Abstract
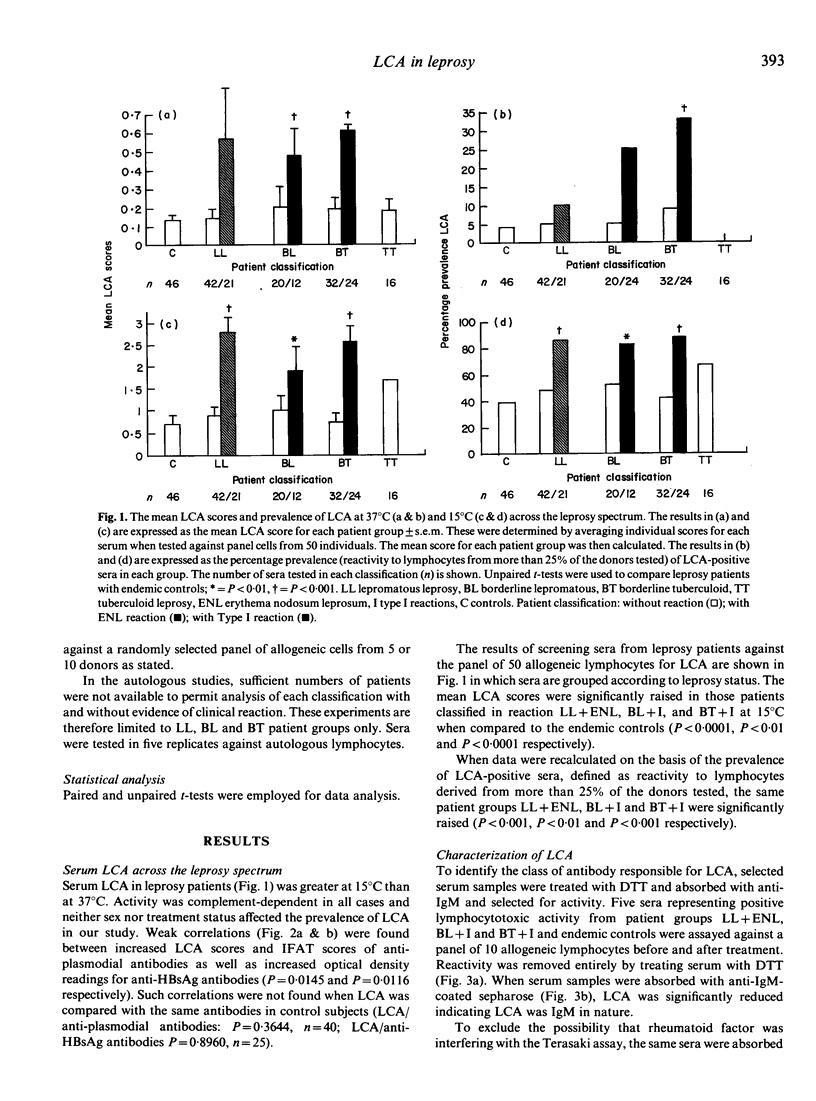
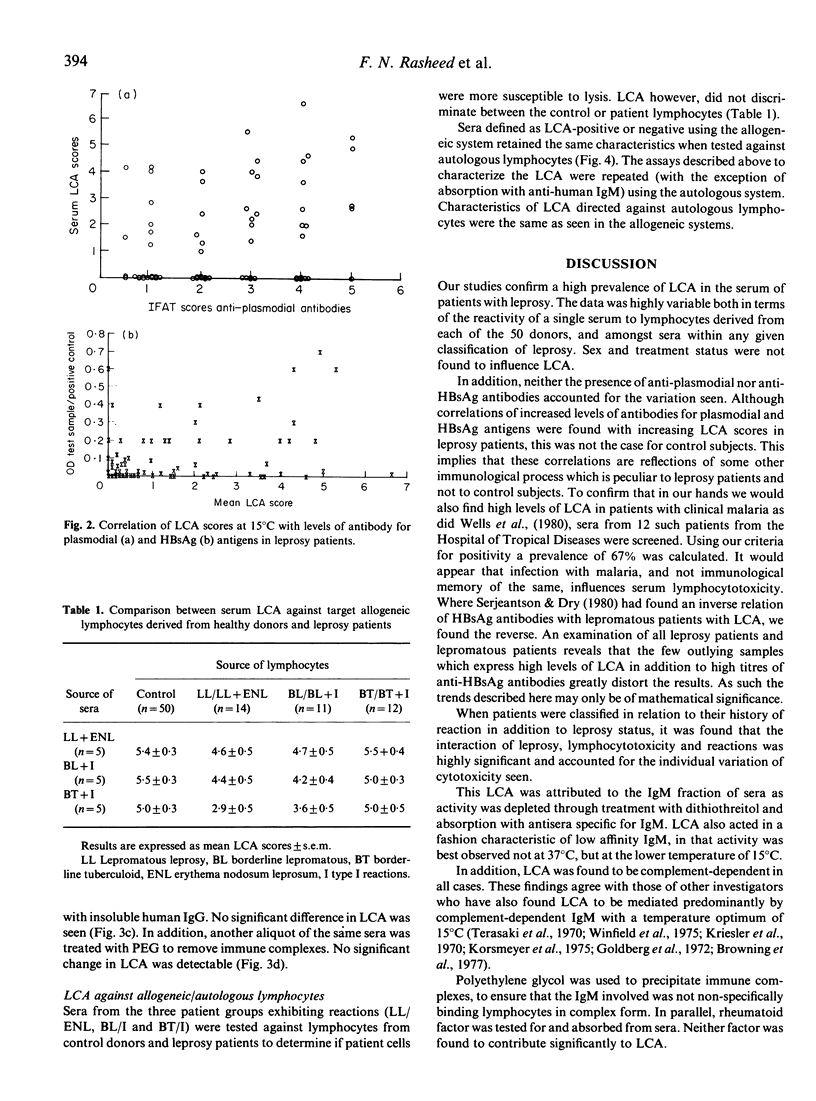
Sera from 167 patients across the spectrum of leprosy and 46 endemic controls were screened for lymphocytotoxic activity (LCA). The Terasaki microdroplet lymphocytotoxicity assay was performed at 37 degrees C and 15 degrees C to test sera for LCA against a panel of lymphocytes from 50 donors which represented most known HLA-ABC antigens. Raised complement-dependent LCA at 15 degrees C was seen in leprosy patients with histories of erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) or reversal/Type I (I) reactions. Eighty-six per cent of lepromatous (LL) patients with a history of ENL (n = 21, P less than 0.001), 83% of borderline lepromatous (BL) and 88% of borderline tuberculoid patients (BT) with a history of Type I reactions (n = 12, P less than 0.01 and n = 24, P less than 0.001 respectively) had LCA compared to 39% of endemic controls (n = 46). LCA was attributed to IgM on the basis of reduced activity when serum was treated with both dithiothreitol or absorbed with antiserum for IgM. Removal of immune complexes and rheumatoid factor did not influence LCA. LCA-positive sera reacted similarly with allogeneic lymphocytes from either healthy donors or leprosy patients. Moreover LCA-positive sera reacted with autologous lymphocytes. Specificities for HLA-ABC antigens were not identified. The potential role of these autoantibodies, manifested in leprosy patients with hypersensitivity reactions remains speculative.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNET F. M., HOLMES M. C. THYMIC CHANGES IN THE MOUSE STRAIN NZB IN RELATION TO THE AUTO-IMMUNE STATE. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:229–241. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Decline in suppressor T cell function with age in female NZB mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning J. D., Dick H. M., El-Ghobarey A., Dick W. C. Levamisole, rheumatoid arthritis, and cold lymphocytotoxic antibodies. Lancet. 1977 Oct 15;2(8042):820–820. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90752-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Messner R. P. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in family members of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1254–1258. doi: 10.1172/JCI108044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deierhoi M. H., Ting A., Morris P. J. Reactivity of lymphocyte cytotoxic autoantibodies from renal patients with cell line K562. Transplantation. 1984 Nov;38(5):557–558. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198411000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. S., Cunningham J. E., Terasaki P. I. Lymphocytotoxins and pernicious anemia. Blood. 1972 Jun;39(6):862–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Pfister R., Stingl G. Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic antibodies (CLA) in systemic lupus erythematosus preferentially inhibit the generation of alloreactive cytotoxic T cells in secondary CML. