Abstract
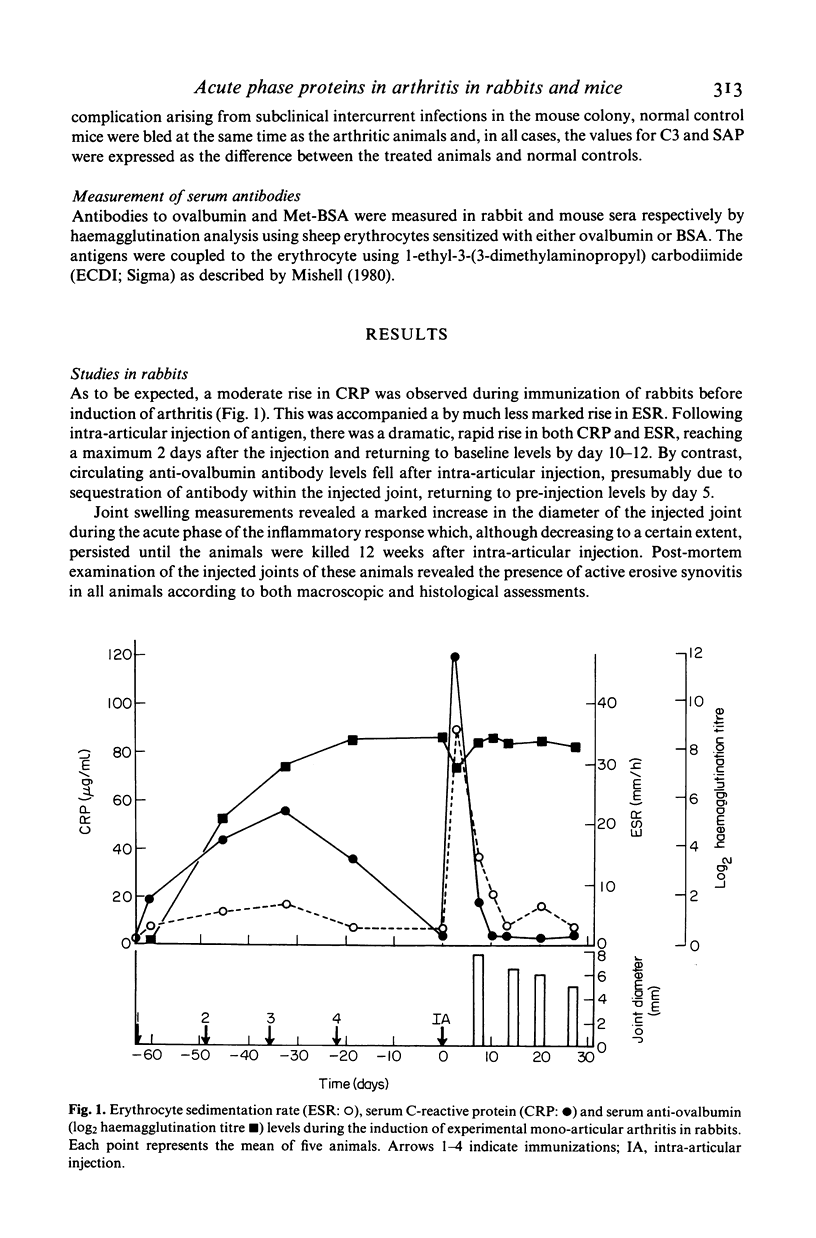
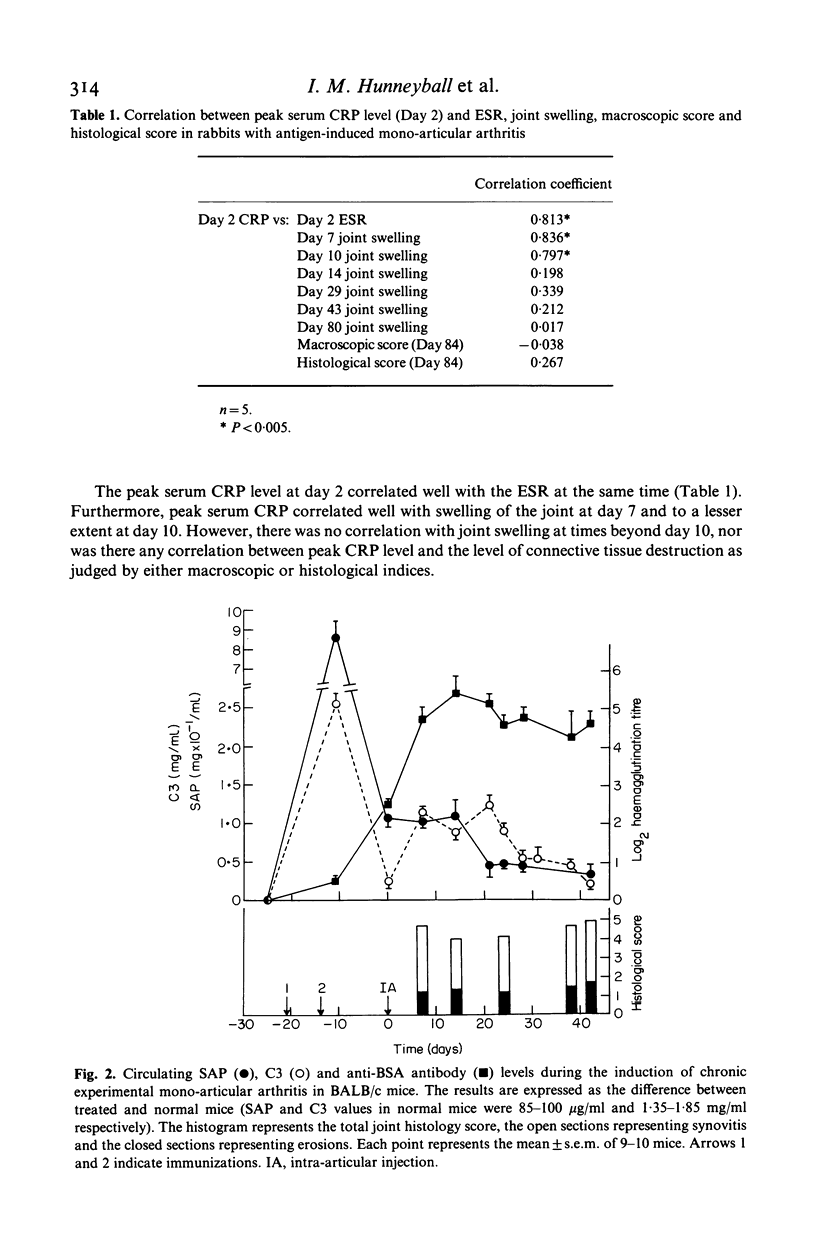
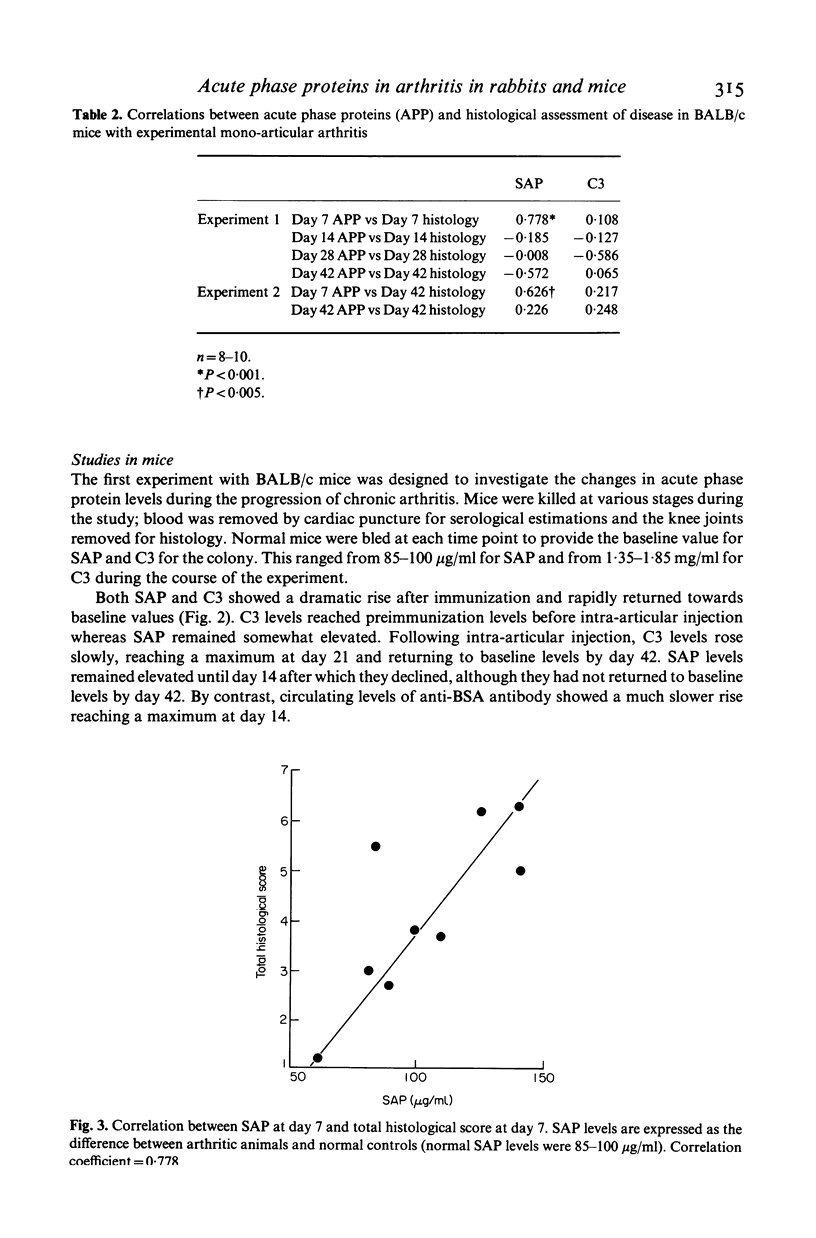
Acute phase protein levels have been measured during the induction and progression of antigen-induced mono-articular arthritis in rabbits and mice. In rabbits there was a short lived elevation in serum C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) immediately following intra-articular injection which returned to baseline levels 10-12 days after the injection. In BALB/c mice, serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and the third component of complement (C3) were elevated after intra-articular injection, returning towards baseline levels 6 weeks after the injection. The levels of CRP and SAP correlated with the inflammatory changes in the joints during the acute phase of the arthritic response (7 days after intra-articular injection). During the chronic phase the levels of these acute phase proteins bore no relationship to the degree of connective tissue destruction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos R. S., Constable T. J., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., McConkey B. Rheumatoid arthritis: relation of serum C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rates to radiographic changes. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 22;1(6055):195–197. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6055.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., Dyck R. F., Pepys M. B. Studies of the in vivo synthesis and catabolism of serum amyloid P component (SAP) in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jan;59(1):235–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., Gomer K., Davies A. J., Evans D. J., Klaus G. G., Pepys M. B. Differences in the acute phase responses of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and C3 to injections of casein or bovine serum albumin in amyloid-susceptible and -resistant mouse strains. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Petersen J., Halkjaer-Kristensen J., Ingemann-Hansen T. Interleukin-1-like activities in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and traumatic synovitis. Rheumatol Int. 1985;5(2):79–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00270301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham M. E. Models of arthritis and the search for anti-arthritic drugs. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;21(3):389–428. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of complement. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:67–118. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60548-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Doble A., Glynn L. E., Nind A. P. Production of a chronic arthritis with ovalbumin. Its retention in the rabbit knee joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):307–315. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. The chronicity of inflammation and its significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):105–121. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. G. S. C-reactive protein in the chronic rheumatic diseases. Lancet. 1951 Nov 3;2(6688):807–811. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)91595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. A spontaneous rheumatoid arthritis-like disease in MRL/l mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1690–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., de Beer F. C., Berry H., Hamilton E. D., Mace B. E., Pepys M. B. Correlation of clinical parameters of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with serum concentration of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. J Rheumatol. 1982 Mar-Apr;9(2):224–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P. The assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. A study based on measurements of the serum acute-phase reactants. Q J Med. 1972 Apr;41(162):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsuume-Sakai S., Motonishi K., Takahashi M. Quantitation of beta 1c/1A globulin (C3) in inbred mice: variation dependent upon strain, age, sex and environment. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;53(3):269–278. doi: 10.1159/000231762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M., Gomer K., Davies A. J., Doenhoff M. Serum amyloid P-component is an acute-phase reactant in the mouse. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):259–261. doi: 10.1038/278259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. Isolation of serum amyloid P-component (protein SAP) in the mouse. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):637–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rordorf C., Schnebli H. P., Baltz M. L., Tennent G. A., Pepys M. B. The acute-phase response in (NZB X NZW)F1 and MRL/l MICE. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1268–1273. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Soutar A. K., Trayner I. M., Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Walker L., Bowyer D., Herbert J., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Rabbit and rat C-reactive proteins bind apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Grindulis K. A., Struthers G. R., Coulton B. L., Popert A. J., Bacon P. A. Progression of radiological changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Feb;43(1):8–17. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöblom K. G., Saxne T., Pettersson H., Wollheim F. A. Factors related to the progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1984;13(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/03009748409102663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M. E., McCrae C. R., Cohen L. D., Schumacher H. R., Jr Pathogenesis of antigen-induced arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;(97):248–260. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197311000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K. Biosynthesis of the complement components and the regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):501–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beusekom H. J., van de Putte L. B., van den Berg W. B., van den Broek W. J. Antigen-induced arthritis: inflammation and antigen handling after two different doses of intra-articularly injected antigen. Immunology. 1982 Feb;45(2):193–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van Beusekom H. J., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., van der Sluis M. Antigen handling in antigen-induced arthritis in mice: an autoradiographic and immunofluorescence study using whole joint sections. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jul;108(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


