Abstract
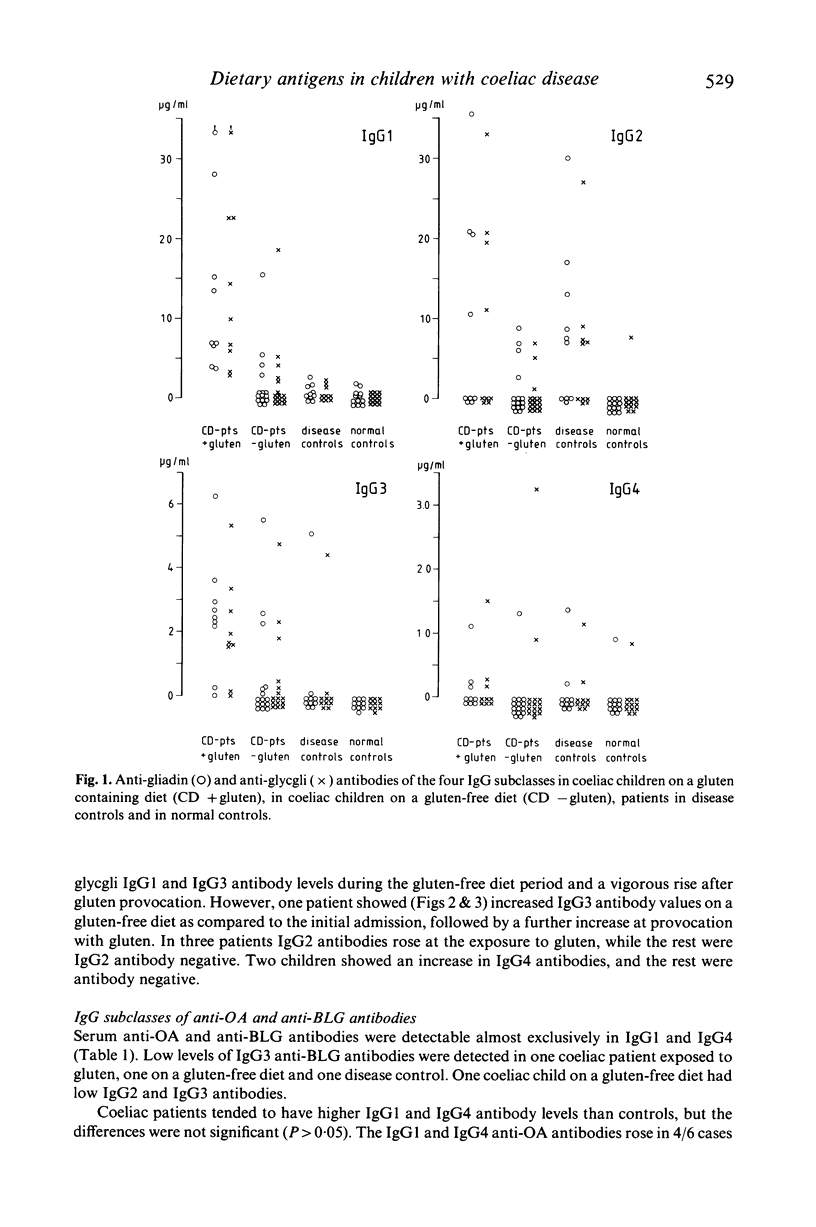
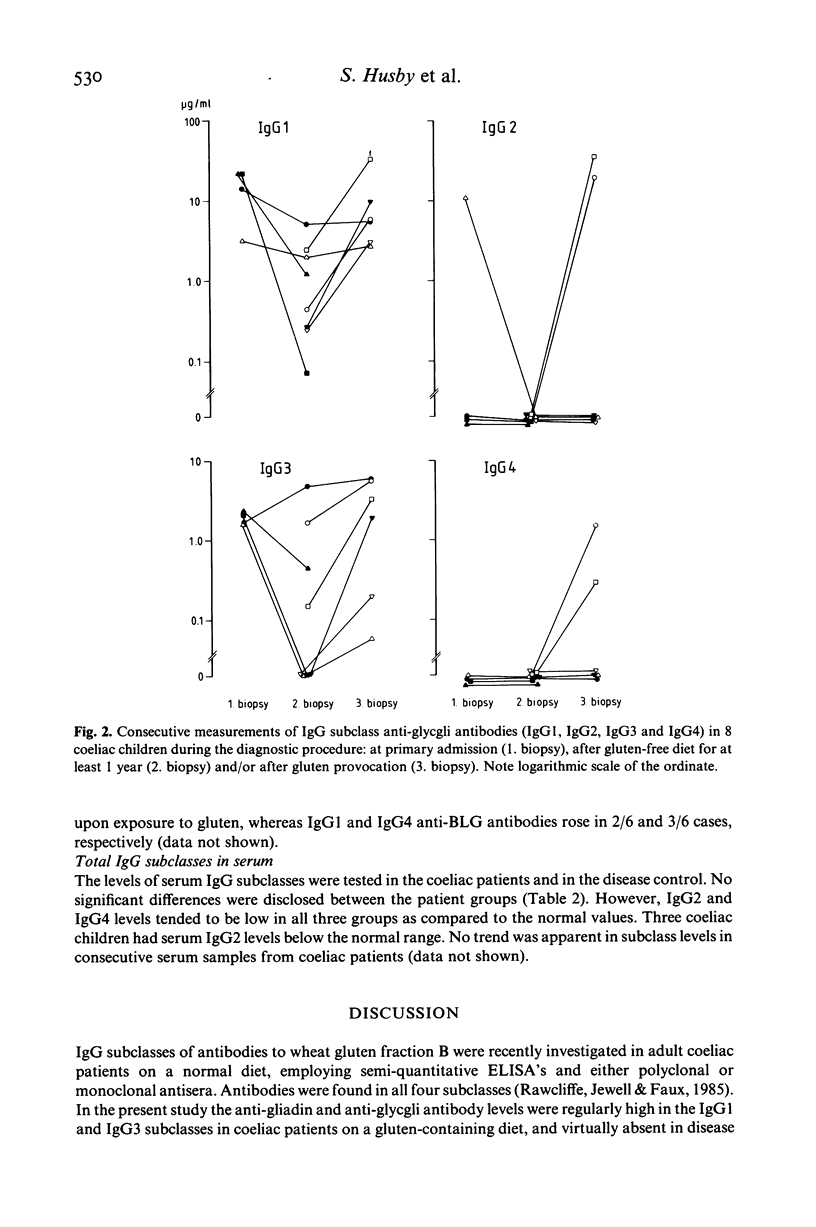
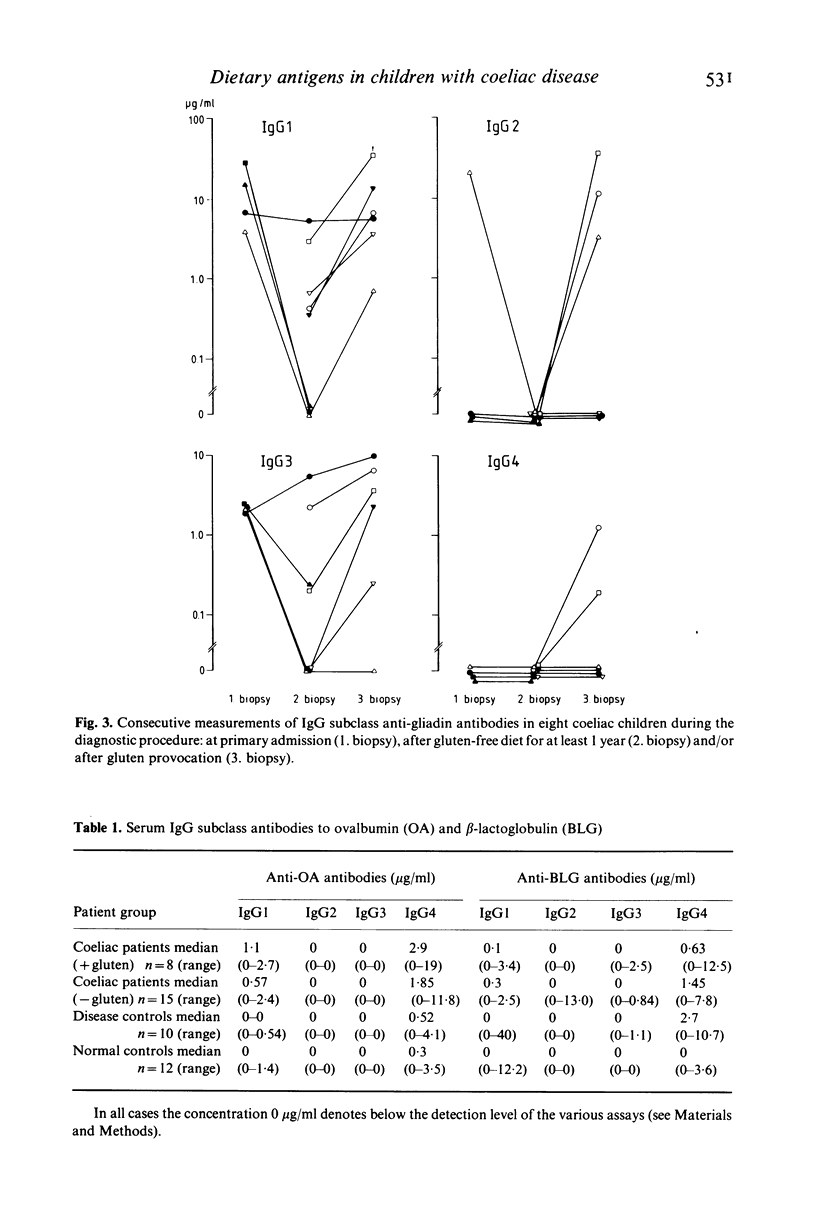
IgG subclasses of antibodies to the dietary antigens gliadin, glycgli (a gluten component), ovalbumin (OA) and beta-lactoglobulin (BLG) were quantified in children with coeliac disease (CD), nine on a gluten-containing diet, 15 on a gluten-free diet, and in appropriate controls. In addition, total serum IgG subclasses were measured. IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies to gluten and glycgli were detected in 9/9 and 8/9 CD-patient on a gluten-containing diet, respectively, and in 4/15 and 6/15 patients on a gluten-free diet. None of the controls had appreciable levels of IgG1 antibodies and only 1/22 of the controls had IgG3 antibodies to gliadin and glycgli. IgG2 and IgG4 antibodies to the same antigens were found in a few coeliacs and controls. Consecutive samples from coeliac children (8 patients) showed a clear relation between the exposure to gluten and a rise in IgG1 (8/8) and IgG3 antibody levels (7/8). In contrast, IgG antibodies to OA and BLG were almost exclusively of the IgG1 and IgG4 subclasses. The highest levels were found in children with CD, but the differences between the groups were not significant. Total serum IgG subclasses did not differ between the groups, but the IgG2 and IgG4 levels in most coeliac children were low. The production of IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies to gluten components may be an important precondition for the development of coeliac disease in susceptible individuals.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand B. S., Piris J., Jerrome D. W., Offord R. E., Truelove S. C. The timing of histological damage following a single challenge with gluten in treated coeliac disease. Q J Med. 1981;50(197):83–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Veall N. A persistent defect in intestinal permeability in coeliac disease demonstrated by a 51Cr-labelled EDTA absorption test. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramble M. G., Zucoloto S., Wright N. A., Record C. O. Acute gluten challenge in treated adult coeliac disease: a morphometric and enzymatic study. Gut. 1985 Feb;26(2):169–174. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R. Immunoglobulin G: functional sites. Mol Immunol. 1985 Mar;22(3):161–206. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick V. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Measurements of intestinal permeability using low molecular weight polyethylene glycols (PEG 400). II. Application to normal and abnormal permeability states in man and animals. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):247–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J. Circulating antibodies to wheat gliadin fractions in coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jun;49(6):454–458. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.6.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. P. The binding of a glycopeptide component of wheat gluten to intestinal mucosa of normal and coeliac human subjects. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Dec 1;73(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Mowat A. M., Strobel S. Abrogation of tolerance to fed antigen and induction of cell-mediated immunity in the gut-associated lymphoreticular tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:486–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby S., Jensenius J. C., Svehag S. E. ELISA quantitation of IgG subclass antibodies to dietary antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 10;82(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90364-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Weiss J. B., Brown R. J., Lee T., Schanfield M. S. Immunoglobulin allotype markers in gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Lancet. 1983 Apr 30;1(8331):952–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenrick K. G., Walker-Smith J. A. Immunoglobulins and dietary protein antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Gut. 1970 Aug;11(8):635–640. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.8.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malizia G., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Wood G. M., Howdle P. D., Janossy G., Losowsky M. S. The microenvironment of coeliac disease: T cell phenotypes and expression of the T2 'T blast' antigen by small bowel lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):437–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Haeney M. R. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. VI--Proliferative response of small intestinal epithelial lymphocytes distinguishes gluten- from non-gluten-induced enteropathy. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Feb;36(2):149–160. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Hinde J. Inflammatory component of celiac sprue mucosa. I. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90749-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Harms H. K., Rey J., Shmerling D. H., Visakorpi J. K., Walker-Smith J. A. The diagnosis of coeliac disease. A commentary on the current practices of members of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (ESPGAN). Arch Dis Child. 1979 Oct;54(10):783–786. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.10.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzies I. S., Laker M. F., Pounder R., Bull J., Heyer S., Wheeler P. G., Creamer B. Abnormal intestinal permeability to sugars in villous atrophy. Lancet. 1979 Nov 24;2(8152):1107–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity reactions in the small intestine. 6. Pathogenesis of the graft-versus-host reaction in the small intestinal mucosa of the mouse. Transplantation. 