Abstract
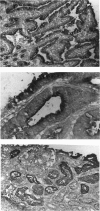
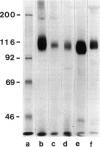
The recently described Ta1 antigen is expressed by activated T cells in vitro and in vivo, as observed in patients with certain immune-mediated diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. In this paper we report on the tissue distribution of the Ta1 antigen. Serological testing of human tumour cell lines and immunohistochemical analysis of human tissue sections revealed a reactivity of the anti-Ta1 antibody with normal and malignant tissues of the upper gastro-intestinal tract, the biliary tract, exocrine pancreas and kidney. SDS-PAGE analysis of immunoprecipitates from 125I-labelled cells, employing the anti-Ta1 antibody, yielded a 113-115 kD band from three serologically Ta1 positive tumour cell lines, from a serologically Ta1 negative human EBV-transformed B lymphoblastoid cell line, from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and, as previously described, a 105 kD band from PHA activated T cells (Fox et al., 1984). After endoglycosidase F treatment similar bands of 85 kD were precipitated from activated T cells and from tumour cell lines. It is therefore likely that very similar glycoproteins, which differ only modestly in the size of carbohydrate chains, bear the Ta1 epitope on Ta1 positive tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dippold W. G., Klingel R., Bernhard H., Dienes H. P., Knuth A., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Secretory epithelial cell marker on gastrointestinal tumors and in human secretions defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2092–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. A novel pathway of human T cell activation via a 103 kD T cell activation antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1346–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schendel D. J., Von Steldern D. Triggering of the lethal hit in human cytotoxic T lymphocytes: a functional role for a 103-kDa T cell-specific activation antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jul;16(7):741–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Acuto O., Poole C., Palley L., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Ta1, a novel 105 KD human T cell activation antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1250–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Benjamin D., Weiner H. L. Antigen reactive memory T cells are defined by Ta1. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):414–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Manning M. E., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. In vivo activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth A., Gabbert H., Dippold W., Klein O., Sachsse W., Bitter-Suermann D., Prellwitz W., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Biliary adenocarcinoma. Characterisation of three new human tumor cell lines. J Hepatol. 1985;1(6):579–596. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Knuth A., Lerch H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Dienes H. P. Expression of a novel T-cell activation antigen on bile canaliculi. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 24;315(4):264–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607243150418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination as a tool for investigation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):214–220. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain P. L., Acuto O., Schlossman S. F. Identification and characterization of human T lymphocyte antigens. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:624–642. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)08123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The structure, function, and expression of interleukin-2 receptors on normal and malignant lymphocytes. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):727–732. doi: 10.1126/science.3008337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]