Abstract
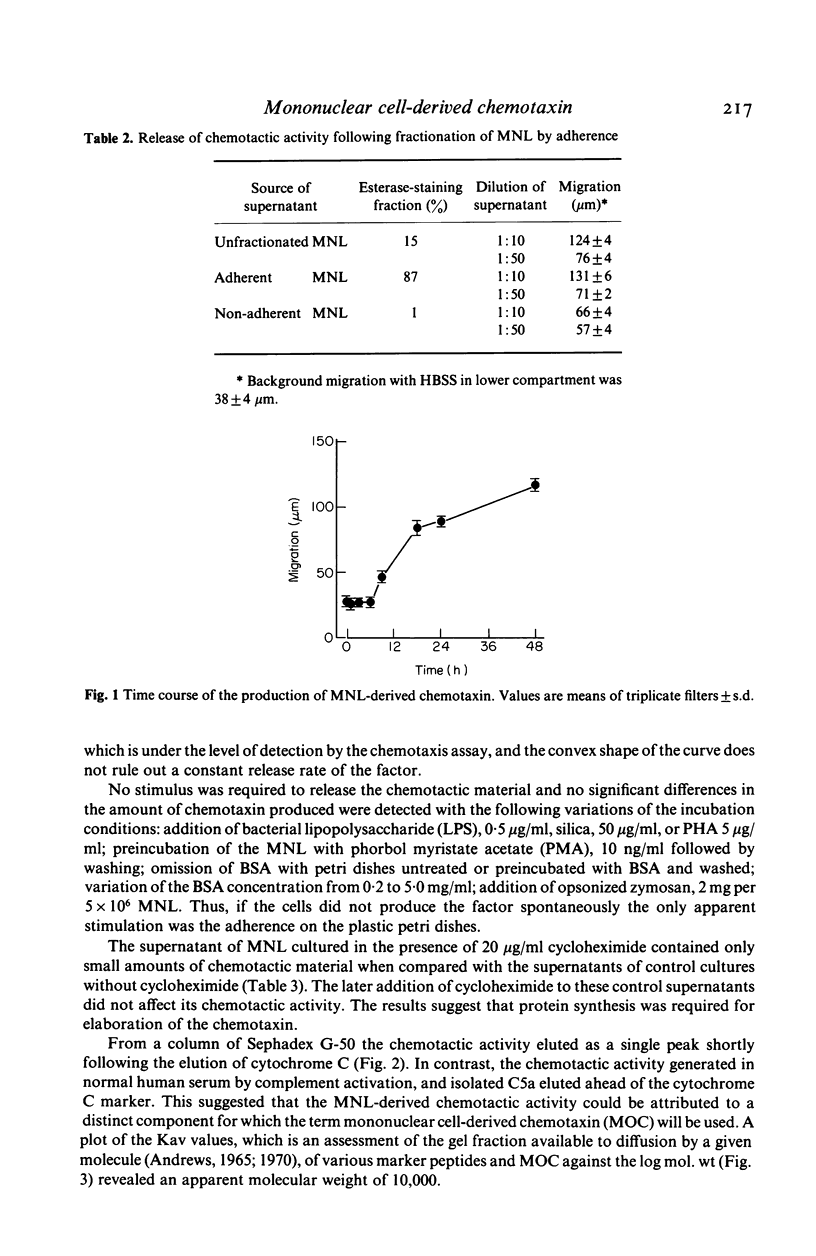
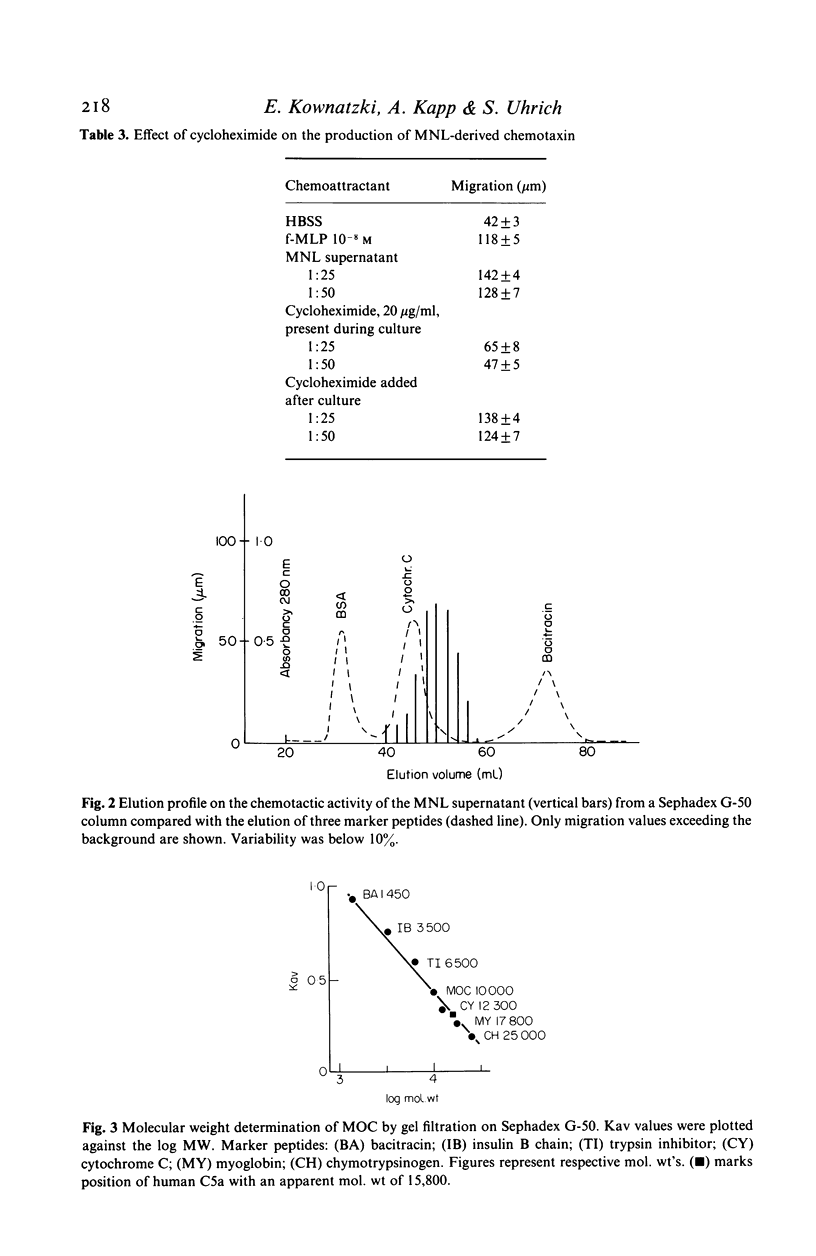
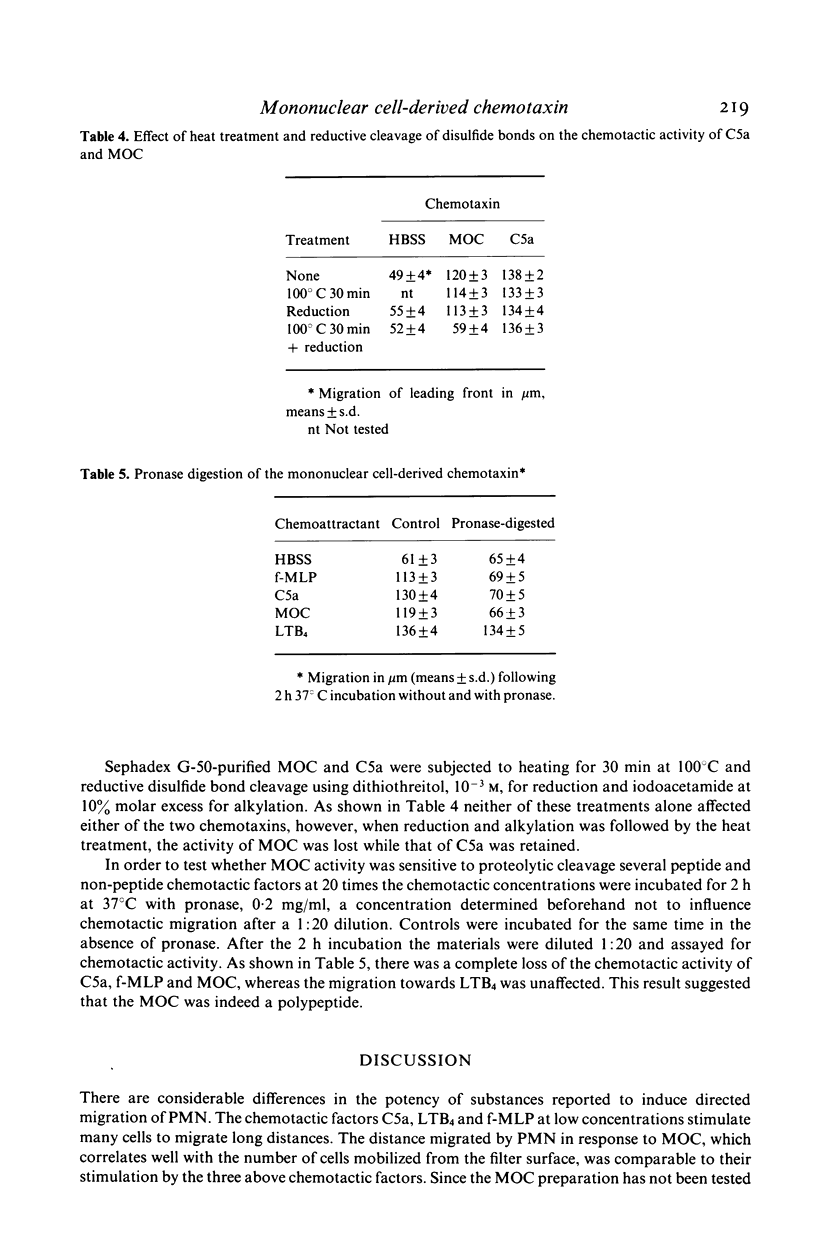
Human mononuclear leucocytes isolated from the peripheral blood by centrifugation on Ficoll-Hypaque cushions and adherent on plastic petri dishes, produced a chemotactic factor that attracted human neutrophilic granulocytes to the same extent as did optimal concentrations of the complement split product C5a and the leukotriene B4. The active component eluted from a Sephadex G-50 gel filtration column as a single peak with an apparent molecular weight of 10,000. The chemotactic activity was resistant to reductive cleavage of disulfide bonds and heating at 100 degrees C for 30 min but was lost when reduction and heating were combined. Digestion with a proteolytic enzyme eliminated the attractive potential. The data suggest that this is a novel chemotactic peptide. It is conceivable that it has been seen previously and was mistaken for a lymphokine or interleukin 1.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of molecular size and molecular weights of biological compounds by gel filtration. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodirker W. B., Bock G. N., Vaughan J. H. Isolation of human PMN leukocytes and granules: observations on early blood diluion and on heparin. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. M. Low molecular weight eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF) production by rat peritoneal mononuclear phagocytes. Immunobiology. 1980 Apr;157(1):62–66. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(80)80063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damerau B., Wüstefeld H., Vogt W. Binding characteristics of the complement peptides C3a and C5a-desArg to cellulose nitrate filters in Boyden chambers. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;12:121–133. