Abstract
S-antigen, a photoreceptor cell protein, induces a predominantly T-cell mediated autoimmune uveitis in many vertebrate animals, including primates. Because of this activity and the finding of immune responses to S antigen in patients with uveitis, this protein has been implicated in the pathogenesis of uveitis in humans. Peptide M, an 18-amino acid component of S antigen, has previously been shown to be highly uveitopathogenic in rats and guinea pigs. We report here that peptide M is immunopathogenic in some monkeys, producing inflammatory changes in eyes and pineal glands similar to those induced by native S antigen. Monkeys with disease also developed intense immune responses to peptide M, measured by the lymphocyte proliferation assay. In addition, lymphocytes from these monkeys reacted against whole S antigen. Furthermore, lymphocytes from certain monkeys immunized with whole S antigen responded well against peptide M, thus indicating that this peptide is an immunodominant epitope in these animals. Two of the four monkeys immunized with peptide M did not develop disease. Lymphocytes from these two animals did not respond in culture against the peptide. Following immunization with the whole protein, these monkeys were capable, however, of developing cellular immunity against S antigen and one of them developed disease. The possible involvement of peptide M in the pathogenesis of uveitis in humans is discussed.
Full text
PDF

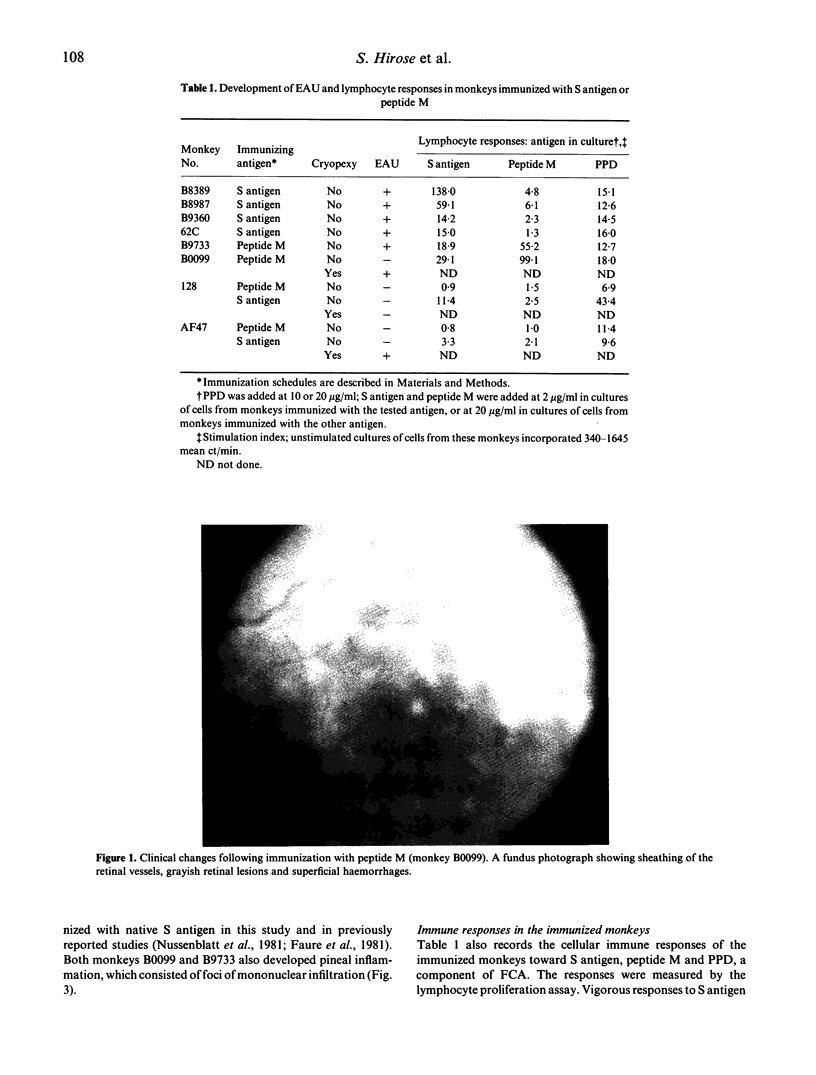



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beraud E., Reshef T., Vandenbark A. A., Offner H., Friz R., Chou C. H., Bernard D., Cohen I. R. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by T lymphocyte lines: genotype of antigen-presenting cells influences immunodominant epitope of basic protein. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):511–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Regulation of autoimmune disease physiological and therapeutic. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:5–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., van der Gaag R., Rothova A., van Kooyk Y., Broersma L., Zaal M. J., Dijkman G., Fortuin M. E., Baarsma G. S., Kijlstra A. Humoral and cellular immune responsiveness to human S-antigen in uveitis. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Jul;6(7):909–919. doi: 10.3109/02713688709034859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso L. A., Merryman C. F., Sery T. W., Shinohara T., Dietzschold B., Smith A., Kalsow C. M. S-antigen: characterization of a pathogenic epitope which mediates experimental autoimmune uveitis and pinealitis in Lewis rats. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Sep;6(9):1151–1159. doi: 10.3109/02713688709034888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso L. A., Merryman C. F., Shinohara T., Dietzschold B., Wistow G., Craft C., Morley W., Henry R. T. S-antigen: identification of the MAbA9-C6 monoclonal antibody binding site and the uveitopathogenic sites. Curr Eye Res. 1986 Dec;5(12):995–1004. doi: 10.3109/02713688608995181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso L. A., Merryman C. F., Shinohara T., Sery T. W., Smith A. S-antigen. Experimental autoimmune uveitis following immunization with a small synthetic peptide. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Jun;105(6):838–840. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060060124046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorey C., Cozette J., Faure J. P. A simple and rapid method for isolation of retinal S antigen. Ophthalmic Res. 1982;14(4):249–255. doi: 10.1159/000265199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure J. P. Autoimmunity and the retina. Curr Top Eye Res. 1980;2:215–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure J. P., Phuc L. H., Takano S., Sterkers M., Thillaye B., de Kozak Y. Uvéo-rétinite expérimentale induite par l'antigène S rétinien chez le singe. Induction, histopathologie. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1981;4(6-7):465–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Wiggert B., Redmond T. M., Kuwabara T., Crawford M. A., Vistica B. P., Chader G. J. Uveoretinitis and pinealitis induced by immunization with interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Aug;27(8):1296–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregerson D. S., Abrahams I. W., Thirkill C. E. Serum antibody levels of uveitis patients to bovine retinal antigens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Nov;21(5):669–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Wiggert B., Redmond T. M., Kuwabara T., Nussenblatt R. B., Chader G. J., Gery I. Uveitis induced in primates by IRBP: humoral and cellular immune responses. Exp Eye Res. 1987 Nov;45(5):695–702. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(87)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsow C. M., Wacker W. B. Pineal gland involvement in retina-induced experimental allergic uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978 Aug;17(8):774–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Henney C. S. BCG-induced suppressor cells. I. Demonstration of a macrophage-like suppressor cell that inhibits cytotoxic T cell generation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A., Murahata R., Sugasawara R., Zighelboim J. Suppressor T cells and suppressor macrophages induced by Corynebacterium parvum. Cell Immunol. 1981 Mar 1;58(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lider O., Karin N., Shinitzky M., Cohen I. R. Therapeutic vaccination against adjuvant arthritis using autoimmune T cells treated with hydrostatic pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4577–4580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers-Elliott R. H., Gammon R. A., Sumner H. L., Shimizu I. Experimental retinal autoimmunity (ERA) in strain 13 guinea pigs: induction of ERA-retinopathy with rhodopsin. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):81–95. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirshahi M., Faure J. P., Brisson P., Falcon J., Guerlotte J., Collin J. S-antigen immunoreactivity in retinal rods and cones and pineal photosensitive cells. Biol Cell. 1984;52(2):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Gery I., Ballintine E. J., Wacker W. B. Cellular immune responsiveness of uveitis patients to retinal S-antigen. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Feb;89(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Kuwabara T., de Monasterio F. M., Wacker W. B. S-antigen uveitis in primates. A new model for human disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Jun;99(6):1090–1092. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930011090021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Mittal K. K., Ryan S., Green W. R., Maumenee A. E. Birdshot retinochoroidopathy associated with HLA-A29 antigen and immune responsiveness to retinal S-antigen. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982 Aug;94(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinelli C. B., Fritz R. B., Chou C. H., McFarlin D. E. Encephalitogenic activity of guinea pig myelin basic protein in the SJL mouse. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1209–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister C., Chabre M., Plouet J., Tuyen V. V., De Kozak Y., Faure J. P., Kühn H. Retinal S antigen identified as the 48K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2988124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara T., Dietzschold B., Craft C. M., Wistow G., Early J. J., Donoso L. A., Horwitz J., Tao R. Primary and secondary structure of bovine retinal S antigen (48-kDa protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. K., Yamaki K., Donoso L. A., Shinohara T. S-antigen: experimental autoimmune uveitis induced in guinea pigs with two synthetic peptides. Curr Eye Res. 1988 Jan;7(1):87–92. doi: 10.3109/02713688809047025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. B., Donoso L. A., Kalsow C. M., Yankeelov J. A., Jr, Organisciak D. T. Experimental allergic uveitis. Isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1949–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Katial A., Craft C., Shinohara T. Sequence analysis of bovine retinal S-antigen. Relationships with alpha-transducin and G-proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki K., Tsuda M., Shinohara T. The sequence of human retinal S-antigen reveals similarities with alpha-transducin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigler J. S., Jr, Mochizuki M., Kuwabara T., Gery I. Purification of retinal S-antigen to homogeneity by the criterion of gel electrophoresis silver staining. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984 Aug;25(8):977–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




