Abstract
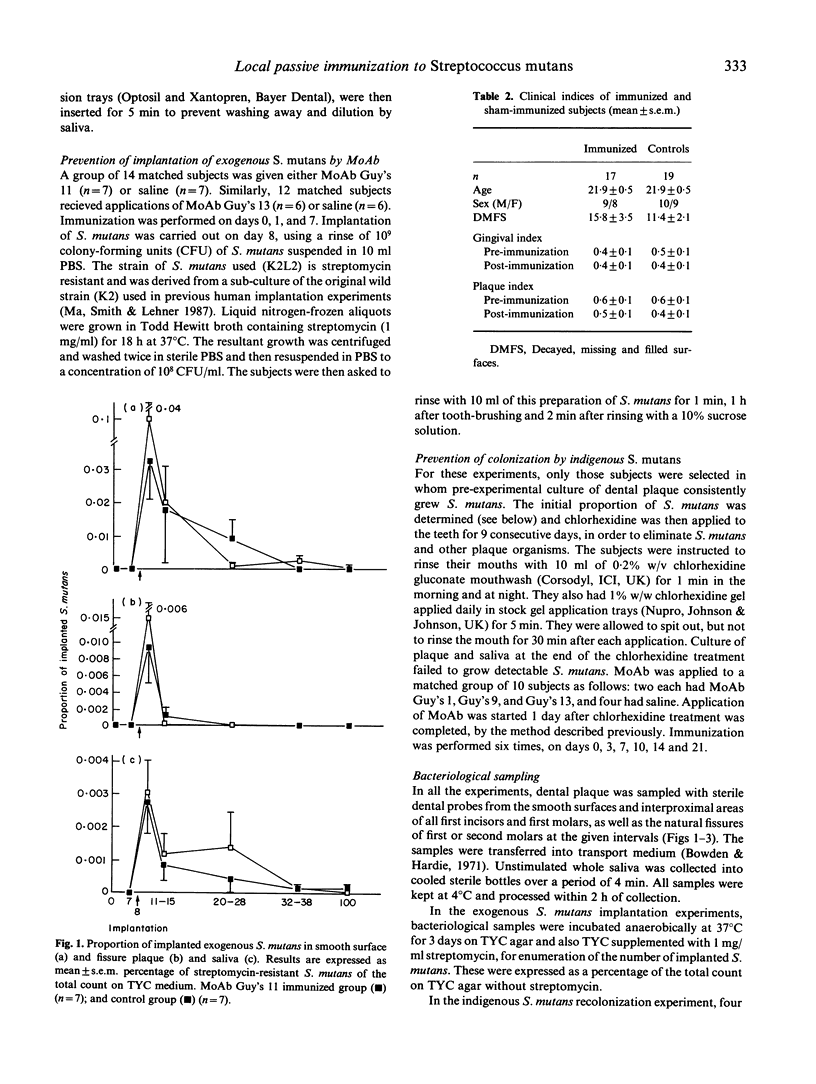
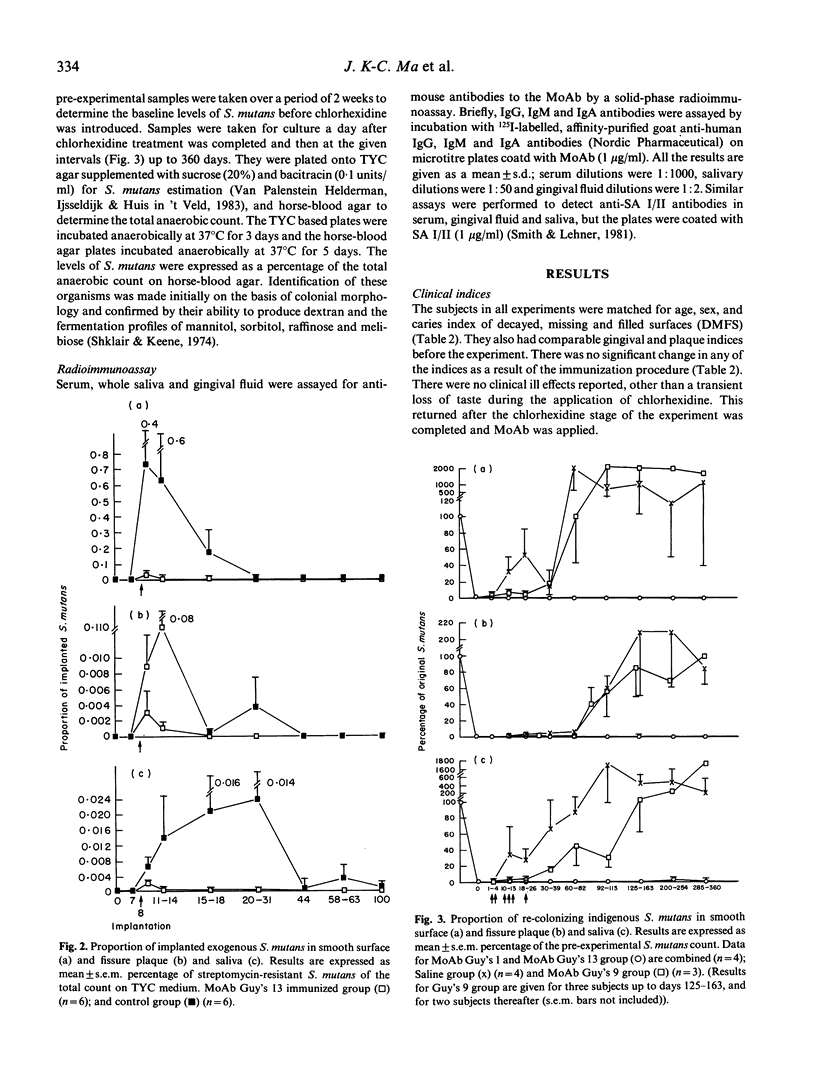
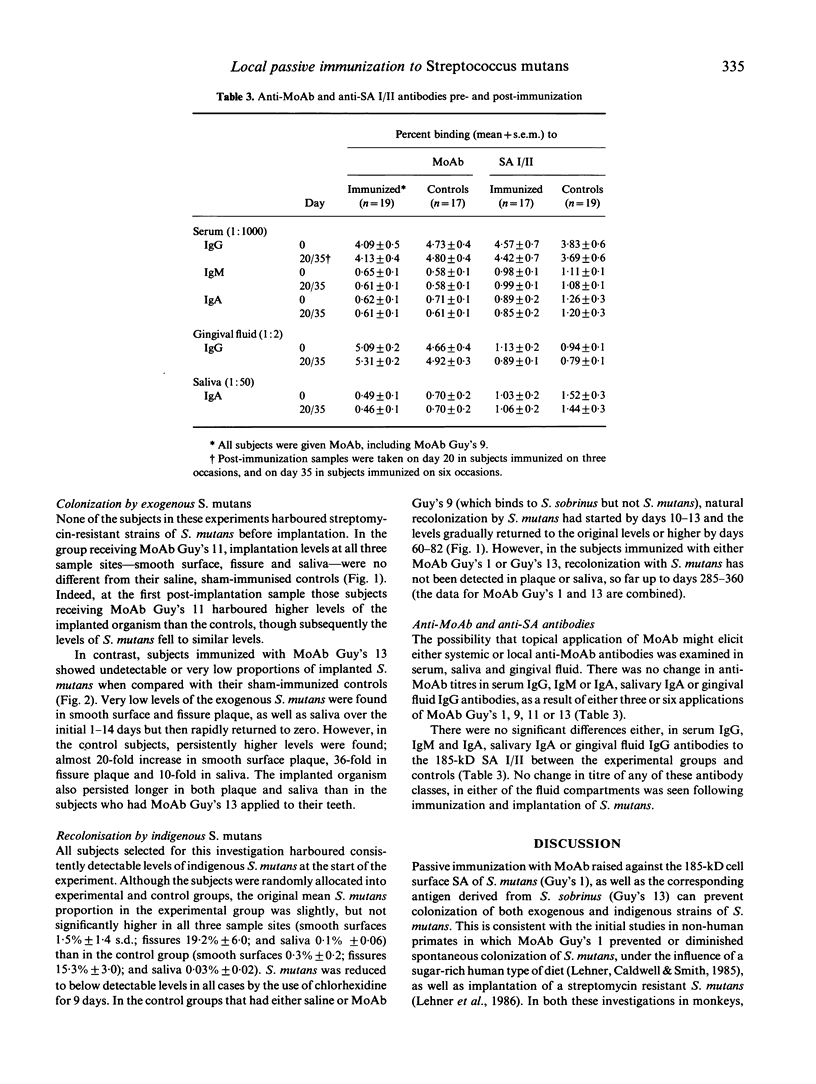
Local oral passive immunization in human subjects with a monoclonal antibody (MoAb) raised against the 185-kD antigen I/II from S. mutans significantly reduced or prevented oral colonization of an exogenous strain of the organism. In subjects sham-immunized with either saline or an unrelated MoAb, however, significantly greater proportions of S. mutans persisted for a longer duration than in those immunized with the specific anti-streptococcal MoAb. Recolonization of indigenous S. mutans after this organism was reduced to undetectable levels by an antimicrobial agent has also been completely prevented with specific MoAb. Indeed, S. mutans was not detected for a period of over 1 year, as compared with recolonization within 10-82 days in the control subjects. The specificity of MoAb in preventing colonization of the streptococci was studied with four MoAb. This revealed that: (1) the sub-class of antibody is not an essential factor, as both MoAb Guy's 1 and 13 prevented colonization, although Guy's 1 is an IgG2a and Guy's 13 is an IgG1 class of antibody; (2) serotype specificity is important, as MoAb Guy's 9, which only recognizes S. sobrinus (serotypes d and g), does not prevent colonisation by S. mutans (serotype c); (3) neither protein nor carbohydrate nature of the putative adhesin was a determining factor, because MoAb Guy's 1 recognizes a carbohydrate and Guy's 13 a protein determinant and both MoAb prevented adherence of S. mutans; and (4) epitope specificity appears to be the most important factor in preventing adherence of S. mutans, as MoAb Guy's 11 and 13 share the same serotype specificity and both recognize a protein determinant, yet only Guy's 13 prevents colonisation. The long duration of protection from re-colonization by indigenous S. mutans, lasting about 1 year after application of the specific MoAb was stopped, cannot be accounted for by functional MoAb remaining on the teeth. We suggest that initially the MoAb prevents colonization by S. mutans and that the ecological niche vacated by this streptococcus is filled by other organisms from the oral flora, thereby discouraging re-colonization by S. mutans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beighton D., Rippon H. R., Thomas H. E. The distribution of Streptococcus mutans serotypes and dental caries in a group of 5- to 8-year-old Hampshire schoolchildren. Br Dent J. 1987 Feb 7;162(3):103–106. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4806033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. H., Cohen B., Cole M. F., Colman G. Immunization against dental caries. Br Dent J. 1975 Jul 15;139(2):45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Russell M. W., Hawkes J. E., Bergmeier L. A., Lehner T. Passage of immunoglobulins from plasma to the oral cavity in rhesus monkeys. Immunology. 1978 Dec;35(6):923–931. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Huehns E. R., Epstein M. A. Therapeutic use of human monoclonal antibodies. Lancet. 1983 May 7;1(8332):1040–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92659-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:253–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Caldwell J., Smith R. Local passive immunization by monoclonal antibodies against streptococcal antigen I/II in the prevention of dental caries. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):796–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.796-799.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. Immunological and bacteriological basis for vaccination against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):517–520. doi: 10.1038/254517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Challacombe S. J., Scully C. M., Hawkes J. E. Passive immunisation with serum and immunoglobulins against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1978 Apr 1;1(8066):693–695. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90803-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Smith R., Lehner T. Use of monoclonal antibodies in local passive immunization to prevent colonization of human teeth by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1274–1278. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1274-1278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Song M., Krasse B., Olsson J. Biochemical and immunological differences between hydrophobic and hydrophilic strains of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.68-75.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Gregory R. L., Harmon C. C., Katz J., Richardson G. J., Hilton T., Filler S. J., McGhee J. R. Protection of gnotobiotic rats against dental caries by passive immunization with bovine milk antibodies to Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2341–2347. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2341-2347.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. G., Smith R., Lehner T. Recognition of carbohydrate and protein epitopes by monoclonal antibodies to a cell wall antigen from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.810-815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro I., Russell M. W. Ultrastructural localization of protein antigens I/II and III in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):410–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.410-413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILNESS J., LOE H. PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN PREGNANCY. II. CORRELATION BETWEEN ORAL HYGIENE AND PERIODONTAL CONDTION. Acta Odontol Scand. 1964 Feb;22:121–135. doi: 10.3109/00016356408993968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandham H. J., Brown J., Phillips H. I., Chan K. H. A preliminary report of long-term elimination of detectable mutans streptococci in man. J Dent Res. 1988 Jan;67(1):9–14. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670011801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shklair I. L., Keene H. J. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Nov;19(11):1079–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Lehner T. A radioimmunoassay for serum and gingival crevicular fluid antibodies to a purified protein of Streptococcus mutans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):417–424. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Lehner T., Beverley P. C. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Streptococcus mutans antigenic determinants I/II, I, II, and III and their serotype specificities. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.168-175.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Palenstein Helderman W. H., Ijsseldijk M., Huis in 't Veld J. H. A selective medium for the two major subgroups of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans isolated from human dental plaque and saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28(7):599–603. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



