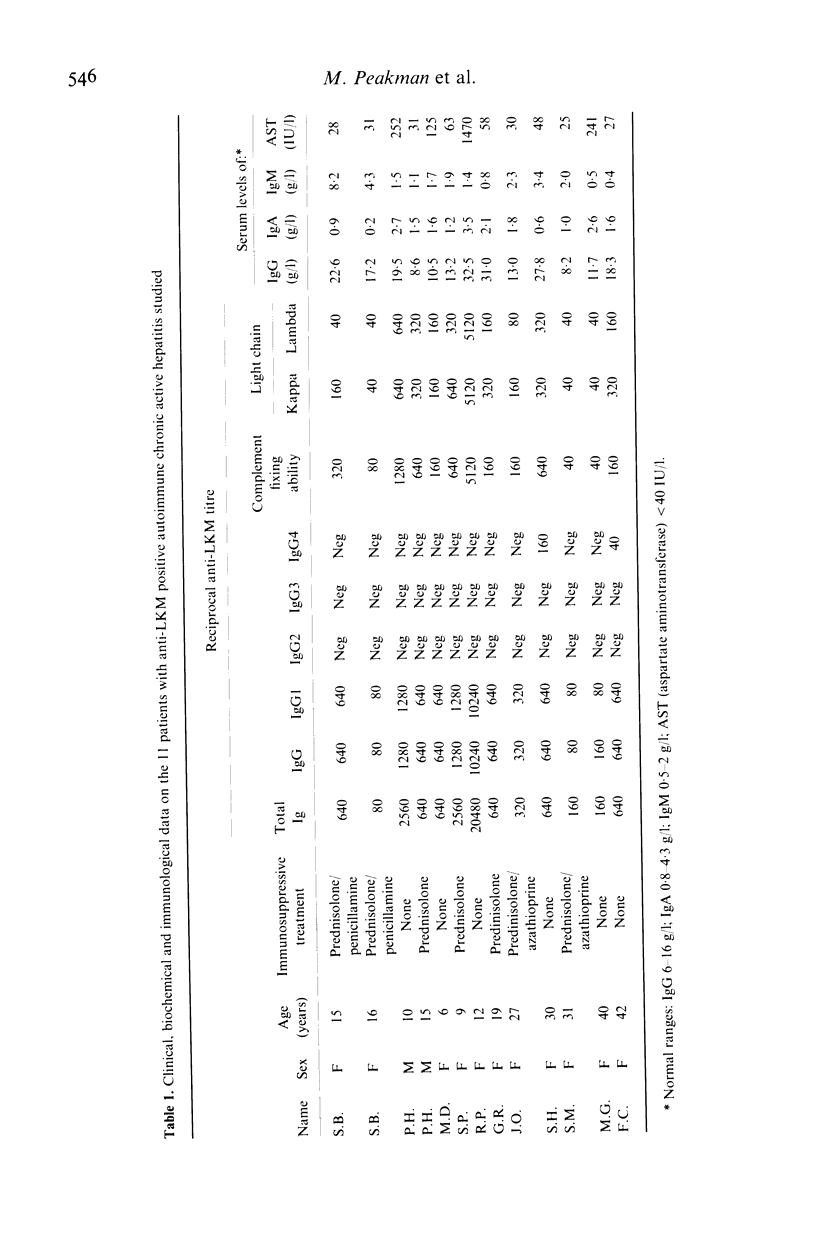
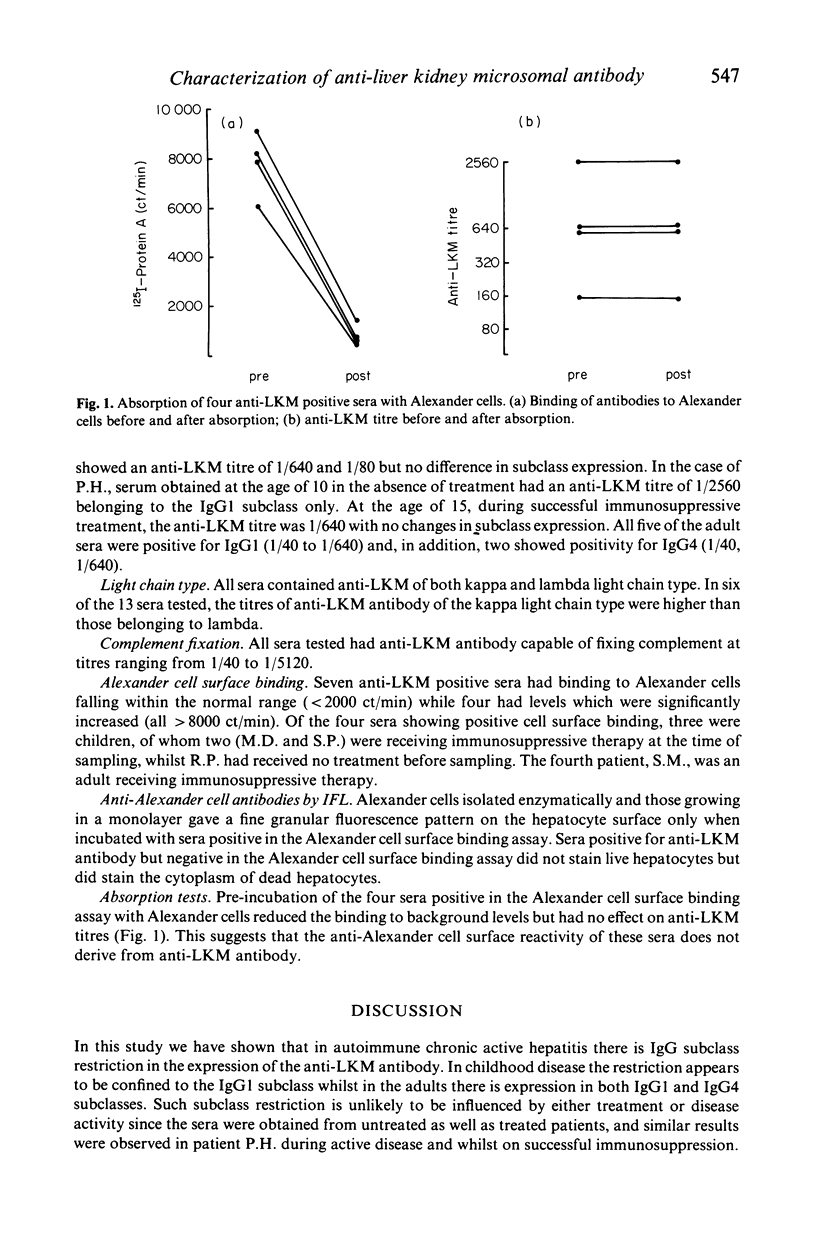
Abstract
An indirect immunofluorescence technique was used to investigate the immunoglobulin class, IgG subclass, light chain type and complement fixing ability of anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody (anti-LKM) in the sera of six children and five adults with autoimmune chronic active hepatitis (aCAH). Anti-LKM titres ranged from 1/80 to 1/20,480. In the children, the antibody belonged to the IgG1 subclass alone (titre 1/80-1/20,480) and was able to fix complement (titre 1/40-1/5120). In the adult group, antibody belonged to the IgG1 subclass in three cases (titre 1/40-1/640) whilst two belonged to both IgG1 (titre 1/640) and IgG4 (titre 1/40, 1/640). Such subclass restriction is similar to that found in other autoimmune disorders and may be genetically determined. Investigation of the light chain constituent of anti-LKM revealed that the kappa to lambda ratio was consistent with a polyclonal antibody response. To investigate the nature of the antigen to which anti-LKM is directed, the ability of these sera to bind to the surface membrane of isolated human hepatoma cells (Alexander cells) was investigated. Four of the eleven sera showed significant binding activity. Prior incubation of these four sera with Alexander cells abolished their membrane binding activity, but did not alter the anti-LKM titre. These results suggest that anti-LKM binds to cytoplasmic constituents alone and does not cross-react with surface antigens.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson N., Gelfand E. W., Jandl J. H., Rosen F. S. The interaction between human monocytes and red cells. Specificity for IgG subclasses and IgG fragments. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1207–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez F., Bernard O., Homberg J. C., Kreibich G. Anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody recognizes a 50,000 molecular weight protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1231–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Bieber M. S., Josepho C. A., Xavier C., Anderson D. S. Functional properties of lymphocyte subpopulations in hepatitis B virus infection. II. Cytotoxic effector cell killing of targets that naturally express hepatitis B surface antigen and liver-specific lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):45–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi M., Bianchi F. B., Cassani F., Pisi E. Liver cell surface expression of the antigen reacting with liver-kidney microsomal antibody (LKM). