Abstract
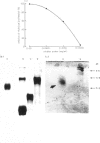
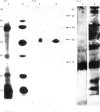
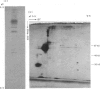
An inhibitor of interleukin-1 (IL-1) was purified to homogeneity from febrile human urine by using a sequence of ammonium sulphate fractionation, DEAE-cellulose chromatography and gel filtration on a column of ACA 54. The inhibitor was a sialoglycoprotein and its molecular weight, examined by SDS-PAGE, was found to be 30 kD. It was acidic in nature and its isoelectric point, determined by electrofocusing on thin-layer polyacrylamide gels, was found to be 3.5-3.6. The inhibitor was sensitive to the action of sialidase from Vibrio cholerae as the enzyme treated material was electrofocused at a higher pH range (4.5-5.2). The inhibitor contained 10% sialic acid as estimated by the Thiobarbituric acid assay. It interacted with the lectins jacalin and concanavalin A, suggesting the presence of carbohydrate moieties such as galactose and mannose. The inhibitor did not block the specific binding of IL-1 to cells, nor did it directly bind IL-1. Early rejection urine from a kidney transplant patient was also found to contain the 30 kD IL-1 inhibitor protein. This was visualised by immunoblotting using specific antibody raised against the 30 kD IL-1 inhibitor isolated from the urine of febrile patients.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L., Tollaksen S. L. Proteins of human urine. I. Concentration and analysis by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1979 Jul;25(7):1199–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak V., Treves A. J., Yanai P., Halperin M., Wasserman D., Biran S., Braun S. Interleukin 1 inhibitory activity secreted by a human myelomonocytic cell line (M20). Eur J Immunol. 1986 Nov;16(11):1449–1452. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. M., Muchmore A. V., Rosenstreich D. L. Uromodulin, an immunosuppressive protein derived from pregnancy urine, is an inhibitor of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9119–9123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. M., Rosenstreich D. L. Mechanism of action of a human interleukin 1 inhibitor. Cell Immunol. 1987 Mar;105(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hession C., Decker J. M., Sherblom A. P., Kumar S., Yue C. C., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Kawashima E., Schmeissner U., Heletky S. Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein): a renal ligand for lymphokines. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1479–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.3498215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Immunological responses of rabbits to various somatic and secreted antigens of Vibrio cholerae after intra-duodenal inoculation. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Aug;24(1):29–40. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Z., Grimshaw R. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Identification of a specific interleukin 1 inhibitor in the urine of febrile patients. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):126–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Z., Haimovitz A., Chen Y., Chan J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of a human interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3882–3886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil J. Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1980;37:157–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Uromodulin. An immunosuppressive 85-kilodalton glycoprotein isolated from human pregnancy urine is a high affinity ligand for recombinant interleukin 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13404–13407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Uromodulin: a unique 85-kilodalton immunosuppressive glycoprotein isolated from urine of pregnant women. Science. 1985 Aug 2;229(4712):479–481. doi: 10.1126/science.2409603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli K. A., Stern A. S., Kilian P. L. Detergent solubilization of the interleukin 1 receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2249–2253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roque-Barreira M. C., Campos-Neto A. Jacalin: an IgA-binding lectin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1740–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Tu J. H., Kinkade P. R., Maurer-Fogy I., Kahn J., Barton R. W., Farina P. R. A human urine-derived interleukin 1 inhibitor. Homology with deoxyribonuclease I. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1767–1779. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Lowenthal J. W., Williamson K., Dayer J. M., MacDonald H. R. A urine inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity that blocks ligand binding. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1546–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Williamson K., Balavoine J. F., Mach B., Mazzei G., Shaw A., Dayer J. M. A urine inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity affects both interleukin 1 alpha and 1 beta but not tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1541–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Bendtzen K. Inhibitor of interleukin 1 in normal human urine. Different effects on mouse thymocytes and on a murine T-cell line. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh L. J., Lander P. E., Seymour G. J., Powell R. N. Isolation and purification of ILS, an interleukin 1 inhibitor produced by human gingival epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):366–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. H. Urinary protein analysis. J Chromatogr. 1988 Jul 29;429:315–344. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83876-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]