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Dec;50(3):525–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloster B. E., Tomar R. H., Spira T. J. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Feb;30(2):330–335. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Williams R. C., Jr, Wilson I. D., Strickland R. G. Lymphocytotoxic antibody in inflammatory bowel disease. A family study. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 27;293(22):1117–1120. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511272932203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisler J. M., Arnaiz A., Perez B., Bootello A. Lumphocytotoxins in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1975 Apr-Jun;43(2):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levo Y., Waisman Y., Ehrenfeld M. Lymphocytotoxins in rheumatoid arthritis. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Nov;16(11):791–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendius J. R., DeHoratius R. J., Messner R. P., Williams R. C. Family distribution of lymphocytotoxins in Hodgkin's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Feb;84(2):151–156. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michlmayr G., Pathouli C., Huber C., Huber H. Antibodies for T lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Apr;24(1):18–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Bakke A. C., Vaccaro S. A., Horwitz D. A., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. Tissue and blood T-lymphocyte subpopulations in erythema nodosum leprosum. Arch Dermatol. 1985 Feb;121(2):216–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Gebhard J. F., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ characterization of T lymphocyte subsets in the reactional states of leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):17–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Borel Y., Schlossman S. F. Direct demonstration of the human suppressor inducer subset by anti-T cell antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Distaso J. A., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus T cell subsets, anti-T cell antibodies, and T cell functions. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):689–700. doi: 10.1172/JCI111261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik S., Kumar B., Kaur S., Sehgal S. Cold reactive lymphocytotoxic antibodies in patients with tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1987 Jun;55(2):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R. B., Laal S., Sharma A. K., Bhutani L. K., Nath I. Differences in predominant T cell phenotypes and distribution pattern in reactional lesions of tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):623–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. S., Orlina A. R., Pesce A. J., Mendoza N., Masaitis L., Pollak V. E. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):237–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parés A., Martorell J., Caballería J., Vives J., Bruguera M., Rodés J. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Sep;30(9):829–833. doi: 10.1007/BF01309512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Capes H., Baur R., Wenzel B. E., Row V. V., Volpé R. Biological activity of lymphocytotoxic antibodies in Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Endocrinol Invest. 1984 Feb;7(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/BF03348368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIDLEY D. S., JOPLING W. H. A classification of leprosy for research purposes. Lepr Rev. 1962 Apr;33:119–128. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19620014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Waters M. F. Significance of variations within the lepromatous group. Lepr Rev. 1969 Jul;40(3):143–152. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumbach L., Tongio M. M., Warter J. M., Marescaux C., Mayer S., Rohmer F. Lymphocytotoxic and monocytotoxic antibodies in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Dec;3(4):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Dysfunction of suppressor T-cell activity related to impaired generation of, rather than response to, suppressor cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):657–664. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S., Dry P. Lymphocytotoxins in leprosy and in asymptomatic hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):289–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker R. B., McHugh T. M., Moody D. J., Morrow W. J., Stites D. P., Shuman M. A., Levy J. A. An AIDS-related cytotoxic autoantibody reacts with a specific antigen on stimulated CD4+ T cells. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):710–713. doi: 10.1038/327710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G., Miller W. C., Volpicelli N. A., Gaeke R. F., Wilson I. D., Kirsner J. B., Williams R. C., Jr Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and their spouses--evidence for a transmissible agent. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):188–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsinger P. D. Relationship of lymphocytotoxic antibodies to lymphopenia and parameters of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1976 Jun;3(2):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. A., Pavanand K., Zolyomi S., Permpanich B., Macdermott R. P. Anti-lymphocytotoxic antibodies in sera of Thai adults infected with Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Mar;39(3):663–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E., Okoye R., Ollier B., Festenstein H. Re.: A simple box method for freezing lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Association of cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies with lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):587–594. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


