Abstract
CD4 monoclonal antibody (MoAb) was able to inhibit T cell proliferation induced in an autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction (AMLR). The effect of CD4 MoAb on cellular proliferation appears to be directly exerted on CD4+ T lymphocytes, and to be due to inhibition of a post-activation event, since the CD4+ T cell proliferation that occurs after an activation pulse of 24 h with autologous non-T cells could be inhibited when CD4 MoAb was added after, but not during, the pulse period, and the inhibition of autologous MLR-induced CD4+ T cell proliferation by CD4 MoAb was observed even if the Moab was added as late as 72 h after the initiation of culture. The presence of CD4 MoAb did not affect the production of interleukin 2 (IL-2). CD4 MoAb had, however, an inhibitory effect on the expression of IL-2 receptors, such that addition of exogenous IL-2 at the initiation of culture did not restore the AMLR-induced CD4+ T cell proliferation. These results indicate that the hindrance of the recognition of HLA class II products is not the only target of the CD4 MoAb effect in the autologous MLR. Rather, the binding of CD4 MoAb to CD4+ T cells interferes with a late event because it is capable of abolishing the proliferative activity of fully activated CD4+ T cells. The data are compatible with the idea that perturbation of the CD4 molecules can transmit a negative signal to CD4+ T cells.
Full text
PDF
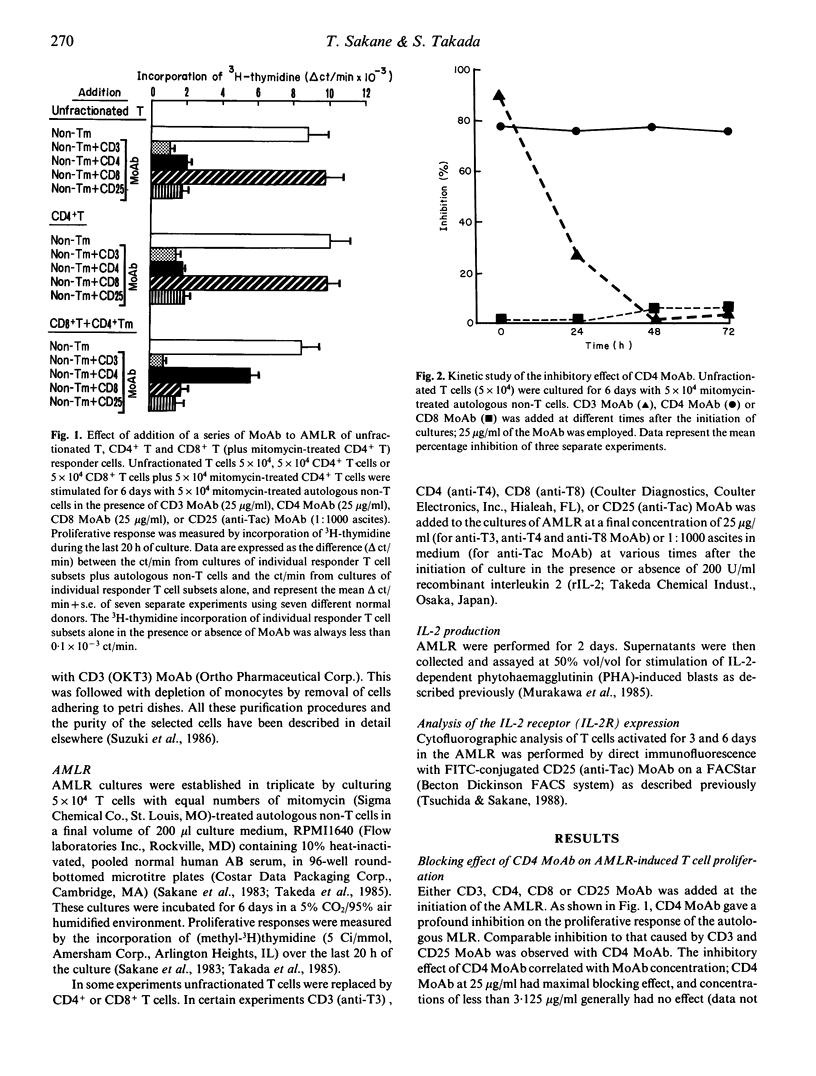
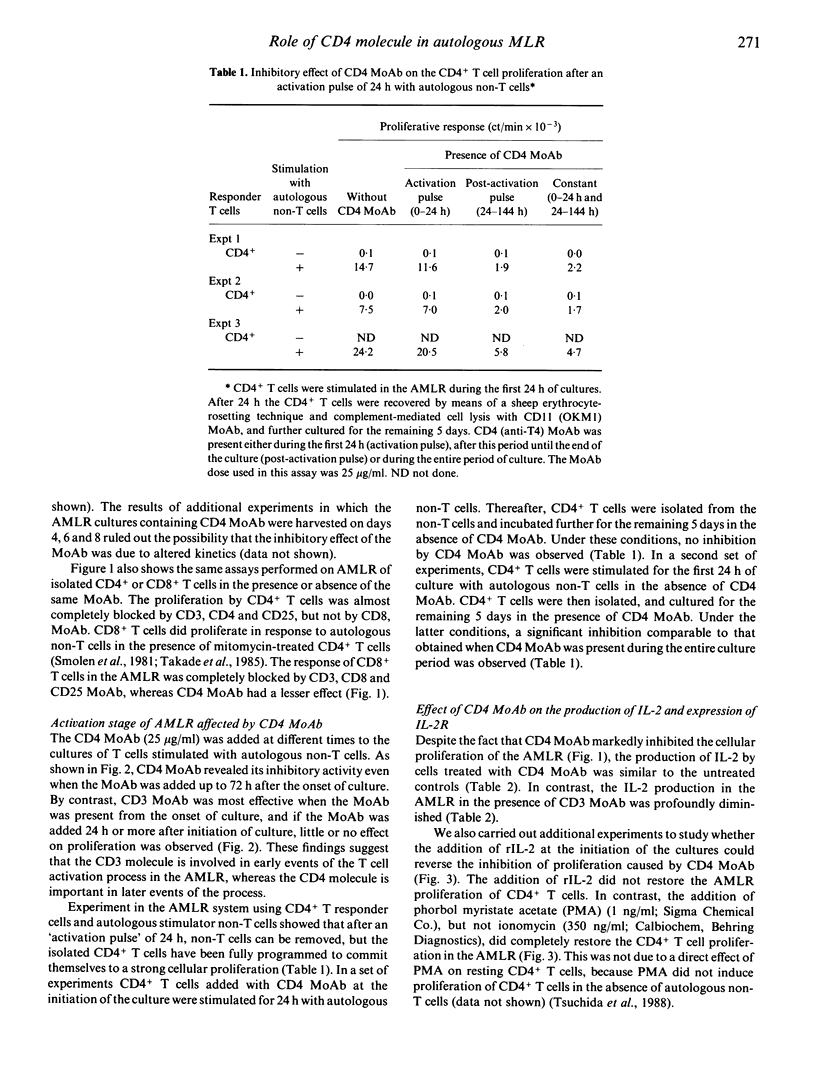



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank I., Chess L. Perturbation of the T4 molecule transmits a negative signal to T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1294–1303. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekoff M., Kakiuchi T., Grey H. M. Accessory cell function in the Con A response: role of Ia-positive and Ia-negative accessory cells. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1337–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Rao P. E., Talle M. A., Goldstein G., Shaw S. Possible involvement of the T4 molecule in T cell recognition of class II HLA antigens. Evidence from studies of CTL-target cell binding. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):783–797. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrera A. C., Sanchez-Madrid F., Lopez-Botet M., Bernabeu C., De Landazuri M. O. Involvement of the CD4 molecule in a post-activation event on T cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Feb;17(2):179–186. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Hansen J. A., Good R. A., Gupta S. Monoclonal antibody analysis of human T lymphocyte subpopulations exhibiting autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5096–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Glickman E., Evans R. L. Antibodies to membrane structures that distinguish suppressor/cytotoxic and helper T lymphocyte subpopulations block the mixed leukocyte reaction in man. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):193–198. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Ruscetti F. W. Association of protein kinase C activation with IL 2 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1266–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein J. L., Kappler J., Marrack P., Burakoff S. J. The role of L3T4 in recognition of Ia by a cytotoxic, H-2Dd-specific T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1213–1224. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Stobo J. D. Specificity and function of a human autologous reactive T cell. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1537–1542. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide J., Takeuchi T., Hosono O., Takano M., Abe T. Defects of autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction-activated immunoregulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Oct;26(4):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. B., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Increase in cytosolic free calcium concentration is an intracellular messenger for the production of interleukin 2 but not for expression of the interleukin 2 receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1640–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa Y., Takada S., Ueda Y., Suzuki N., Hoshino T., Sakane T. Characterization of T lymphocyte subpopulations responsible for deficient interleukin 2 activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain P. L., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Surface molecules involved in self-recognition and T cell activation in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1093–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Specificity and suppressor function of human T cells responsive to autologous non-T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Kotani H., Takada S., Murakawa Y., Ueda Y. A defect in the suppressor circuits among OKT4+ cell populations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus occurs independently of a defect in the OKT8+ suppressor T cell function. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):753–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions between T and non-T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Talal N. Significance of self-recognition and interleukin-2 for immunoregulation, autoimmunity and cancer. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Oct;16(4):269–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:165–179. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60844-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Luger T. A., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. Responder cells in the human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1601–1604. doi: 10.1172/JCI110416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Sakane T., Ueda Y., Murakawa Y., Tsunematsu T. Implications for the role of cognate interactions in in vitro human B cell activation by Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I and pokeweed mitogen. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):294–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI112290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada S., Ueda Y., Suzuki N., Murakawa Y., Hoshino T., Green I., Steinberg A. D., Horwitz D. A., Sakane T. Abnormalities in autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction-activated immunologic processes in systemic lupus erythematosus and their possible correction by interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):262–267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Rudd C. E., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Induction of suppression following autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction; role of a novel 2H4 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):97–103. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida T., Sakane T. Intracellular activation signal requirements for the induction of IL-2 responsiveness in resting T cell subsets in humans. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3446–3449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Stouwe R. A., Kunkel H. G., Halper J. P., Weksler M. E. Autologous mixed lymphocyte culture reactions and generation of cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1809–1814. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E., Moody C. E., Jr, Kozak R. W. The autologous mixed-lymphocyte reaction. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:271–312. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60923-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


