Abstract
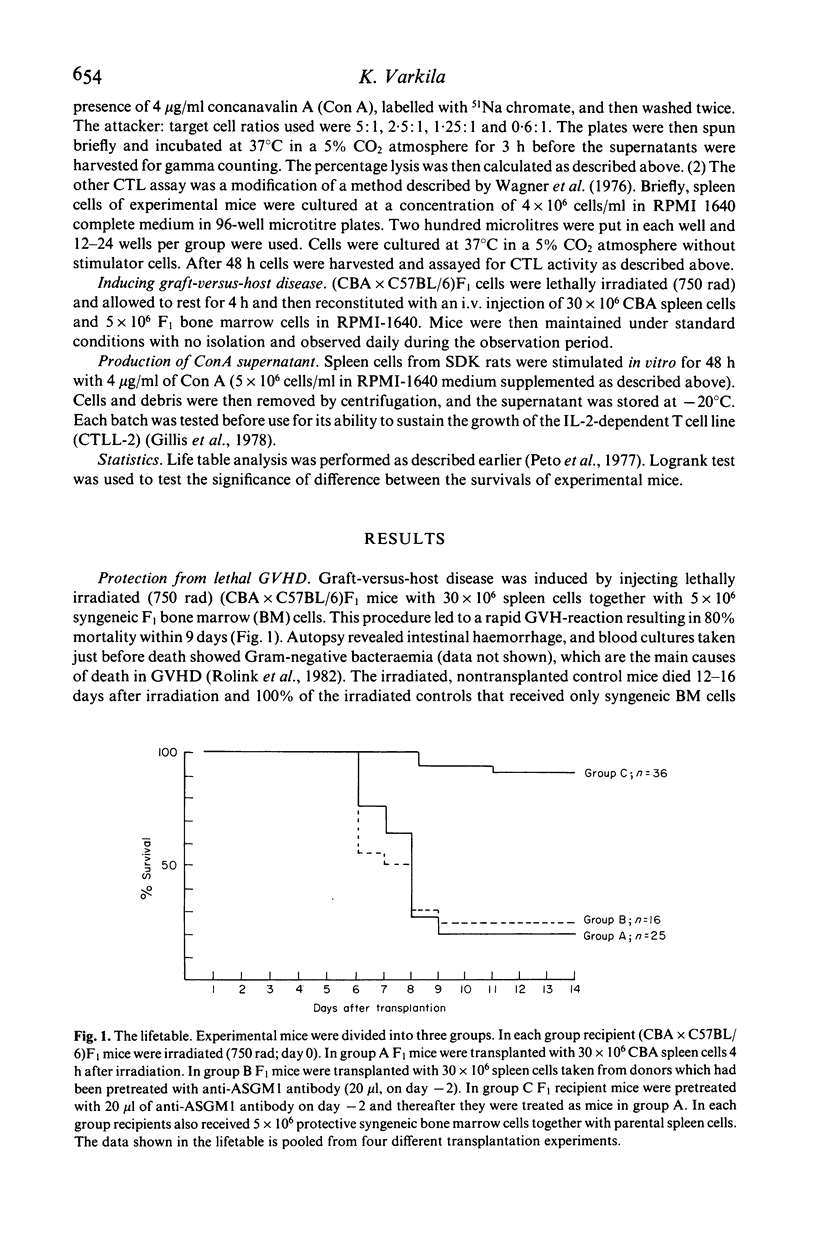
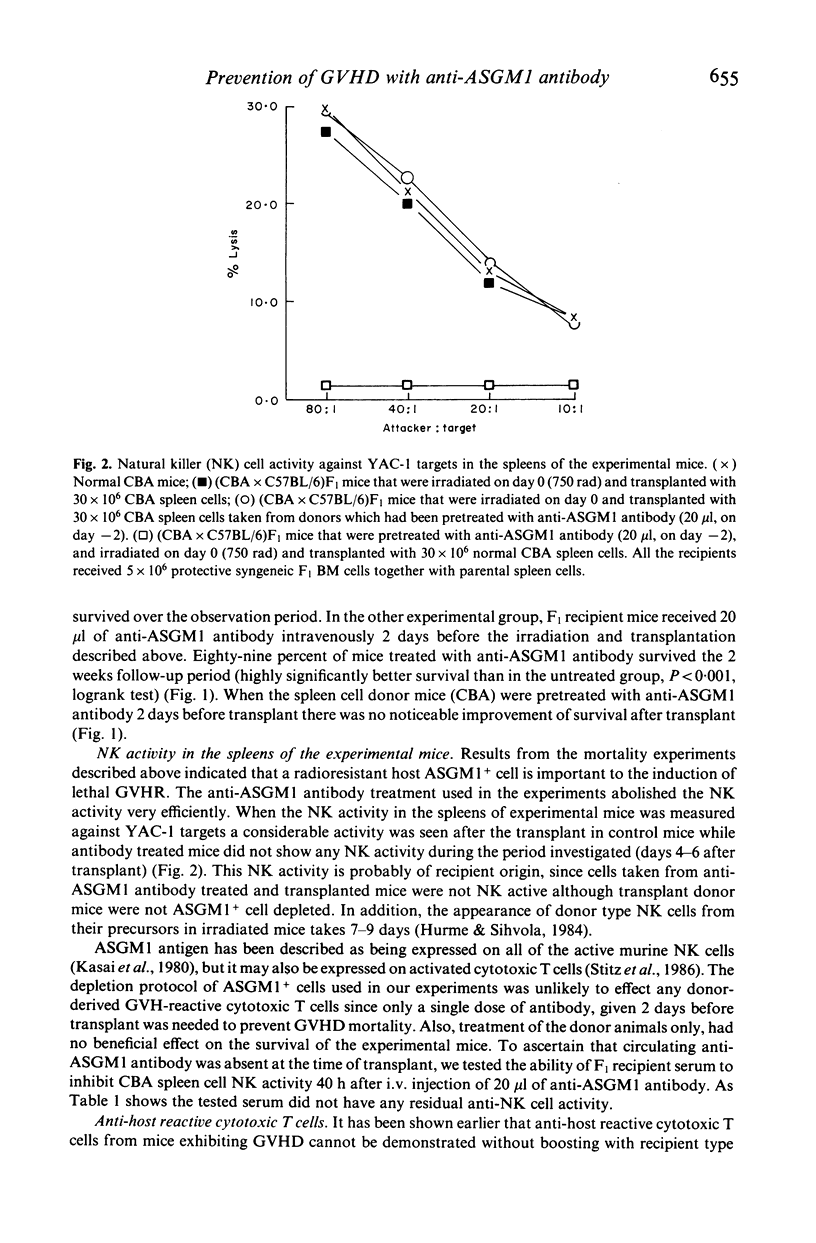
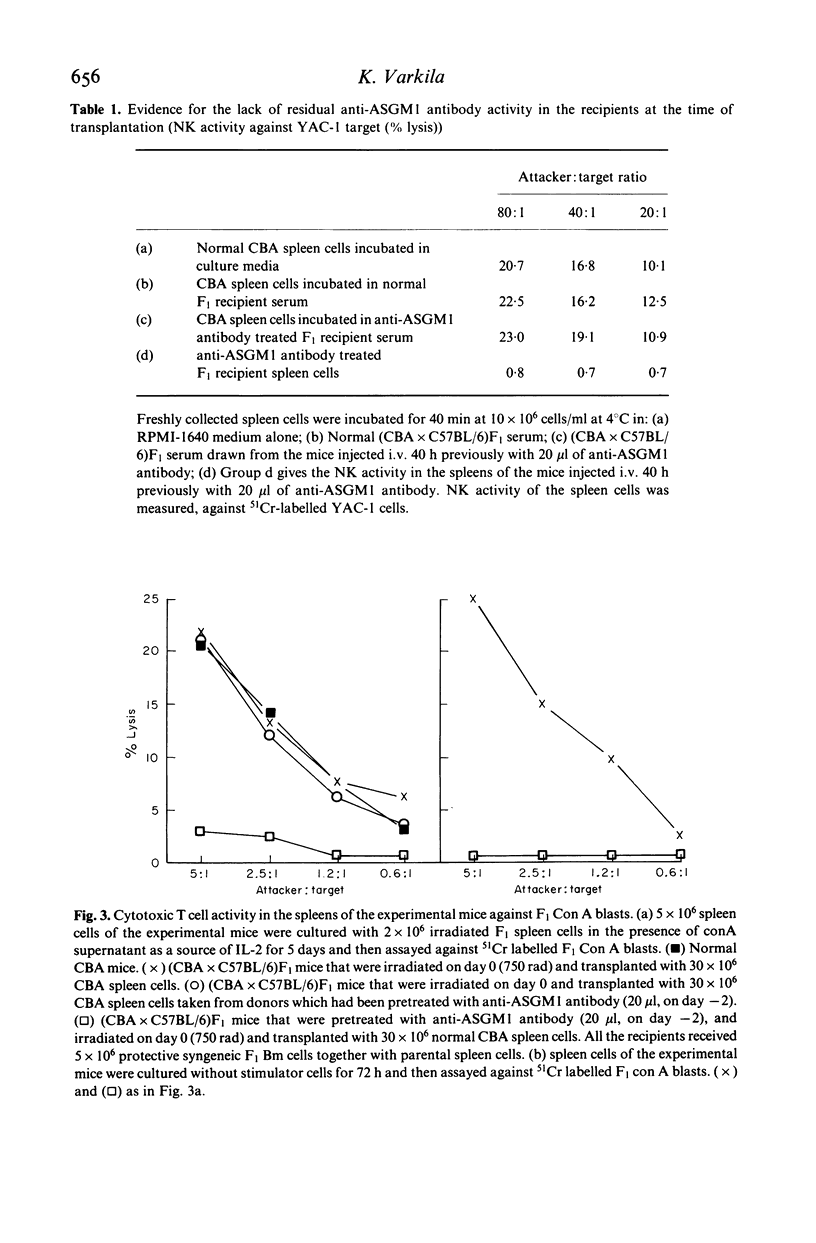
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was induced in irradiated (750 rad) (CBA x C57BL/6)F1 hybrid mice by an intravenous injection of 30 x 10(6) CBA spleen cells and 5 x 10(6) syngeneic F1 bone marrow cells. The GVHD resulted in the death of 80% of recipients within 9 days. However, when radioresistant Asialo-GM1+ cells were depleted from the recipients with a single injection of anti-Asialo-GM1 antibody 2 days before irradiation and transplantation, mortality decreased significantly (to 11%). During the GVHD, anti-host specific cytotoxic T cell (CTL) activity could be shown in vitro in the spleens of mice suffering from the GVHD if suppressor activity was first abolished by in vitro culture procedures. This CTL activity, however, was not detectable in the spleens of anti-ASGM1 antibody pretreated hosts. The results indicate that radioresistant ASGM1+ cells of host origin are necessary for the induction of both anti-host CTL and lethal GVHD.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charley M. R., Mikhael A., Bennett M., Gilliam J. N., Sontheimer R. D. Prevention of lethal, minor-determinate graft-host disease in mice by the in vivo administration of anti-asialo GM1. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2101–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Martin G., Qin S., Waldmann H. Monoclonal antibodies to promote marrow engraftment and tissue graft tolerance. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):164–166. doi: 10.1038/323164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokhelar M. C., Wiels J., Lipinski M., Tetaud C., Devergie A., Gluckman E., Tursz T. Natural killer cell activity in human bone marrow recipients: early reappearance of peripheral natural killer activity in graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1981 Jan;31(1):61–65. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198101000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. P., Reisner Y. Graft rejection and graft-versus-host disease: mirror images. Lancet. 1986 Jun 28;1(8496):1468–1470. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91503-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Volkman D. J., Jurgensen C. H., Fauci A. S. Activated human T cells can present alloantigens but cannot present soluble antigens. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 1;95(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillén F. J., Ferrara J., Hancock W. W., Messadi D., Fonferko E., Burakoff S. J., Murphy G. F. Acute cutaneous graft-versus-host disease to minor histocompatibility antigens in a murine model. Evidence that large granular lymphocytes are effector cells in the immune response. Lab Invest. 1986 Jul;55(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton B. L., Bevan M. J., Parkman R. Anti-recipient cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors are present in the spleens of mice with acute graft versus host disease due to minor histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):621–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman P. S., Cudkowicz G., Dausset J. Decline of natural killer cell activity in sublethally irradiated mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jul;61(1):265–268. doi: 10.1093/jnci/61.1.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurme M., Sihvola M. High expression of the Thy-1 antigen on natural killer cells recently derived from bone marrow. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 1;84(2):276–284. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Hochman P. S., Haller O., Shearer G. M., Wigzell H., Cudkowicz G. Evidence for a similar or common mechanism for natural killer cell activity and resistance to hemopoietic grafts. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):655–663. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korngold R., Sprent J. Lethal graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation across minor histocompatibility barriers in mice. Prevention by removing mature T cells from marrow. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1687–1698. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota E., Ishikawa H., Saito K. Modulation of F1 cytotoxic potentials by GvHR. Host- and donor-derived cytotoxic lymphocytes arise in the unirradiated F1 host spleens under the condition of GvHR-associated immunosuppression. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1142–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Kirkpatrick D., Livnat S., Storb R. Natural killer cells in bone marrow transplantation. Lancet. 1980 Nov 8;2(8202):1025–1025. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotzová E., Savary C. A., Pollack S. B. Prevention of rejection of allogeneic bone marrow transplants by NK 1.1 antiserum. Transplantation. 1983 May;35(5):490–494. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198305000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T., Holda J. H., Claman H. N. Graft-vs-host reactions (GVHR) across minor murine histocompatibility barriers. II. Development of natural suppressor cell activity. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1644–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norin A. J., Emeson E. E., Veith F. J. Long-term survival of murine allogeneic bone marrow chimeras: effect of anti-lymphocyte serum and bone marrow dose. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. G., Blacklock H. A., Janossy G., Gilmore M. J., Price-Jones L., Tidman N., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Skeggs D. B., Panjwani D., Ball S. Depletion of T lymphocytes in donor marrow prevents significant graft-versus-host disease in matched allogeneic leukaemic marrow transplant recipients. Lancet. 1984 Mar 3;1(8375):472–476. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92848-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Radaszkiewicz T., Pals S. T., van der Meer W. G., Gleichmann E. Allosuppressor and allohelper T cells in acute and chronic graft-vs-host disease. I. Alloreactive suppressor cells rather than killer T cells appear to be the decisive effector cells in lethal graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1501–1522. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Ghayur T., Kongshavn P. A., Lapp W. S. Natural killer activity by spleen, lymph node, and thymus cells during the graft-versus-host reaction. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):144–146. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Allavena P., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B., Oppenheim J. J. Subsets of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) exhibit accessory cell functions. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3049–3055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Baenziger J., Pircher H., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Effect of rabbit anti-asialo GM1 treatment in vivo or with anti-asialo GM1 plus complement in vitro on cytotoxic T cell activities. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4674–4680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varkila K., Hurme M. Natural killer (NK) cells and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): no correlation between the NK cell levels and GVHD in the murine P----F1 model. Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):121–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


