Abstract
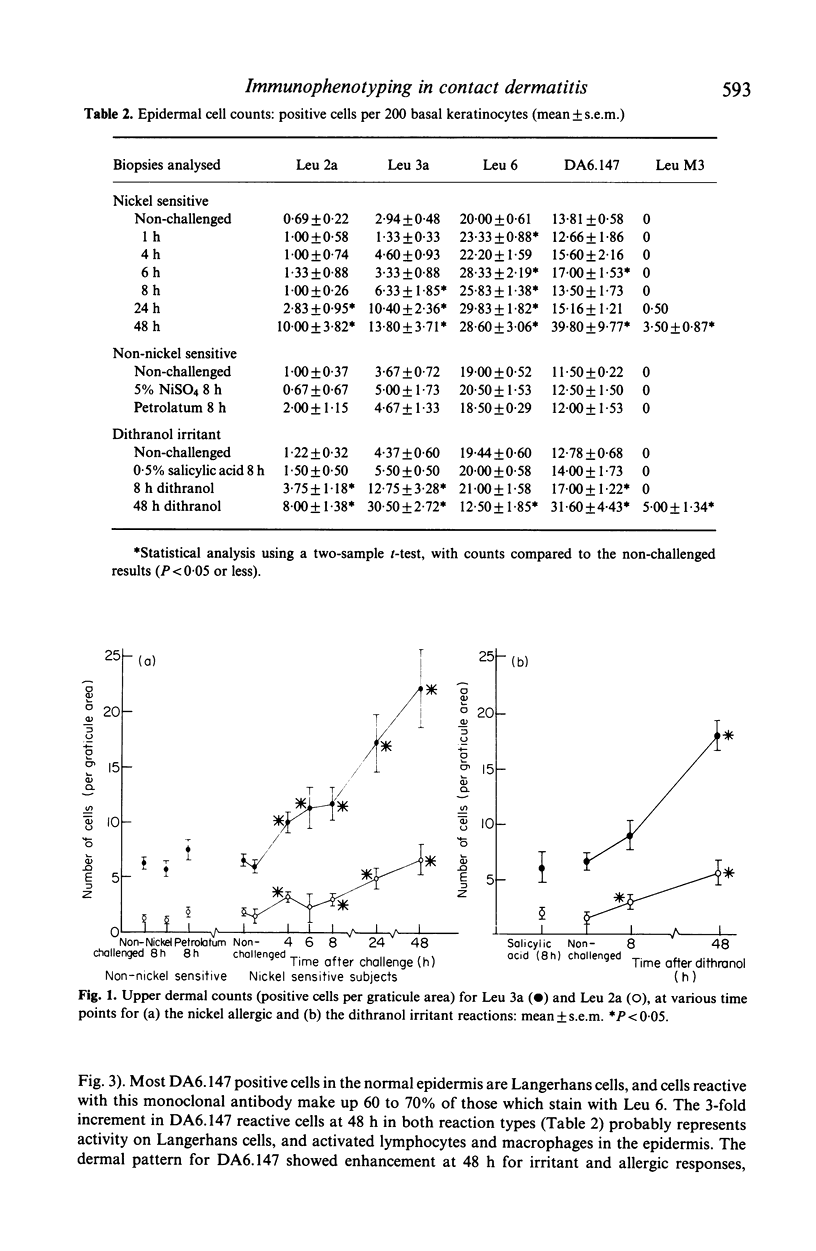
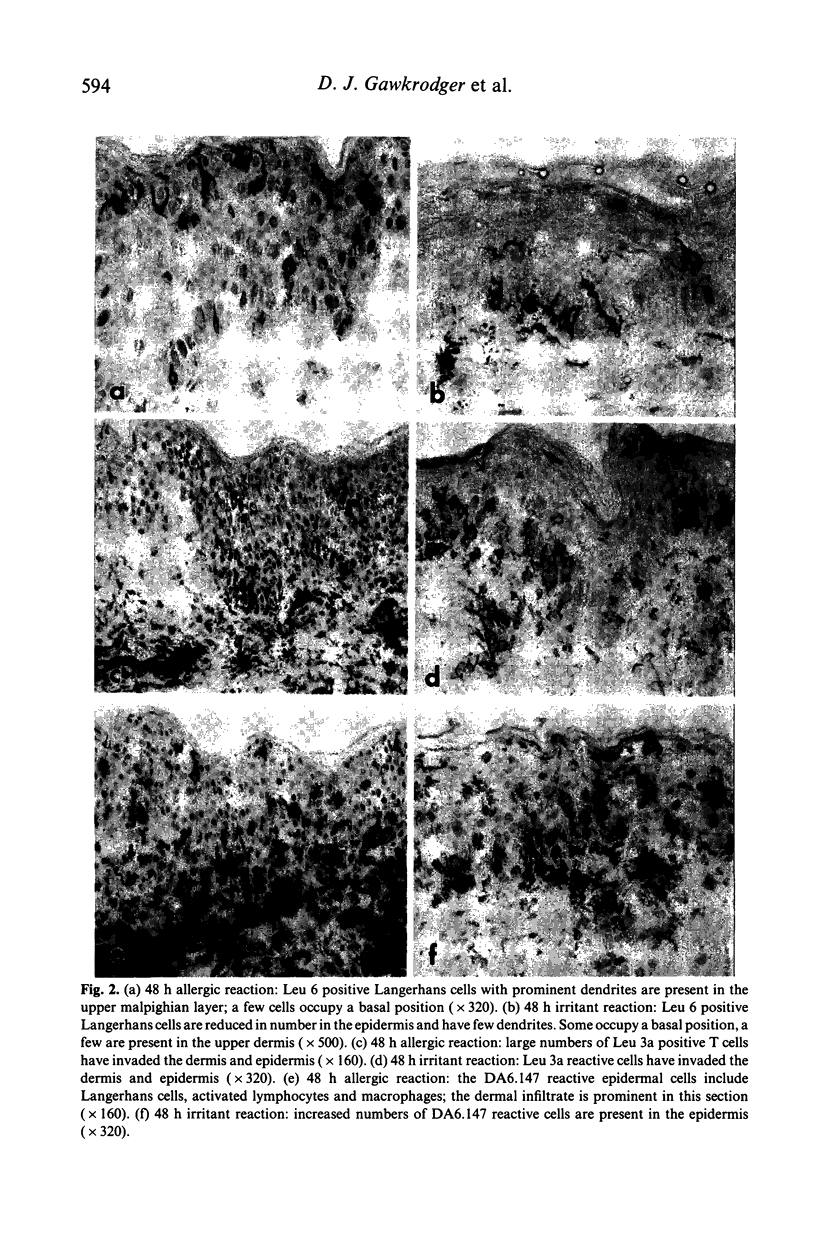
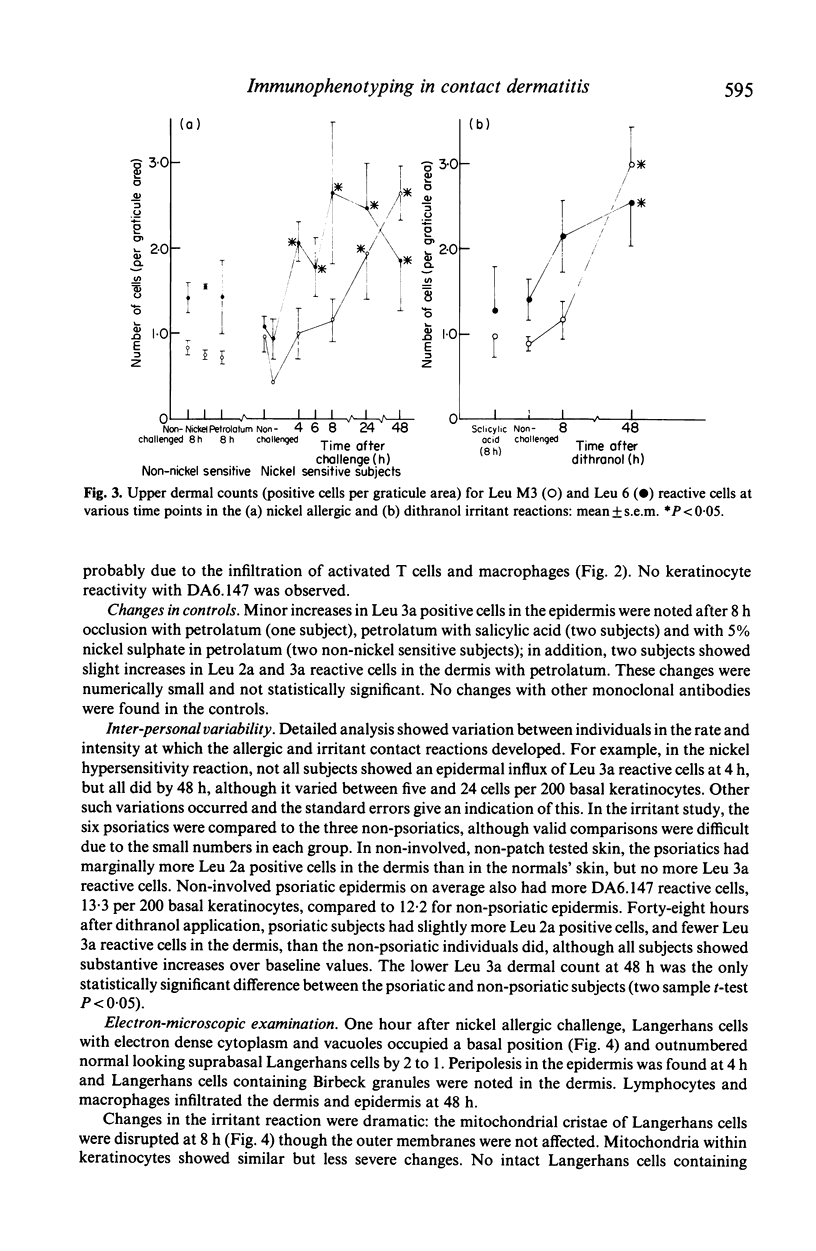
Despite qualitative similarities there were subtle differences between the nickel allergic and dithranol irritant dermatitis reactions. In both responses, dermal and epidermal cellular infiltrates developed, which were predominantly of Leu 3a phenotype with lesser numbers of Leu 2a positive cells. Dermal infiltrates were larger in the allergic response, but epidermal invasion was greater in the irritant reaction. In the allergic challenge response, Leu 3a reactive cells appeared in the dermis and epidermis by 4 h. At 48 h, both reactions showed skin infiltration by Leu M3 positive macrophages, and had increased numbers of cells in the epidermis expressing class II antigens. The number of Leu 6 reactive Langerhans cells in the epidermis was almost halved at 48 h in the irritant reaction, but Langerhans cell counts were increased by a third between 24 and 48 h of the allergic response. Ultrastructural studies showed disruption of the Langerhans cell mitochondrial cristae at 8 h in the irritant reaction, with few identifiable epidermal Langerhans cells at 48 h. At 1 h in the allergic response, electron microscopy identified two populations of Langerhans cells; the majority showed an electron-dense cytoplasm with vacuoles, and the rest appeared normal. Peripolesis was noted in both types of reaction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Swain A. F., Fry L., Valdimarsson H. Epidermal T lymphocytes and HLA-DR expression in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1984 