1981 Sep;32(3):238–243. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Whelan C. A., Feighery C. F., Weir D. G. Suppressor-cell activity in coeliac disease induced by alpha-gliadin, a dietary antigen. Lancet. 1984 Dec 8;2(8415):1305–1307. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90822-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis and electroimmunoassay of human IgG subclasses. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Jun;86C(3):109–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. IgG subclass levels in infancy and childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jan;68(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkkiö M., Savilahti E., Kuitunen P. Semi-quantitative analysis of immunoglobulins and complement fractions 3 and 4 in the jejunal mucosa in coeliac disease and in food allergy in childhood. Immunohistochemical study by light and electron microscopy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1981 Sep;89(5):343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Mann D. L., Hague N. E., Heck J. A., van Leeuwen H. A., van Rood J. J., Strober W. Genetic basis of gluten-sentitive enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher-Wilmott R. W., Booth I., Harries J., Levinsky R. J. Intestinal absorption of food antigens in coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Jun;57(6):462–466. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.6.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawcliffe P. M., Jewell D. P., Faux J. A. Specific IgG subclass antibodies, IgE and IgG S-TS antibodies to wheat gluten fraction B in patients with coeliac disease. Clin Allergy. 1985 Mar;15(2):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb02268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Viander M., Perkkiö M., Vainio E., Kalimo K., Reunala T. IgA antigliadin antibodies: a marker of mucosal damage in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):320–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Ek J., Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Immunoglobulin-producing cells in jejunal mucosa of children with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet and after gluten challenge. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(1):81–88. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Ek J., Brandtzaeg P. Changes of serum antibody activities to various dietary antigens related to gluten withdrawal or challenge in children with coeliac disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(2):138–144. doi: 10.1159/000233680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Fausa O., Ek J., Brandtzaeg P. Immune response patterns in coeliac disease. Serum antibodies to dietary antigens measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):25–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Hirschberg H., Thorsby E. HLA-DR3- and HLA-DR7-restricted T-cell hyporesponsiveness to gluten antigen: a clue to the aetiology of coeliac disease? Scand J Immunol. 