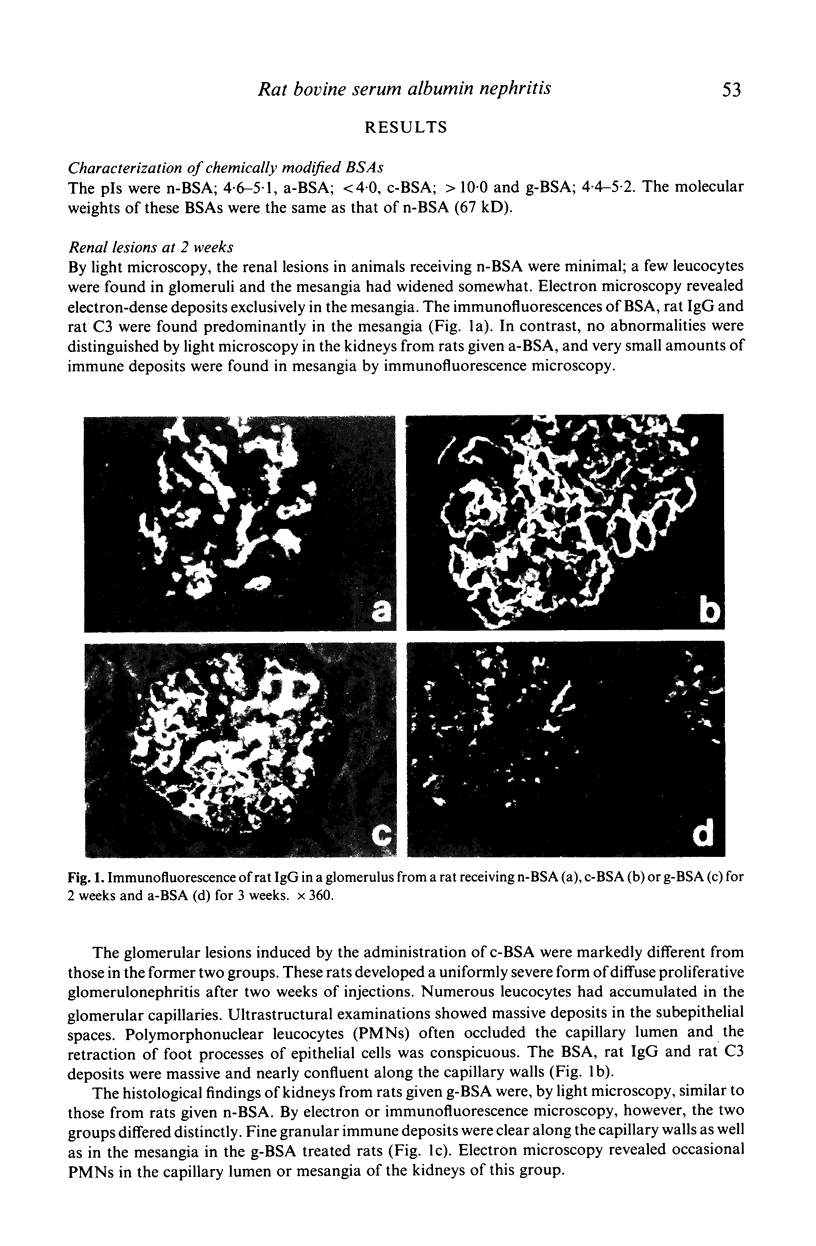
Abstract
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) used to incite chronic serum sickness glomerulonephritis in rats was chemically modified to study the effect of antigenic alteration. The BSA was used in its native form (n-BSA) as well as anionic (a-BSA), cationic (c-BSA) or glycosylated (g-BSA) forms. Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) preimmunized 8 weeks earlier received daily intravenous injections of the respective BSA preparations for the ensuing 3 weeks. Histological examination of their kidneys revealed that c-BSA given for 2 weeks induced a severe diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis and profound proteinuria. Electron-dense deposits localized preferentially in the subepithelial spaces of renal glomeruli from these rats, but a few in the mesangia. Quite differently, rats receiving n-BSA or g-BSA developed a less severe form of glomerulonephritis even after 3 weeks of injections. Besides the massive mesangial deposits, the subepithelial deposits were conspicuous in the glomeruli from rats given g-BSA for 2 weeks, but deposition in glomerular capillaries was rare in rats given n-BSA for the same duration. In contrast, the administration of a-BSA resulted in minimal abnormalities visible by light microscopy and a few immune deposits in the mesangia even at the third week. The antibody response in rats given c-BSA or a-BSA was apparently different from n-BSA treated rats. The present study shows the important role of the antigen's electric charge in the pathogenesis of proliferative glomerulonephritis. The foregoing results also foster our proposal that the carbohydrate content of the antigen influences the development of this renal disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassiouny A. R., Rosenberg H., McDonald T. L. Glucosylated collagen is antigenic. Diabetes. 1983 Dec;32(12):1182–1184. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.12.1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Kamil E. S., Ward H. J., Cohen A. H. Antigenic changes as a determinant of immune complex localization in the rat glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):442–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H. Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):451–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI110469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Pongor S., Cerami A. Covalent attachment of soluble proteins by nonenzymatically glycosylated collagen. Role in the in situ formation of immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1739–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Farquhar M. G. Distribution of annionic sites in glomerular basement membranes: their possible role in filtration and attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Lamm M. E. Charge of circulating immune complexes as a factor in glomerular basement membrane localization in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. G., Koshland D. E., Jr A method for the quantitative modification and estimation of carboxylic acid groups in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Miller F. Role of antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Anionic sites in the glomerular basement membrane. In vivo and in vitro localization to the laminae rarae by cationic probes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):137–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oite T., Batsford S. R., Mihatsch M. J., Takamiya H., Vogt A. Quantitative studies of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by planted, cationized antigen. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):460–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. J., Cohen A. H., Border W. A. In situ formation of subepithelial immune complexes in the rabbit glomerulus: requirement of a cationic antigen. Nephron. 1984;36(4):257–264. doi: 10.1159/000183165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kihara I., Hara M., Kawasaki K., Yaoita E. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) nephritis in rats II. Histological findings and complement activation by immune complex in SHR rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1983 Dec;64(6):660–669. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



