Abstract
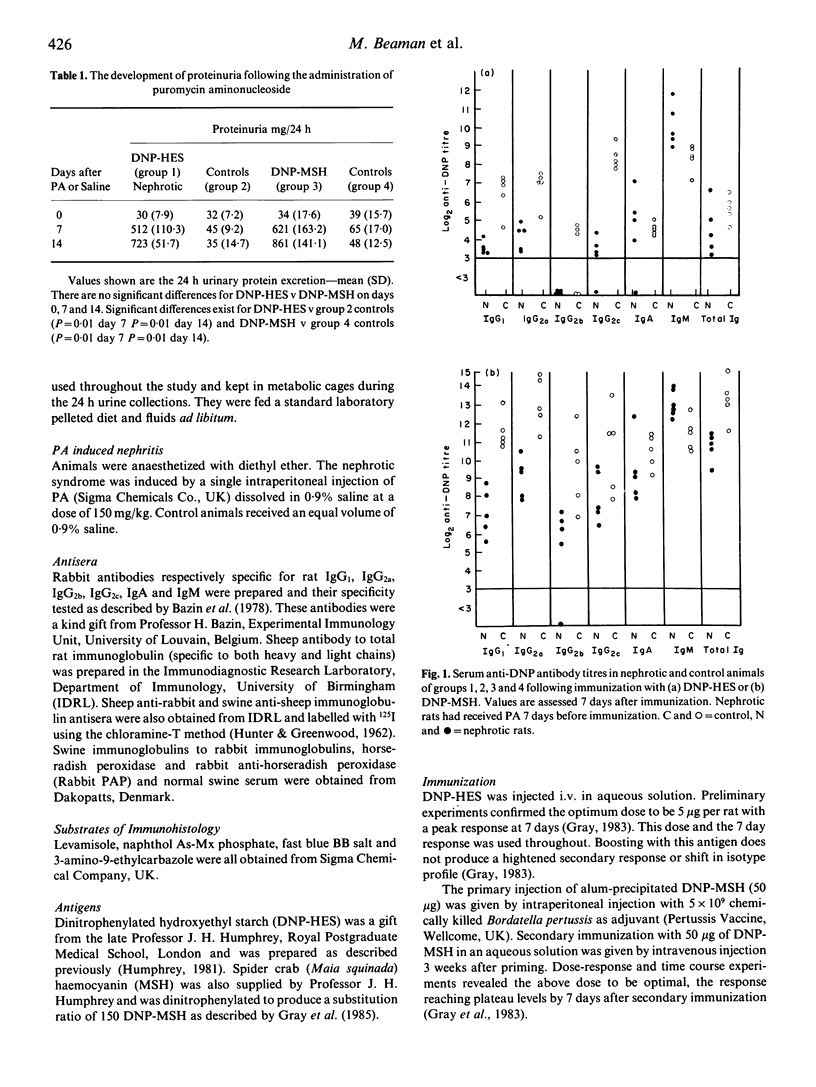
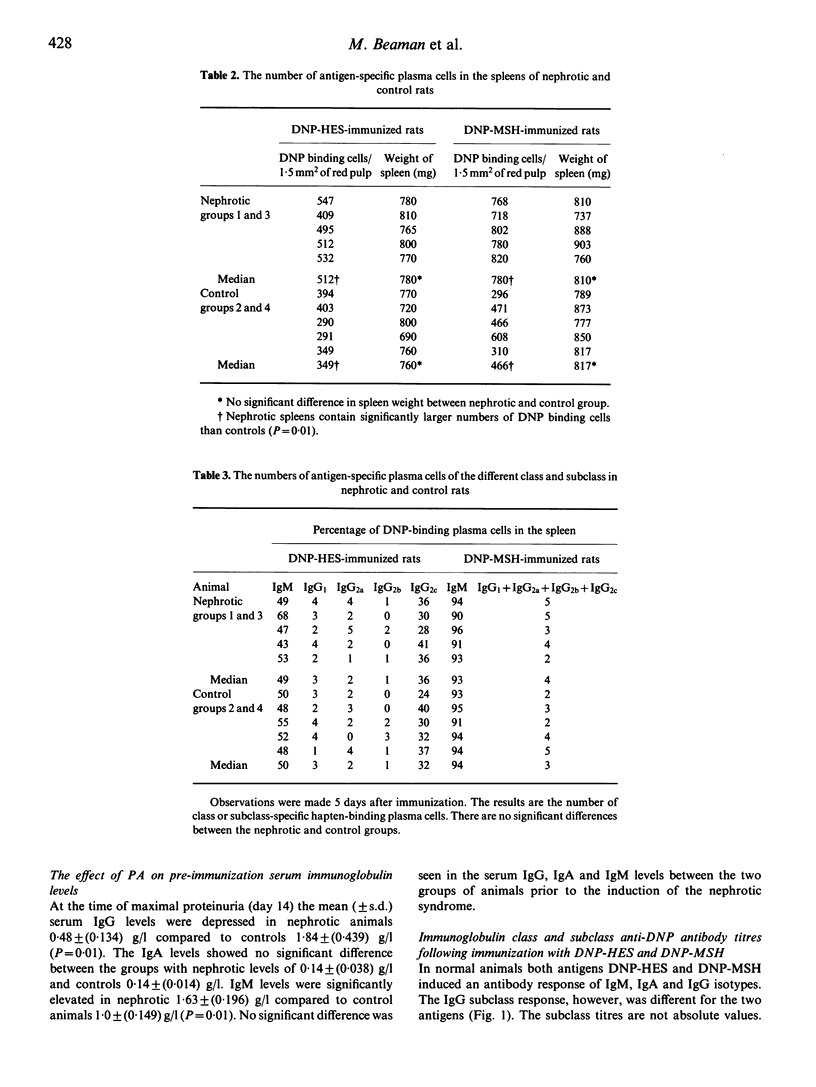
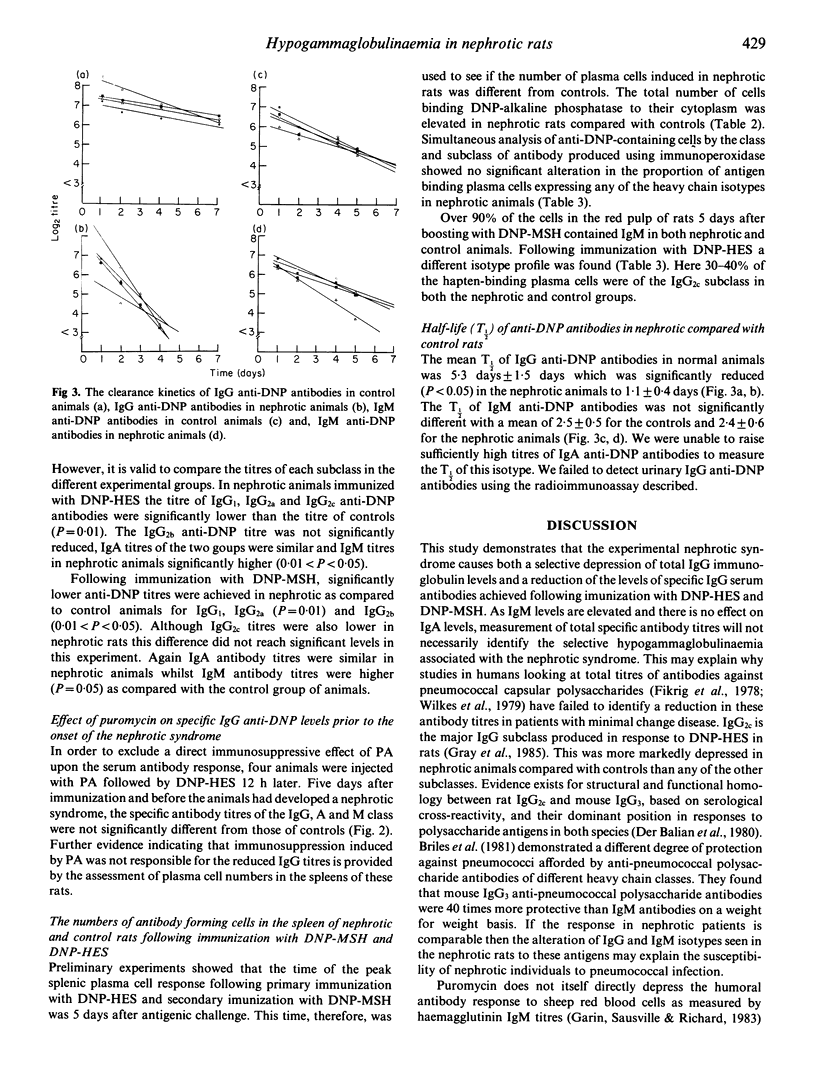
The effect of the nephrotic syndrome induced by puromycin aminonucleoside (PA) in rats on specific antibody responses to 2,4 dinitrophenyl (DNP) conjugated to either spider crab haemocyanin (MSH), a T cell-dependent antigen, or hydroxyethyl starch (HES), a T cell-independent type 2 antigen were studied. The serum IgG anti-DNP levels following immunization with both antigens were reduced in nephrotic animals compared with controls while IgM anti-DNP antibody titres were higher. The half-life of IgG anti-DNP antibodies passively transferred into non-immunized nephrotic rats was markedly reduced while the half-life of anti-DNP antibodies of the IgM class was comparable to that in controls. Low serum IgG and elevated IgM levels were seen in nephrotic animals compared to controls. Antibody-forming cells specific for DNP were demonstrated by immunohistology on rat spleens and the numbers of both IgG and IgM-producing cells were found to be significantly increased (P less than 0.05) in nephrotic animals in response to both DNP-HES and DNP-MSH. These data indicate that in nephrotic rats the alteration seen in the serum immunoglobulin levels is not attributable to reduced antibody production but increased catabolism of serum IgG antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazin H., Platteau B., Beckers A., Pauwels R. Differential effect of neonatal injections of anti-mu or anti-delta antibodies on the synthesis of IgM, IgD, IgE, IgA, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG2c immunoglobulin classes. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2083–2087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale M. G., Nash G. S., Bertovich M. J., MacDermott R. P. Immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1983 Feb;23(2):380–386. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Claflin J. L., Schroer K., Forman C. Mouse Igg3 antibodies are highly protective against infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):88–90. doi: 10.1038/294088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claassen E., Kors N., Van Rooijen N. Influence of carriers on the development and localization of anti-trinitrophenyl antibody-forming cells in the murine spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):271–276. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der Balian G. P., Slack J., Clevinger B. L., Bazin H., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. III. Antigens that stimulate IgG3 in mice stimulate IgG2c in rats. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):209–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig S. M., Schiffman G., Phillipp J. C., Moel D. I. Antibody response to capsular polysaccharide vaccine of Streptococcus pneumoniae in patients with nephrotic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):818–821. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garin E. H., Sausville P. J., Richard G. A. Impaired primary antibody response in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):595–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangiacomo J., Cleary T. G., Cole B. R., Hoffsten P., Robson A. M. Serum immunoglobulins in the nephrotic syndrome. A possible cause of minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 3;293(1):8–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507032930103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D., Chassoux D., MacLennan I. C., Bazin H. Selective depression of thymus-independent anti-DNP antibody responses induced by adult but not neonatal splenectomy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):78–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslan J. M., Lautie J. P., Intrator L., Blanc C., Lagrue G., Sobel A. T. Impaired IgG synthesis in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol. 1982 Sep;18(3):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Ratte J., Potter A. H., Michael A. F. Transfer of aminonucleoside nephrosis by renal transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2777–2780. doi: 10.1172/JCI107099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H. Tolerogenic or immunogenic activity of hapten-conjugated polysaccharides correlated with cellular localization. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):212–220. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. S., Ooi Y. M., Hsu A., Hurtubise P. E. Diminished synthesis of immunoglobulin by peripheral lymphocytes of patients with idiopathic membranous glomerulonephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):789–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI109729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R. Principles and methods for the morphometric study of the lung and other organs. Lab Invest. 1963 Feb;12:131–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFSON W. Q., CHON C. A rapid procedure for the estimation of total protein, true albumin, total globulin, alpha globulin, beta globulin and gamma globulin in 1.0 ml of serum. Am J Clin Pathol. 1948 Sep;18(9):723–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfert C. M., Katz S. L. Etiology of bacterial sepsis in nephrotic children 1963-1967. Pediatrics. 1968 Nov;42(5):840–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama H., Kida H., Tani Y., Abe T., Tomosugi N., Koshino Y., Hattori N. Immunodynamics of minimal change nephrotic syndrome in adults T and B lymphocyte subsets and serum immunoglobulin levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):601–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


