Abstract
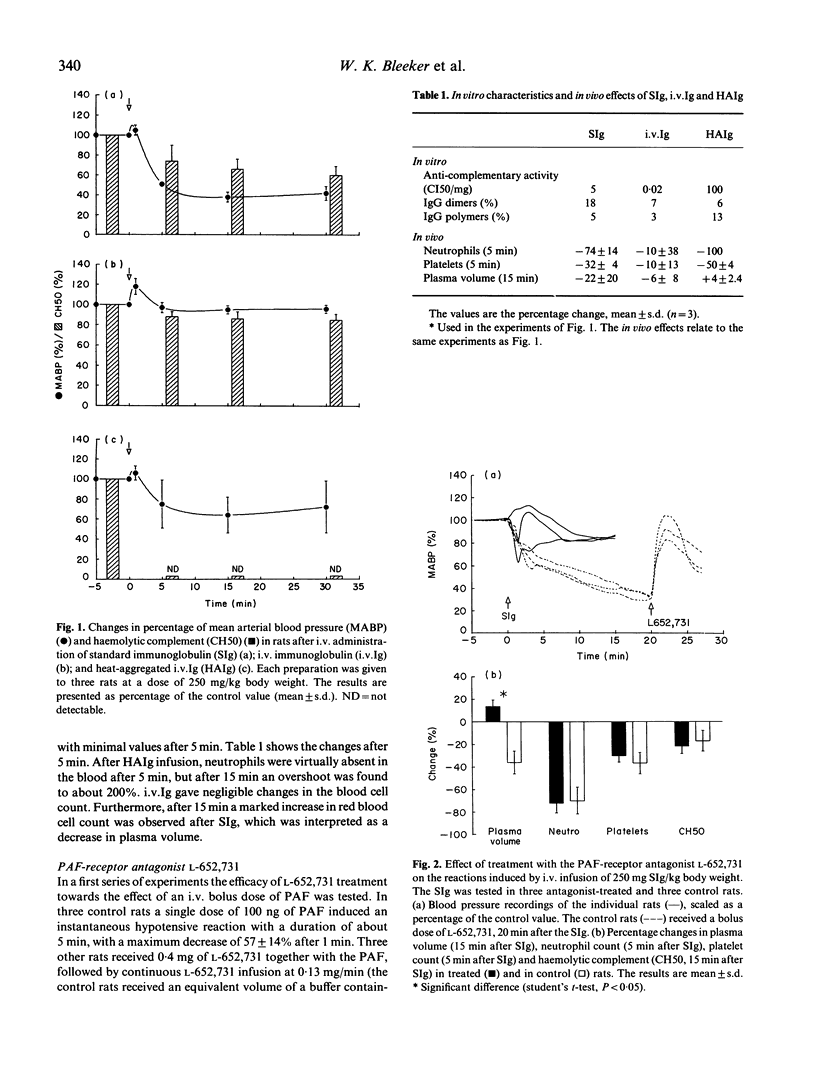
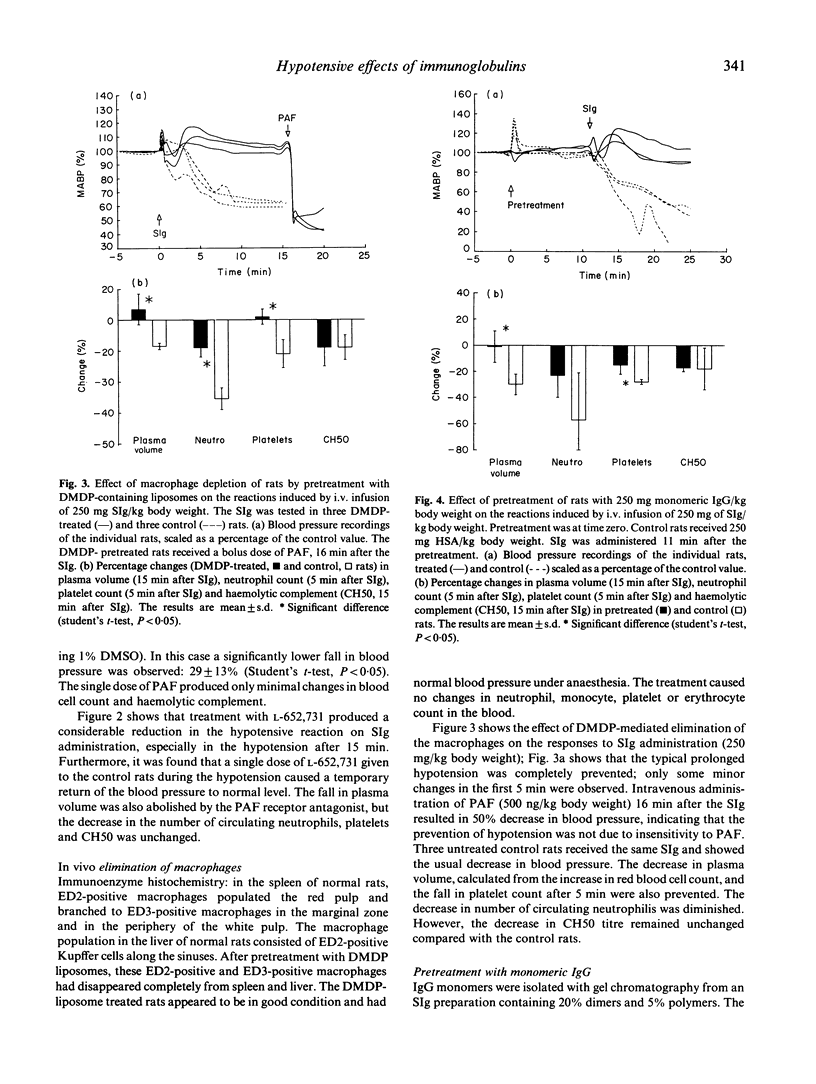
Intravenous administration of certain immunoglobulin preparations may cause severe adverse reactions, especially in hypogammaglobulinaemic patients. Because the exact mechanism of the adverse reactions is still unknown, we investigated the severe, prolonged hypotension induced in anaesthetized rats on rapid i.v. infusion of standard immunoglobulin preparations. The hypotensive response was previously shown to be associated with IgG aggregates in the preparations but independent of complement activation. We found that the hypotension could be prevented by treating the rats with a specific receptor antagonist of platelet-activating factor; or by depletion of the macrophages of the rats; or by pretreatment with monomeric IgG. This provided evidence that the hypotension is initiated by interaction of IgG-aggregates with Fc-receptors on macrophages, leading to the production of platelet-activating factor. We conclude that the rat model provides a sensitive and reproducible test system for macrophage-activating properties of immunoglobulin preparations for i.v. administration which may lead to vasoactive side effects.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving B. M., Tankersley D. L., Mason B. L., Rossi F., Aronson D. L., Finlayson J. S. Contact-activated factors: contaminants of immunoglobulins preparations with coagulant and vasoactive properties. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Aug;96(2):334–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barandun S., Isliker H. Development of immunoglobulin preparations for intravenous use. Vox Sang. 1986;51(2):157–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb00235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleeker W. K., Agterberg J., Rigter G., de Vries-van Rossen A., Bakker J. C. An animal model for the detection of hypotensive side effects of immunoglobulin preparations. Vox Sang. 1987;52(4):281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1987.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleeker W. K., Van Rosevelt R. F., Ufkes J. G., Loos J. A., Van Mourik J. A., Bakker J. C. Hypotensive effects of plasma protein fraction. The relation between prekallikrein activator, bradykinin generation, and blood pressure in an animal model. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Oct;100(4):540–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., Vanes L. A., Daha M. R. Influence of aggregate size on the binding and activation of the first component of human complement by soluble IgG aggregates. