Abstract
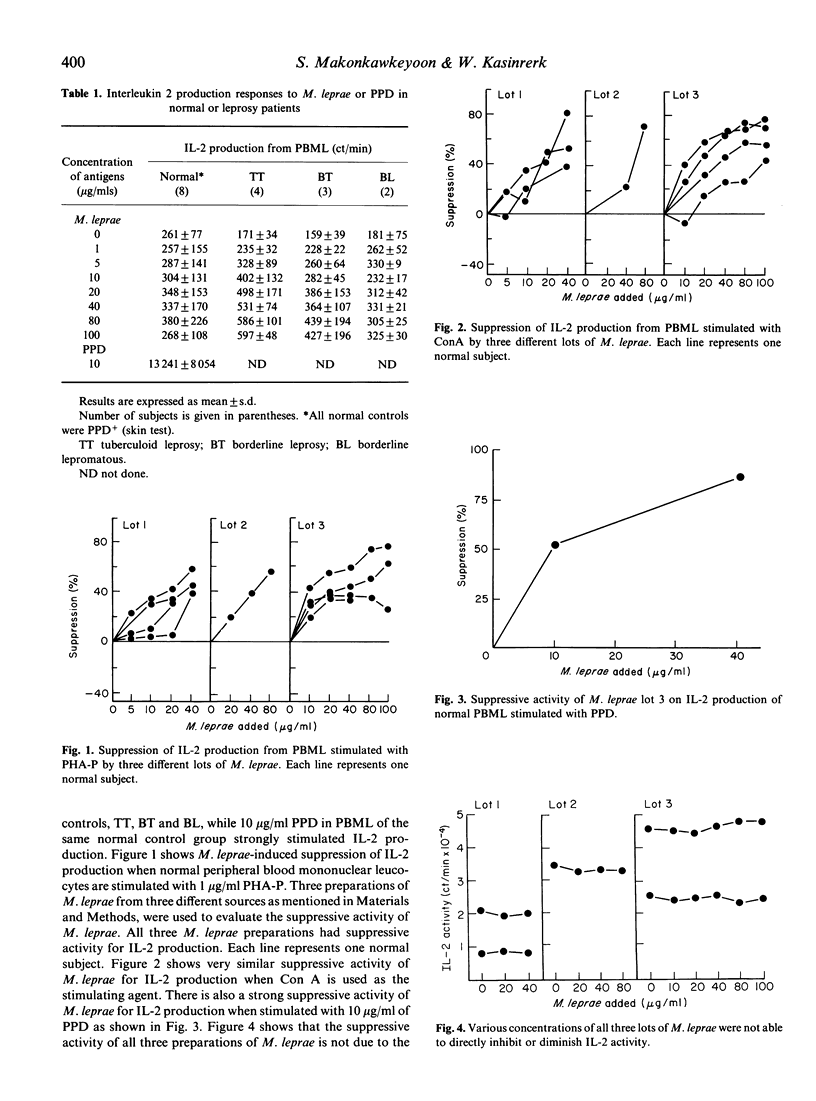
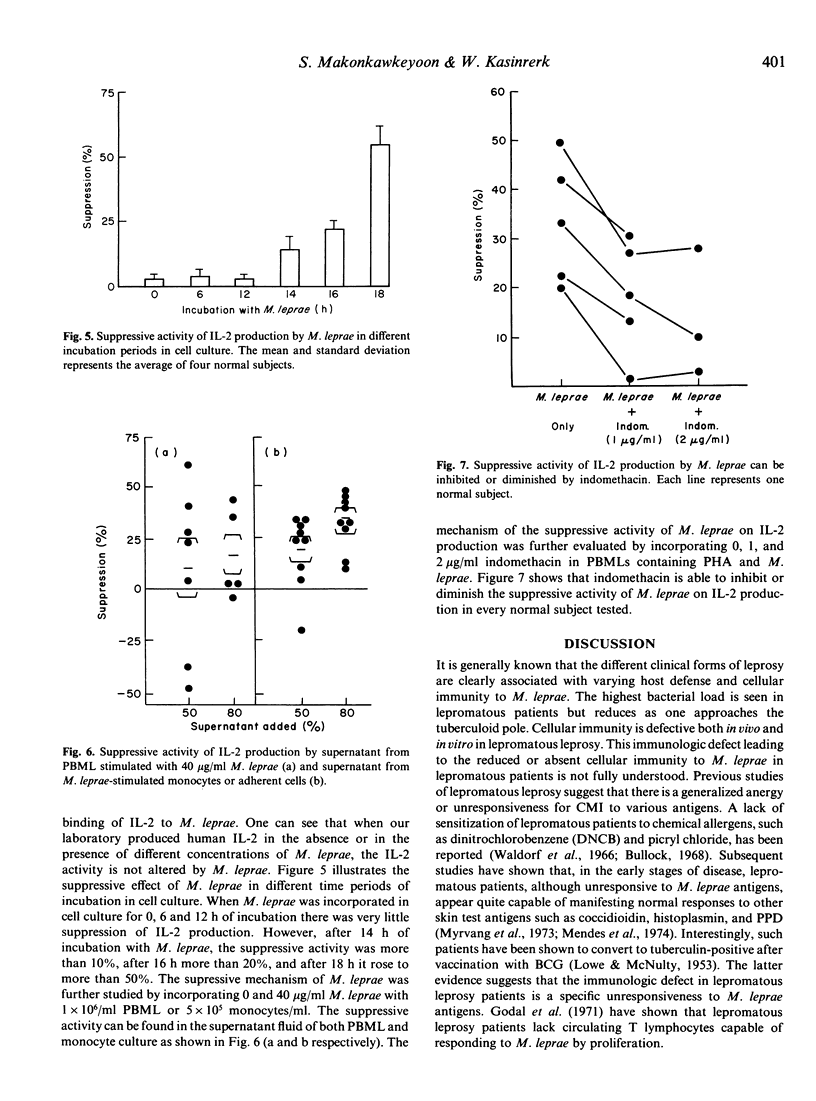
The suppressive activity of three different lots and sources of Mycobacterium leprae (M. leprae) was studied by measuring the inhibitory effect on interleukin 2 (IL-2) production in normal subjects. All three M. leprae preparations had suppressive activity on IL-2 production when peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes (PBML) were stimulated with the mitogens PHA-P or Con A in a dose response. M. leprae also had suppressive activity on IL-2 production when PBML were stimulated with the specific antigen, PPD. The inhibitory activity of M. leprae on IL-2 was not due to the direct interaction of M. leprae and IL-2 because direct mixing of IL-2 with different concentrations of M. leprae did not alter the activity of IL-2. Incorporation of M. leprae for 0, 6 and 12 h in PHA-P and PBML cultures had no inhibitory effect on IL-2 production; however, after 14, 16 and 18 h of M. leprae incorporation, significant inhibitory effects were noted on IL-2 production. The suppressive mechanism of M. leprae was studied by incorporating M. leprae into PBML or adherent cells. The suppressive activity could be detected in both M. leprae-stimulated PBML and M. leprae-stimulated monocyte supernatant fluids. The suppressive mechanism of M. leprae was further evaluated by incorporating 1 and 2 micrograms/ml of indomethacin in PBML containing PHA-P and M. leprae. The suppressive activity of M. leprae was significantly diminished by indomethacin, suggesting that the inhibitory effect of M. leprae may result from the induction of PBML and adherent cells to produce the immunosuppressive activity of prostaglandin(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birdi T. J., Mistry N. F., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Antigen specific macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in lepromatous leprosy. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1984 Apr;13(4):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G. In vitro lymphocyte stimulation in leprosy; simultaneous stimulation with Mycobacterium leprae antigens and phytohaemagglutinin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jun;36(3):479–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Watson S., Nelson K. E., Schauf V., Makonkawkeyoon S., Jacobson R. R. Aberrant immunoregulatory control of B lymphocyte function in lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):105–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Myklestad B., Samuel D. R., Myrvang B. Characterization of the cellular immune defect in lepromatous leprosy: a specific lack of circulating Mycobacterium leprae-reactive lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Dec;9(6):821–831. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Purification of murine T cell growth factor. A lymphocyte mitogen with helper activity. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):422–431. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Gandhi R. R., Weinstein D. E., Levis W. R., Patarroyo M. E., Brennan P. J., Cohn Z. A. Mycobacterium leprae antigen-induced suppression of T cell proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE J., MCNULTY F. [Tuberculosis and leprosy; immunological studies]. Lepr Rev. 1953 Apr;24(2):61–90. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19530008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makonkawkeyoon S., Hirunpetcharat C., Kasinrerk W., Vithayasai V. Enumeration of interleukin 2-producing cells from rat spleen. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 1987 Dec;5(2):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Brennan P. J., Rada E., Convit J., Bloom B. R. Lymphocyte suppression in leprosy induced by unique M. leprae glycolipid. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):194–196. doi: 10.1038/308194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Fields J. P., Bloom B. R. Lepromin-induced suppressor cells in patients with leprosy. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1813–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Rothman W., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. F., Bloom B. R. Delineation of a human T cell subset responsible for lepromin-induced suppression in leprosy patients. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1183–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes E., Raphael A., Mota N. G., Mendes N. F. Cell-mediated immunity in leprosy and transfer of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Apr;53(4):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvang B., Godal T., Ridley D. S., Fröland S. S., Song Y. K. Immune responsiveness to Mycobacterium leprae and other mycobacterial antigens throughout the clinical and histopathological spectrum of leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):541–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Singh R. The suppressive effect of M. leprae on the in vitro proliferative responses of lymphocytes from patients with leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):406–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. E., Wong L., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Modlin R. L. Lepromin-induced suppressor cells in lepromatous leprosy. Cell Immunol. 1987 Jan;104(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W. Leukotrienes and prostaglandins in the immune system. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1986;16:113–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad H. K., Mishra R. S., Nath I. Phenolic glycolipid-I of Mycobacterium leprae induces general suppression of in vitro concanavalin A responses unrelated to leprosy type. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):239–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P. R., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Mechanism of immunosuppression in leprosy: presence of suppressor factor(s) from macrophages of lepromatous patients. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1119–1126. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1119-1126.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathish M., Bhutani L. K., Sharma A. K., Nath I. Monocyte-derived soluble suppressor factor(s) in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):890–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.890-899.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Mshana R. N., Touw J., Belehu A. Studies on the defect in cell-mediated immunity in lepromatous leprosy using HLA-D-identical siblings. Absence of circulating suppressor cells and evidence that the defect is in the T-lymphocyte, rather than the monocyte, population. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Jan;15(1):33–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Bryceson A. D. Immunological phenomena in leprosy and related diseases. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:209–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf D. S., Sheagren J. N., Trautman J. R., Block J. B. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Lancet. 1966 Oct 8;2(7467):773–776. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


