Abstract
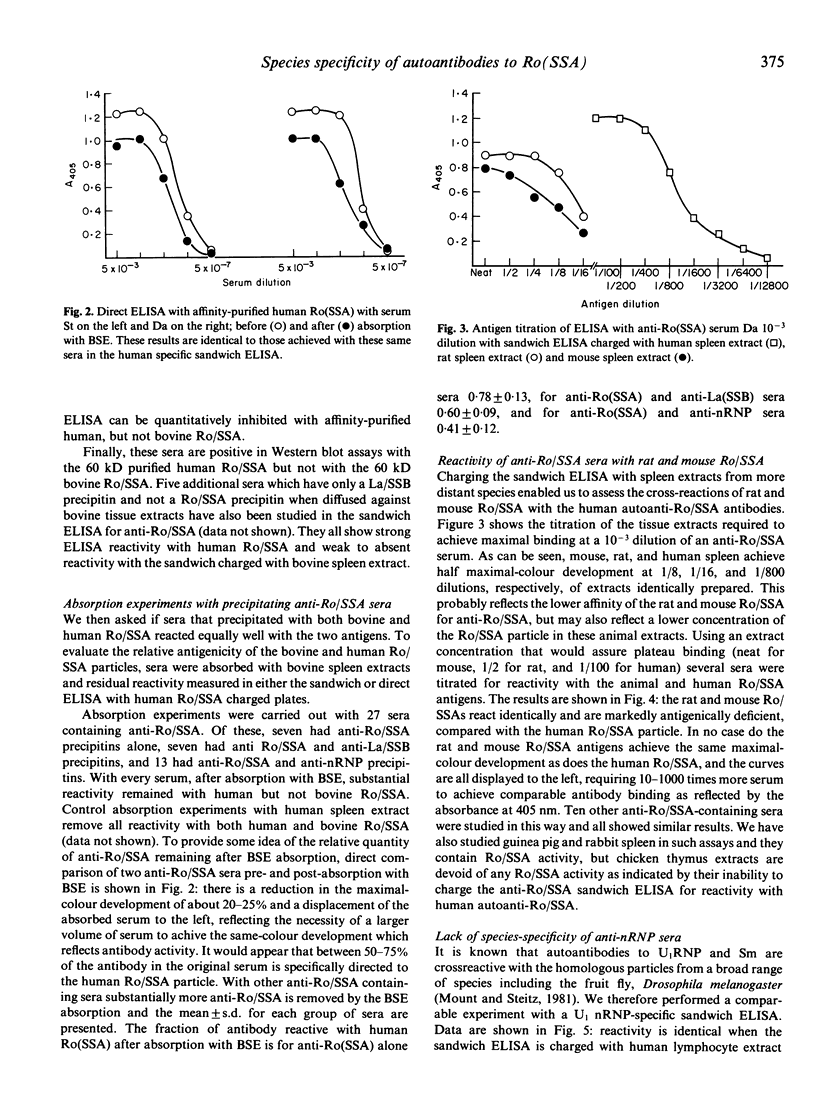
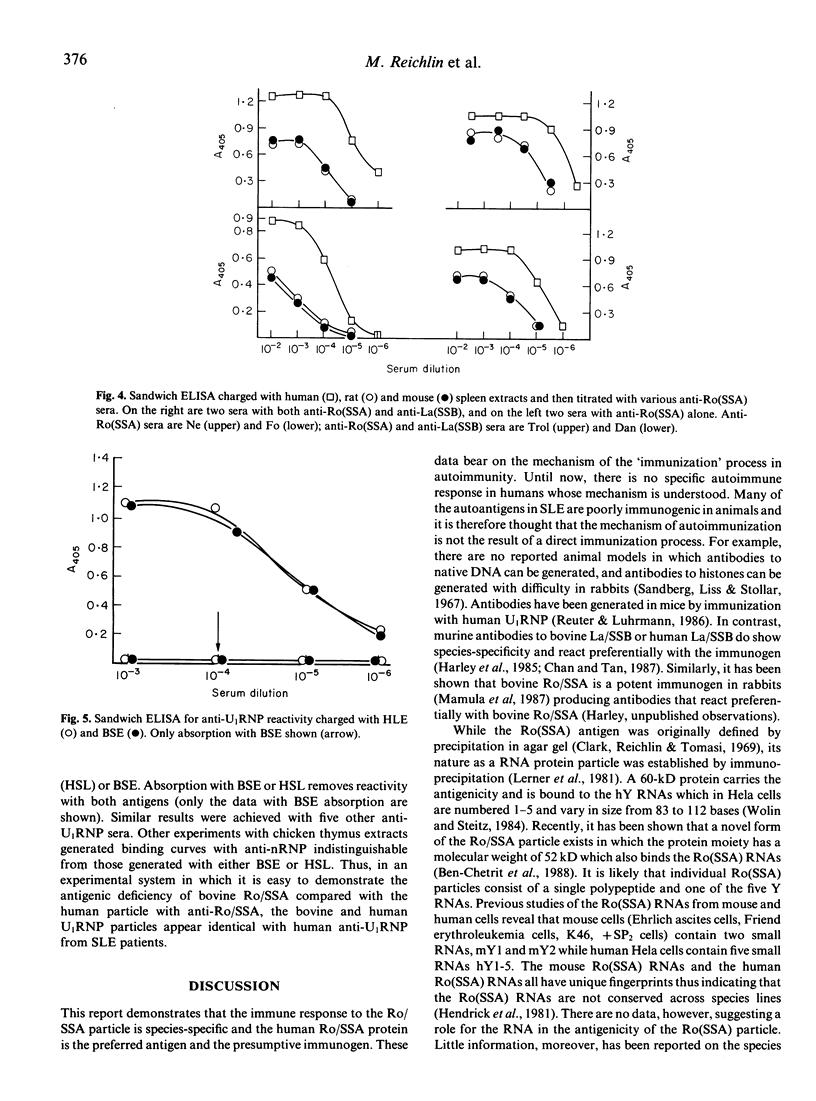
Autoantibodies to defined cellular antigens in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are usually directed to conserved epitopes on ubiquitous macromolecules including histone, Sm + nRNP (URNP particles), DNA, and La(SSB). We report here that the autoimmune response to the Ro(SSA) RNA protein particle is directed to epitopes on the human antigen which are not conserved in evolution. Ro(SSA) from bovine, rat, and mouse Ro(SSA) particles cross-react with human autoantibodies less effectively than does human Ro(SSA), and antigenically active Ro(SSA) is not detectable in chicken thymus extracts with the assays employed. These data suggest a special role for the Ro(SSA) antigen in the initiation and/or perpetuation of the anti-Ro(SSA) response in autoimmune disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Chetrit E., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. A 52-kD protein is a novel component of the SS-A/Ro antigenic particle. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1560–1571. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. T., Byfield P. G., Himsworth R. L., Shepherd P. Human autoantibodies to thyroglobulin are directed towards a restricted number of human specific epitopes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):516–523. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Tan E. M. Human autoantibody-reactive epitopes of SS-B/La are highly conserved in comparison with epitopes recognized by murine monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1627–1640. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G., Reichlin M., Tomasi T. B., Jr Characterization of a soluble cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythmatosus. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Tan E. M., Traugh J. A. Myositis autoantibody reactivity and catalytic function of threonyl-tRNA synthetase. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2376–2379. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.2452112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Alexander E. L., Bias W. B., Fox O. F., Provost T. T., Reichlin M., Yamagata H., Arnett F. C. Anti-Ro (SS-A) and anti-La (SS-B) in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;29(2):196–206. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Rosario M. O., Yamagata H., Fox O. F., Koren E. Immunologic and structural studies of the lupus/Sjögren's syndrome autoantigen, La/SSB, with a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):801–806. doi: 10.1172/JCI112037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs R. L., Reddy R., Cook R. G., Yeoman L. C., Tan E. M., Reichlin M., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of a nucleolar scleroderma antigen (Mr = 34,000; pI, 8.5) rich in NG,NG-dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14304–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M. Myositis autoantibody inhibits histidyl-tRNA synthetase: a model for autoimmunity. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):177–179. doi: 10.1038/304177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Reichlin M., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R. M. Anti-threonyl-tRNA synthetase, a second myositis-related autoantibody. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):420–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Akizuki M., Yamagata H., Inada S., Yoshida S., Homma M. Characterization of a high molecular weight acidic nuclear protein recognized by autoantibodies in sera from patients with polymyositis-scleroderma overlap. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):611–620. doi: 10.1172/JCI110295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikai M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of precipitating antibodies in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Characterization of the Jo-1 antibody system. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):881–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye L., Pontes de Carvalho L. C., Roitt I. M. Restrictions in the response to autologous thyroglobulin in the human. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Harley J. B. Detection by ELISA of antibodies to small RNA protein particles in systemic lupus erythematosus patients whose sera lack precipitins. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1986;99:161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Lührmann R. Immunization of mice with purified U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RNP) induces a pattern of antibody specificities characteristic of the anti-Sm and anti-RNP autoimmune response of patients with lupus erythematosus, as measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8689–8693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLAR D., LEVINE L., MARMUR J. Antibodies to enatured deoxyribonucleic acid in lupus erythematosus serum. II. Characterization of antibodies in several sera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 9;61:7–18. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Liss M., Stollar B. D. Rabbit antibodies induced by calf thymus histone-serum albumin complexes. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1182–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Hall R. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves' disease. Lancet. 1974 Aug 24;2(7878):427–431. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91815-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Varying specificity of systemic lupus erythematosus sera for histone fractions and a periodate-sensitive antigen associated with histone. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):804–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIENER A. S., UNGER L. J., COHEN L., FELDMAN J. Type-specific cold auto-antibodies as a cause of acquired hemolytic anemia and hemolytic transfusion reactions: biologic test with bovine red cells. Ann Intern Med. 1956 Feb;44(2):221–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-44-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. The Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins: identification of the antigenic protein and its binding site on the Ro RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Harley J. B., Reichlin M. Molecular properties of the Ro/SSA antigen and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of antibody. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):625–633. doi: 10.1172/JCI111460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D. C., Dang C. V., Arnett F. C. Rat liver histidyl-tRNA synthetase. Purification and inhibition by the myositis-specific anti-Jo-1 autoantibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



