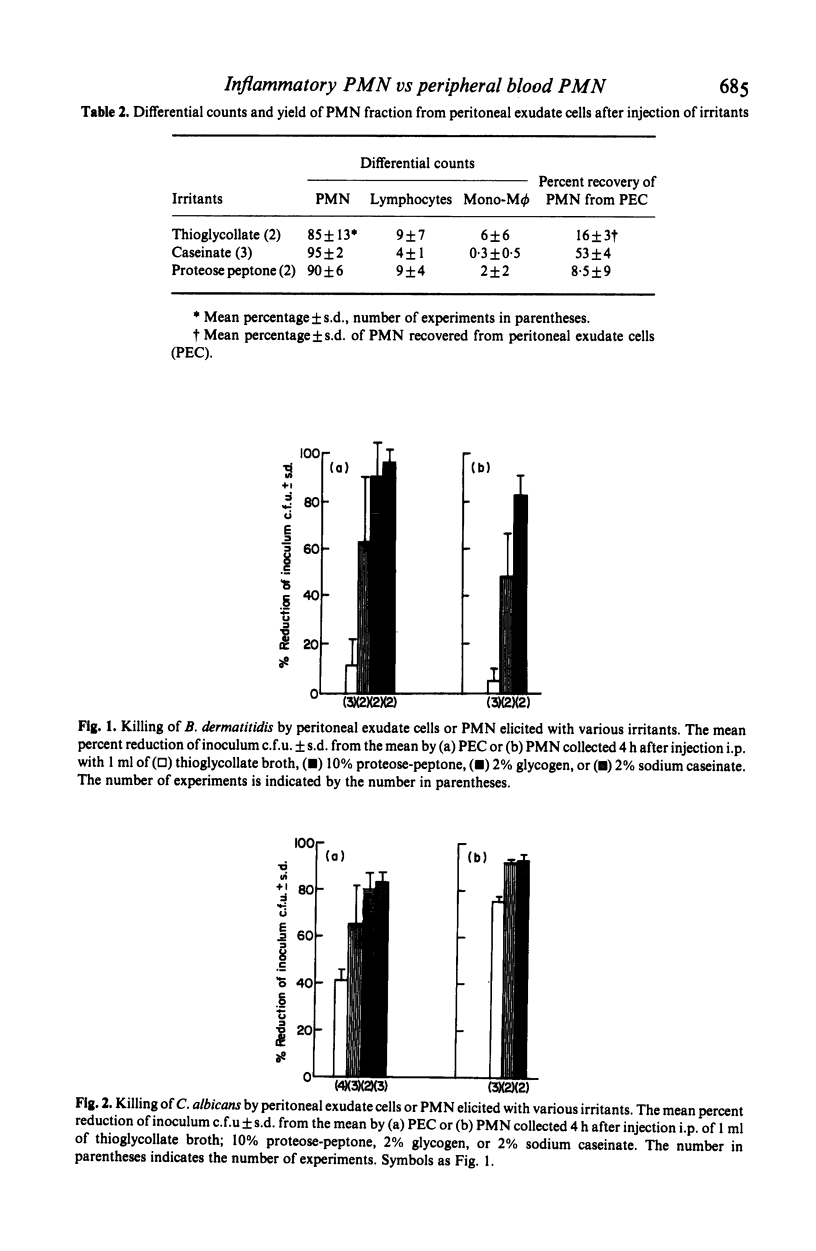
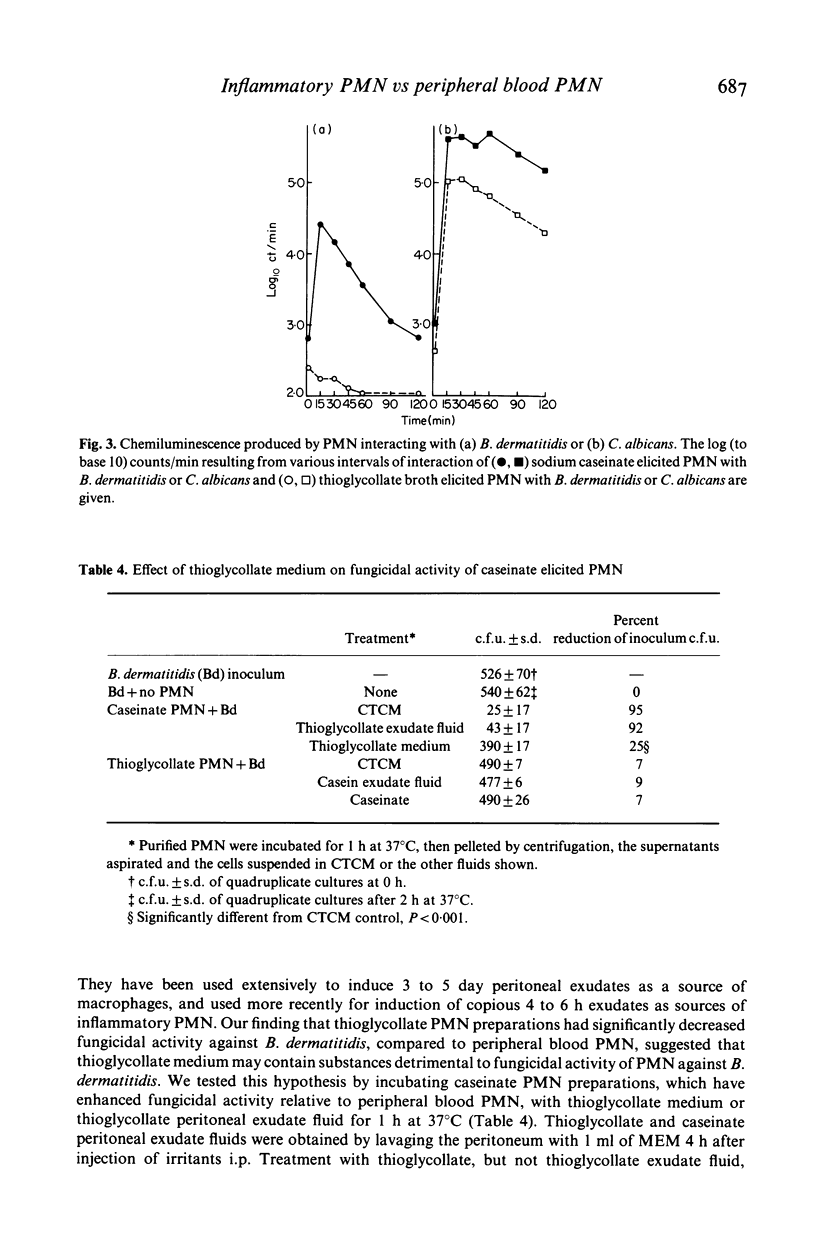
Abstract
A characteristic of inflammation is the influx of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) from peripheral blood to the inflammatory reaction. We report on metabolic alterations and alterations in fungicidal activity in PMN elicited intraperitoneally with different inflammatory agents. The fungicidal activity of murine peripheral blood PMN (PB-PMN) against phagocytosable Candida albicans and nonphagocytosable Blastomyces dermatitidis was compared to that of murine inflammatory PMN. PMN elicited with sodium caseinate exhibited enhanced killing of B. dermatitidis (93 +/- 3%) compared to PB-PMN (38 +/- 11.7%). In contrast, thioglycollate medium elicited PMN had significantly less ability to kill B. dermatitidis (3 +/- 5%) than PB-PMN. Incubation of caseinate PMN with thioglycollate medium for 1 h significantly reduced their ability to kill B. dermatitidis (95% vs 25%). This effect was not due to cytotoxicity of thioglycollate medium for PMN. Candidacidal activity of inflammatory PMN (caseinate or proteose peptone-elicited) was not significantly greater than that of peripheral blood PMN. However, inflammatory PMN had significantly greater candidacidal activity than thioglycollate-elicited PMN.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell M. L., Clay R. C., Howe C. W., Rutenburg A. M. Antibacterial properties of human inflammatory leukocytes; a comparison with leukocytes derived from peripheral blood. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Feb;11(2):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass C., Volkmann C. M., Klein H. P., Halde C. J., Archibald R. W., Stevens D. A. Pathogen factors and host factors in murine pulmonary blastomycosis. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jun 18;78(3):129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00466066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Activation of murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils for fungicidal activity with supernatants from antigen-stimulated immune spleen cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):447–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.447-452.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Opposite effects of human monocytes, macrophages, and polymorphonuclear neutrophils on replication of Blastomyces dermatitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.297-303.