May;110(5):555–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. M., Botham P. A., Gawkrodger D. J., McVittie E., Ross J. A., Stewart I. C., Hunter J. A. Early cellular reactions induced by dinitrochlorobenzene in sensitized human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Jun;110(6):637–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. D., Fox P., Neises G., Katz S. I. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on human epidermal cell alloantigen presentation: initial depression of Langerhans cell-dependent function is followed by the appearance of T6- Dr+ cells that enhance epidermal alloantigen presentation. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):129–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Johnson R. A., Manseau E. J., Morgan E., Colvin R. B. Morphology of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in man. I. Quantitative description of the inflammatory response. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):111–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J., Gibbs J. H., Beck J. S. Lymphocyte subsets and Langerhans cells in allergic and irritant patch test reactions: histometric studies. Contact Dermatitis. 1985 Sep;13(3):166–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1985.tb02530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groh V., Tani M., Harrer A., Wolff K., Stingl G. Leu-3/T4 expression on epidermal Langerhans cells in normal and diseased skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Feb;86(2):115–120. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12284090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanerva L., Ranki A., Lauharanta J. Lymphocytes and Langerhans cells in patch tests. An immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Contact Dermatitis. 1984 Sep;11(3):150–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1984.tb00961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor F., Hindson C. Allergy to dithranol. Contact Dermatitis. 1982 Mar;8(2):137–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1982.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., Drexhage H. A., Benson W., Balfour B. M. A study of cells present in lymph draining from a contact allergic reaction in pigs sensitized to DNFB. Immunology. 1983 Jul;49(3):415–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malten K. E., den Arend J. A., Wiggers R. E. Delayed irritation: hexanediol diacrylate and butanediol diacrylate. Contact Dermatitis. 1979 May;5(3):178–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Fischer T., Forsum U., Klareskog L. Phenotypic characterization in situ of inflammatory cells in allergic and irritant contact dermatitis in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):81–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg I., Baer R. L., Rosenthal S. A., Thorbecke G. J., Berezowsky V. Dermal and intravascular Langerhans cells at sites of passively induced allergic contact sensitivity. Cell Immunol. 1975 Aug;18(2):435–453. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Stingl G. The Langerhans cell. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jun;80 (Suppl):17s–21s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]