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9352-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):264–265. doi: 10.1038/286264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Hugli T. E. Identification of classical anaphylatoxin as the des-Arg form of the C5a molecule: evidence of a modulator role for the oligosaccharide unit in human des-Arg74-C5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabbe J., Czarnetzki B. M., Rosenbach T., Mardin M. Identification of chemotactic lipoxygenase products of arachidonate metabolism in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 May;82(5):477–479. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12260985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANKS J. H., WALLACE J. H. Determination of cell viability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 May;98(1):188–192. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. The structural basis for anaphylatoxin and chemotactic functions of C3a, C4a, and C5a. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Feb;1(4):321–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Fales H. M., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Stimuli and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI109878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Lawley T. J., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of neutrophil accumulation in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):259–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierowski J. A., Gallin J. I., Reynolds H. Y. Mechanism for the inflammatory response in primate lungs. Demonstration and partial characterization of an alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor with preferential activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Wilkinson P. C., Abercrombie M., Becker E. L., Hirsch J. G., Miller M. E., Scottramsey W., Zigmond S. H. A proposal for the definition of terms related to locomotion of leucocytes and other cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):377–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Stadler B. M., Luger B. M., Sztein M. B., Schmidt J. A., Hawley-Nelson P., Grabner G., Oppenheim J. J. Characteristics of an epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor (ETAF) produced by human epidermal cells and a human squamous cell carcinoma cell line. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Sep;81(3):187–193. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12517658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Oppenheim J. J. Bidirectional amplification of macrophage-lymphocyte interactions: enhanced lymphocyte activation factor production by activated adherent mouse peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Mizel D. Purification to apparent homogeneity of murine interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):834–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Bendtzen K., Greineder D. Mediators of immunity: lymphokines and monokines. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:55–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A., Rosenthal A. S. Adherent cell function in murine T-lymphocyte antigen recognition. IV. Enhancement of murine T-cell antigen recognition by human leukocytic pyrogen. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):709–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauder D. N., Mounessa N. L., Katz S. I., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Chemotactic cytokines: the role of leukocytic pyrogen and epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor in neutrophil chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Gallin J. I. Biochemistry of phagocyte chemotaxis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:203–261. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152815-7.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Goetzl E. J. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of leukocyte chemotaxis. Science. 1981 Aug 21;213(4510):830–837. doi: 10.1126/science.6266014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Meadows L., Amos D. B. Characterization of human chemotactic lymphokine production induced by mitogens and mixed leukocyte reactions using a new microassay. Cell Immunol. 1977 May;30(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Franklin M., Sun F. F., Goetzl E. J. Alveolar macrophage lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid: isolation and recognition as the predominant constituents of the neutrophil chemotactic activity elaborated by alveolar macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