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):705–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga T. W., Kerst M., Nuyens J. H., Vlug A., von dem Borne A. E., Roos D., Tetteroo P. A. Binding characteristics of dimeric IgG subclass complexes to human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2359–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lam M. H., Biftu T., Beattie T. R., Shen T. Y. trans-2,5-Bis-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)tetrahydrofuran. An orally active specific and competitive receptor antagonist of platelet activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15639–15645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hässig A. Intravenous immunoglobulins: pharmacological aspects and therapeutic use. Vox Sang. 1986;51(1):10–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñarrea P., Alonso F., Sanchez-Crespo M. Platelet-activating factor: an effector substance of the vasopermeability changes induced by the infusion of immune aggregates in the mouse. Immunopharmacology. 1983 Jun;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(83)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungi T. W., Santer M., Lerch P. G., Barandun S. Effect of various treatments of gamma-globulin (IgG) for achieving intravenous tolerance on the capacity to interact with human monocyte Fc receptors. A comparative study. Vox Sang. 1986;51(1):18–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberly R. P., Salmon J. E., Bussel J. B., Crow M. K., Hilgartner M. W. Modulation of mononuclear phagocyte function by intravenous gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):745–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medgyesi G. A., Kovács J., Füst G., Merétey K. Safety aspects of intravenous immunoglobulins. Immunol Invest. 1988 Apr;17(2):121–133. doi: 10.3109/08820138809055724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E. Evaluating the quality of immunoglobulin G preparations for intravenous therapy. Vox Sang. 1985;49 (Suppl 1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Fernández-Gallardo S., Nieto M. L., Baranès J., Braquet P. Inhibition of the vascular actions of IgG aggregates by BN 52021, a highly specific antagonist of paf-acether. Immunopharmacology. 1985 Oct;10(2):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(85)90031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Preston M. S., Finlayson J. S. Immunoglobulin G dimer: an idiotype-anti-idiotype complex. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jan;25(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen N., van Nieuwmegen R., Kamperdijk E. W. Elimination of phagocytic cells in the spleen after intravenous injection of liposome-encapsulated dichloromethylene diphosphonate. Ultrastructural aspects of elimination of marginal zone macrophages. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1985;49(4):375–383. doi: 10.1007/BF02912114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



