Abstract
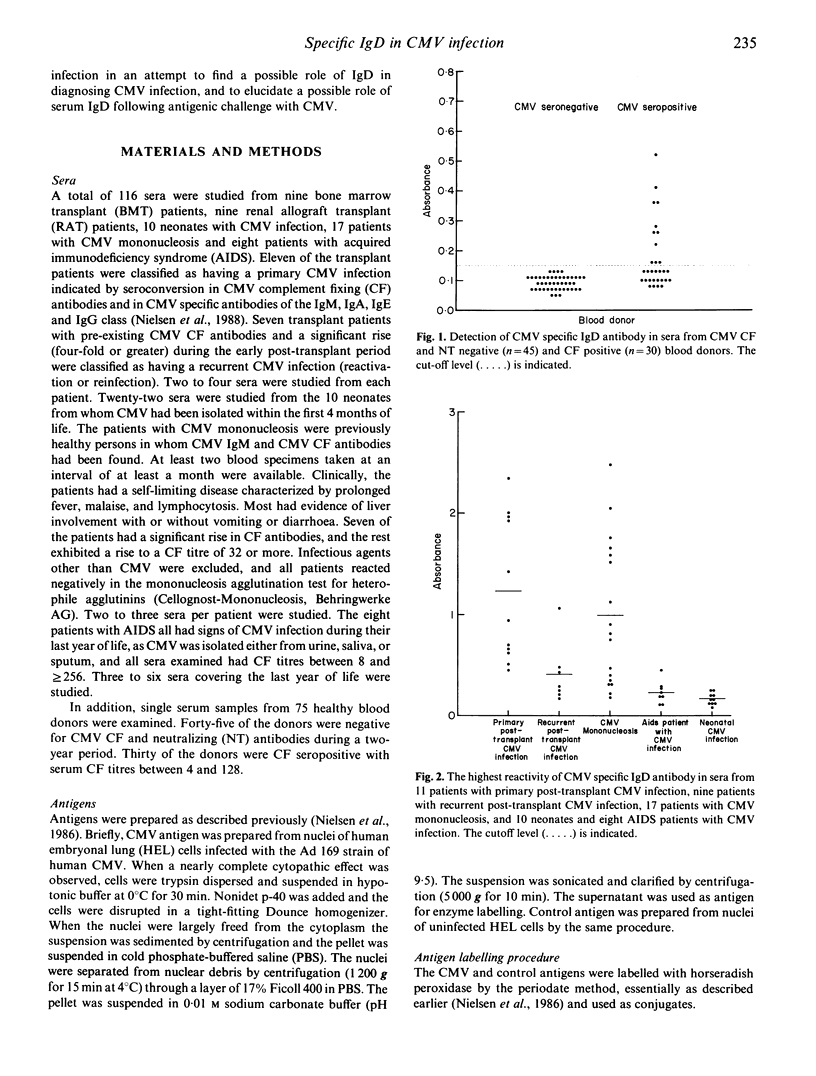
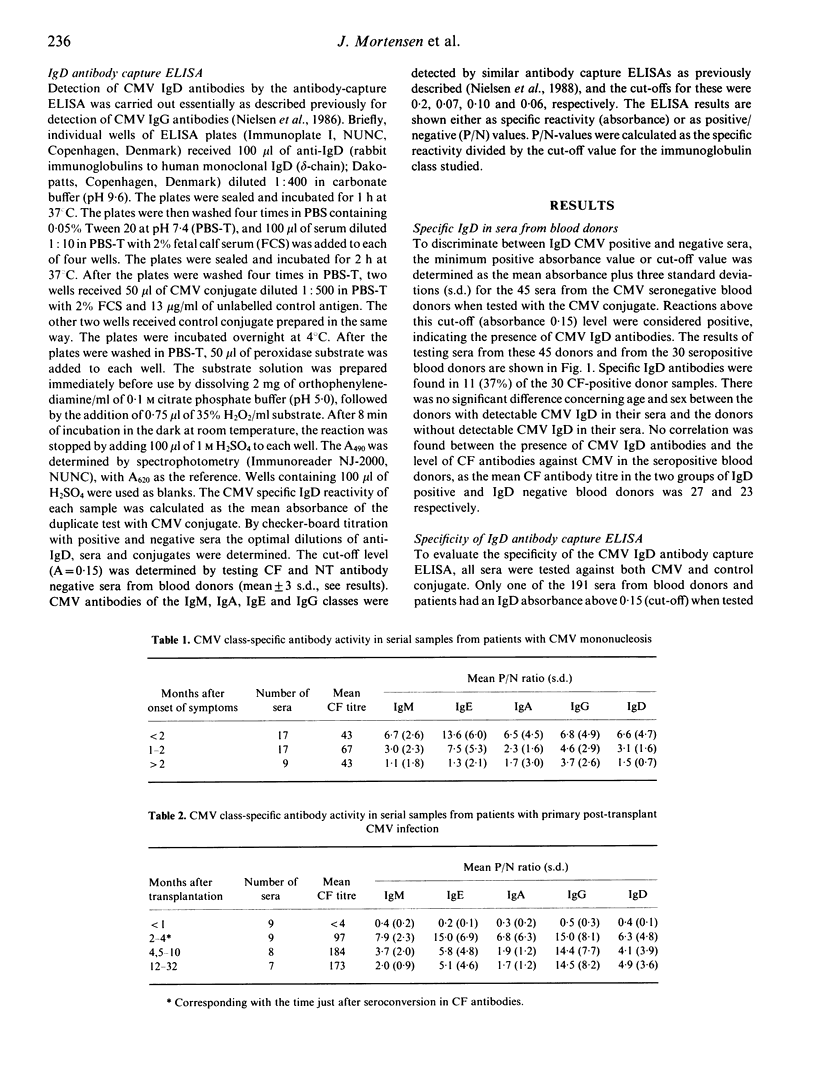
An antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed for the detection of immunoglobulin D (IgD) antibodies to cytomegalovirus (CMV) in sera from blood donors and various groups of patients infected with CMV. This method has previously been found especially valuable in detecting specific antibodies of the IgM, IgE, IgA and IgG class in patients with CMV infection. Specific CMV IgD antibodies were found in 37% of CMV seropositive blood donors and in 47 (88%) of the 53 patients investigated, including bone marrow transplant and renal allograft transplant patients, patients with CMV mononucleosis, neonates with CMV infection and AIDS patients with CMV infection. The highest IgD reactivity was found in patients having either a primary post-transplant CMV infection or CMV mononucleosis. The IgD reactivity in patients with AIDS and in neonates was low. It was also found that in the acute phase of CMV infection the development of CMV antibodies of the IgD class was similar to the development of antibodies of the other classes. The maintenance of IgD activity in some patients together with the presence of CMV IgD antibodies in a great proportion of the blood donors indicates that the development of CMV IgD antibodies resembles that of the IgG class. Determination of specific IgD antibodies offered no advantage over determination of specific antibodies of the IgM, IgE and IgA classes in the diagnosis of CMV infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahna S. L., Heiner D. C., Horwitz C. A. Sequential changes of the five immunoglobulin classes and other responses in infectious mononucleosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;74(1):1–8. doi: 10.1159/000233507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C. E., Trayer H. R. Serum IgD concentrations in sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):257–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Xue B., Wallace D., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Physiology of IgD. VI. Transfer of the immunoaugmenting effect of IgD with T delta-containing helper cell populations. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1852–1861. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiner D. C., Rose B. A study of antibody responses by radioimmunodiffusion with demonstration of gamma D antigen-binding activity in four sera. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):691–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. B., Xue B., O'Neil M. A., Siskind G. W., Pernis B., Thorbecke G. J. Physiology of IgD. V. Enhancement of antibody responses in vivo by allo anti-IgD is due primarily to an indirect effect on B cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2293–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lertora J. J., Gomez-Perez F. J., Leslie G. A. Structure and biological functions of human IgD. V. Insulin antibodies of the IgD class in sera from some diabetic patients. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(5):597–606. doi: 10.1159/000231441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Lopez Correa R. H., Holmes J. N. Structure and biological functions of human IgD. IV. Ontogeny of human serum immunoglobulin D(IgD) as related to IgG, IgA and IgM. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(3):350–357. doi: 10.1159/000231416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster M. I., Armen R. C., Hallum J. V., Leslie G. A. Measles virus-specific IgD antibodies in patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1297–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster M. I., Leslie G. A., Bardana E. J. Structure and biological functions of human IgD. VII. IgD antinuclear antibodies in sera of patients with autoimmune disorders. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;52(1-4):212–218. doi: 10.1159/000231684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuma H., Zolla-Pazner S., Litwin S., el-Sadr W., Sharpe S., Zehr B., Weiss S., Saxinger W. C., Marmor M. Serum IgD elevation is an early marker of B cell activation during infection with the human immunodeficiency viruses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):5–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen C. M., Hansen K., Andersen H. M., Gerstoft J., Vestergaard B. F. An enzyme labelled nuclear antigen immunoassay for detection of cytomegalovirus IgM antibodies in human serum: specific and non-specific reactions. J Med Virol. 1987 May;22(1):67–76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Rønholm E., Sørensen I., Andersen H. K. Detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to cytomegalovirus antigens by antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.998-1003.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Rønholm E., Sørensen I., Jaeger P., Andersen H. K. Improvement of serological diagnosis of neonatal cytomegalovirus infection by simultaneously testing for specific immunoglobulins E and M by antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1406–1410. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1406-1410.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Sørensen I., Andersen H. K. Kinetics of specific immunoglobulins M, E, A, and G in congenital, primary, and secondary cytomegalovirus infection studied by antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):654–661. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.654-661.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE D. S., FAHEY J. L. A NEW CLASS OF HUMAN IMMUNOGLOBULINS. I. A UNIQUE MYELOMA PROTEIN. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:171–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Crabbé P. A., Turner M. W. Immunoglobulin D in serum, body fluids and lymphoid tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jul;3(6):477–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Hovi T., Meurman O., Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Kinetics of specific IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM antibody responses in rubella. J Med Virol. 1985 May;16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., von Deimling U., Flehmig B. Detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus (CMV) using an enzyme-labelled antigen (ELA). J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Paul W. E., Terry W. D., Green I. Communications. IgD-bearing human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):648–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue B., Coico R., Wallace D., Siskind G. W., Pernis B., Thorbecke G. J. Physiology of IgD. IV. Enhancement of antibody production in mice bearing IgD-secreting plasmacytomas. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):103–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Logt J. T., Heessen F. W., van der Veen J. Quantitation of immunoglobulin E antibody to cytomegalovirus by antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.558-561.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


