Vierling J. M., Strober W. The role of the immune response in the pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 1981 Nov;1(4):322–337. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Clayberger C., Greenstein J. L., Crimmins M., Burakoff S. J. A DC-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte line is OKT8+1. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2777–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmeyer J., Rieber P., Feucht H., Johnson J., Hadam M., Riethmüller G. A subset of human cells isolated and characterized by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Dec;11(12):997–1001. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonal analysis of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes: T4+ and T8+ effector T cells recognize products of different major histocompatibility complex regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4395–4399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Corte G., Mingari M. C., Moretta L. Human T cell subpopulations defined by a monoclonal antibody. II. Evidence for cell cooperation in the response to alloantigens and generation of cytolytic cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Moretta L., Cerottini J. C., Mingari M. C. Direct demonstration of the clonogenic potential of every human peripheral blood T cell. Clonal analysis of HLA-DR expression and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):743–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Cerottini J. C. Quantitative assessment of the pool size and subset distribution of cytolytic T lymphocytes within human resting or alloactivated peripheral blood T cell populations. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):571–585. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Moretta L., Troye M., Perlmann P. Natural cytotoxicity of human Fc gamma-receptor-positive T lymphocytes after surface modulation with immune complexes. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):291–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Rieber E. P., Eisenburg J., Hoffmann R., Balch C. M., Paumgartner G., Riethmüller G. Involvement of the cytotoxic/suppressor T-cell subset in liver tissue injury of patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Troye M., Axelsson B., Perlmann P. Simultaneous occurrence of immunoglobulin-dependent and immunoglobulin-independent mechanisms in natural cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2251–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Lectin-dependent and anti-CD3 induced cytotoxicity are preferentially mediated by peripheral blood cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing Leu-7 antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1579–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Schaffner F. Nonsuppurative destructive chronic cholangitis and chronic hepatitis. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:336–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber P., Lohmeyer J., Schendel D. J., Riethmüller G. Human T cell differentiation antigens characterizing a cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset. Hybridoma. 1981;1(1):59–69. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1981.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold H., Kraft D., Gastl G., Huber C. The relationship of HNK-1 (Leu 7) and VEP13 antigens on human cells mediating natural killing. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Sep;57(3):703–709. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandilands G. P., Galbraith I., Reid F. M., Mills P. R., MacSween R. N. Immune-complex inhibition of lymphocyte Fc gamma-receptors in primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible immunomodulatory mechanism. Lancet. 1980 Jul 5;2(8184):9–13. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92890-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler U., Pape G. R., Hoffmann R. M., Johnson J. P., Eisenburg J., Paumgartner G., Riethmüller G. Differential expression of MHC class II subregion products on bile duct epithelial cells and hepatocytes in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):459–462. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Borst J., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. The role of T cell differentiation markers in antigen-specific and lectin-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by T8+ and T4+ human cytotoxic T cell clones directed at class I and class II MHC antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1563–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassman G., Bach F. H. OKT4+ cytotoxic T cells can lyse targets via class I molecules and can be blocked by monoclonal antibody against T4 molecules. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1705–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidović D., Klein J., Nagy Z. A. The role of T cell subsets in the generation of secondary cytolytic responses in vitro against class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1113–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling J. M., Nelson D. L., Strober W., Bundy D. M., Jones E. A. In vitro cell-mediated cytotoxicity in primary biliary cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. Dysfunction of spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1116–1128. doi: 10.1172/JCI108863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada G., Hyodo I., Tobe K., Mizuno M., Nishihara T., Kobayashi T., Nagashima H. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical analysis of lymphocytes infiltrating bile duct epithelia in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):385–391. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