1983 Aug;18(2):163–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Lymphocyte subpopulations in the human small intestine. The findings in normal mucosa and in the mucosa of patients with adult coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Jewell D. P. Immunohistological characterisation of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1981 Mar;22(3):169–176. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.3.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenhammar L., Kilander A. F., Nilsson L. A., Strömberg L., Tarkowski A. Serum gliadin antibodies for detection and control of childhood coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Sep;73(5):657–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Busuttil A., Ferguson A. Human intestinal mucosal mast cells: expanded population in untreated coeliac disease. Gut. 1983 Mar;24(3):222–227. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.3.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Falchuk Z. M., Rogentine G. N., Nelson D. L., Klaeveman H. L. The pathogenesis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Aug;83(2):242–256. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-2-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Fleit H., Mellman I. S. Structural Aspects and Heterogeneity of Immunoglobulin Fc Receptors. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:247–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Manuel P. D., Walker-Smith J. A., Campbell C. A., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J. New immunofluorescent blood test for gluten sensitivity. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Nov;56(11):864–868. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.11.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Holborow E. J. Gliadin and reticulin antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Apr 16;1(8329):874–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Walker-Smith J. A., McCarthy D., Holborow E. J. Studies on the significance of the R1 anti-reticulin antibody associated with gluten sensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(1):47–51. doi: 10.1159/000233660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Austin R. K., Schanfield M. S., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Immunoglobulin G heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Giessen M., Rossouw E., van Veen T. A., van Loghem E., Zegers B. J., Sander P. C. Quantification of IgG subclasses in sera of normal adults and healthy children between 4 and 12 years of age. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Sep;21(3):501–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