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):36–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Tait B. D. HLA associations with autoimmune-type chronic active hepatitis: identification of B8-DRw3 haplotype by family studies. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G. Autoimmunity in liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Dec;67(6):569–578. doi: 10.1042/cs0670569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes A. B., McLachlan S. M., Bird P., Rees Smith B. The distribution of microsomal and thyroglobulin antibody activity among the IgG subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):239–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggione O., Stokes R. P., Thompson R. A. Predominance of IgG3 subclass in primary cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 26;286(6370):1015–1016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6370.1015-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Bianchi F. B., Doniach D. Characterization of the microsomal antigen related to a subclass of active chronic hepatitis. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):589–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. G., Williams R., Walker G., Rizzetto M., Doniach D. Hepatic disorders associated with liver-kidney microsomal antibodies. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 13;2(5910):80–84. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5910.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Wells L., Larcher V. F., Nasaruddin B. A., Davies E. T., Mieli-Vergani G., Mowat A. P. Genetically determined low C4: a predisposing factor to autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 10;2(8450):294–298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. The IgG subclass responses of human lymphocytes to B-cell activators. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):269–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Schanfield M. S., Tait B. D., Mackay I. R. Interaction of HLA and Gm in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):80–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Jefferis R., Eyquem A. IgG subclass distribution of autoantibodies to DNA and to nuclear ribonucleoproteins in autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):595–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