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Sugar A. M., Stevens D. A. Enhanced oxidative burst in immunologically activated but not elicited polymorphonuclear leukocytes correlates with fungicidal activity. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):396–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.396-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Sugar A. M., Stevens D. A. Immunological activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils for fungal killing: studies with murine cells and blastomyces dermatitidis in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Oct;36(4):505–520. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.4.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Lowell G. H. Stimulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte bactericidal activity by supernatants of activated human mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.502-507.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhet E., Dupont B., Pelletier M., Giroud J. P. Acute non-specific inflammatory reactions and protection against experimental Candida albicans infection. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):629–631. doi: 10.1007/BF01978770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S. Gastrointestinal carriage of group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):361–362. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Mocatta T. J. Human neutrophils require activation by mononuclear leucocyte conditioned medium to kill the pathogenic free-living amoeba, Naegleria fowleri. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellum K. B., Solberg C. O. Human leucocyte migration: studies with an improved skin chamber technique. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Dec;85C(6):413–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sendo F. In vitro induction of cytotoxic polymorphonuclear leukocytes by supernatant from a concanavalin A-stimulated spleen cell culture. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2508–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Lee K. Y., Biggar W. D. Enhancement of human neutrophil bactericidal activity by chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.295-301.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Gallin J. I. Separation and functional characterization of human neutrophil subpopulations. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A. K., Kahle J., Berek J., Zighelboim J. Successful immunotherapy with intraperitoneal Corynebacterium parvum in a murine ovarian cancer model is associated with the recruitment of tumor-lytic neutrophils into the peritoneal cavity. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Robertson D. C. Ingestion and intracellular survival of Brucella abortus in human and bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.224-230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Karnovsky M. L., Karnovsky M. J. Glycogen accumulation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and other intracellular alterations that occur during inflammation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):933–942. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. B., Cooper L. W. Leucocyte glycogen response in inflammatory exudates. Br J Haematol. 1974 Mar;26(3):485–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamori K., Yamashita T. Biochemical properties of polymorphonuclear neutrophils from venous blood and peritoneal exudates of rabbits. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):395–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.395-400.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N., Lopez A. F., Metcalf D., Johnson G., Pereira A. Mononuclear cell-mediated enhancement of granulocyte function in man. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Garcia M. L. Enhancement of neutrophils function as a result of prior exposure to chemotactic factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):167–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI109841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe S., Sendo F., Kimura S., Arai S. Activation of cytotoxic polymorphonuclear leukocytes by in vivo administration of a streptococcal preparation, OK-432. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jun;72(6):1365–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton J. M., Renggli H. H., Lehner T. The role of Fc and C3b receptors in phagocytosis by inflammatory polymorphonuclear leucocytes in man. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):955–961. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Gallin J. I. Secretory responses of human neutrophils: exocytosis of specific (secondary) granules by human neutrophils during adherence in vitro and during exudation in vivo. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Cohen H. J., Waldvogel F. A. Comparative superoxide-generating system of granulocytes from blood and peritoneal exudates. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):625–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.625-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



