Abstract
Goat mammary macrophage division in vivo was assessed by detection of mitotic figures, by autoradiographic measurement of the uptake of 3H thymidine, and by a 96-well proliferation assay. Autoradiography revealed that 3.74 +/- 0.77% of nonstimulated mammary macrophages were actively synthesizing DNA. Eight days of sterile inflammation, induced by lipopolysaccharide or thioglycollate, increased mammary macrophage division (10.9 +/- 2.1%). The division increased within 2 h after inducing inflammation with thioglycollate. After 1 day, the rate of division decreased, and another increase occurred 3-4 days later. The high rate of division was maintained for greater than 60 days after the induction of sterile inflammation. Division was further shown to occur by injecting 3H-thymidine directly into the mammary gland, harvesting the macrophages 1.5 h later, and determining incorporation by autoradiography. The results of all assays of division were in agreement, suggesting they reflected the same event. The dividing cells were nonspecific esterase-positive, adherent, motile, phagocytic, and had morphological characteristics of macrophages.
Full text
PDF


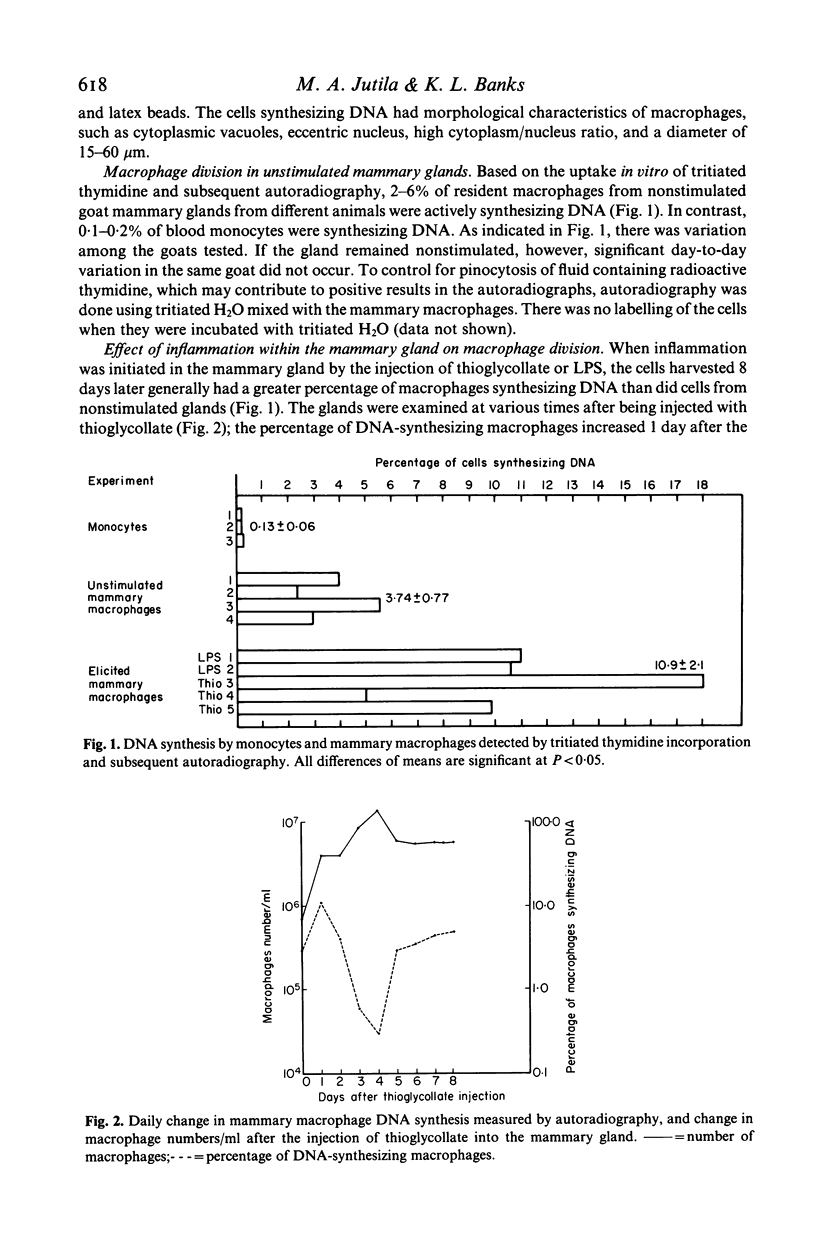
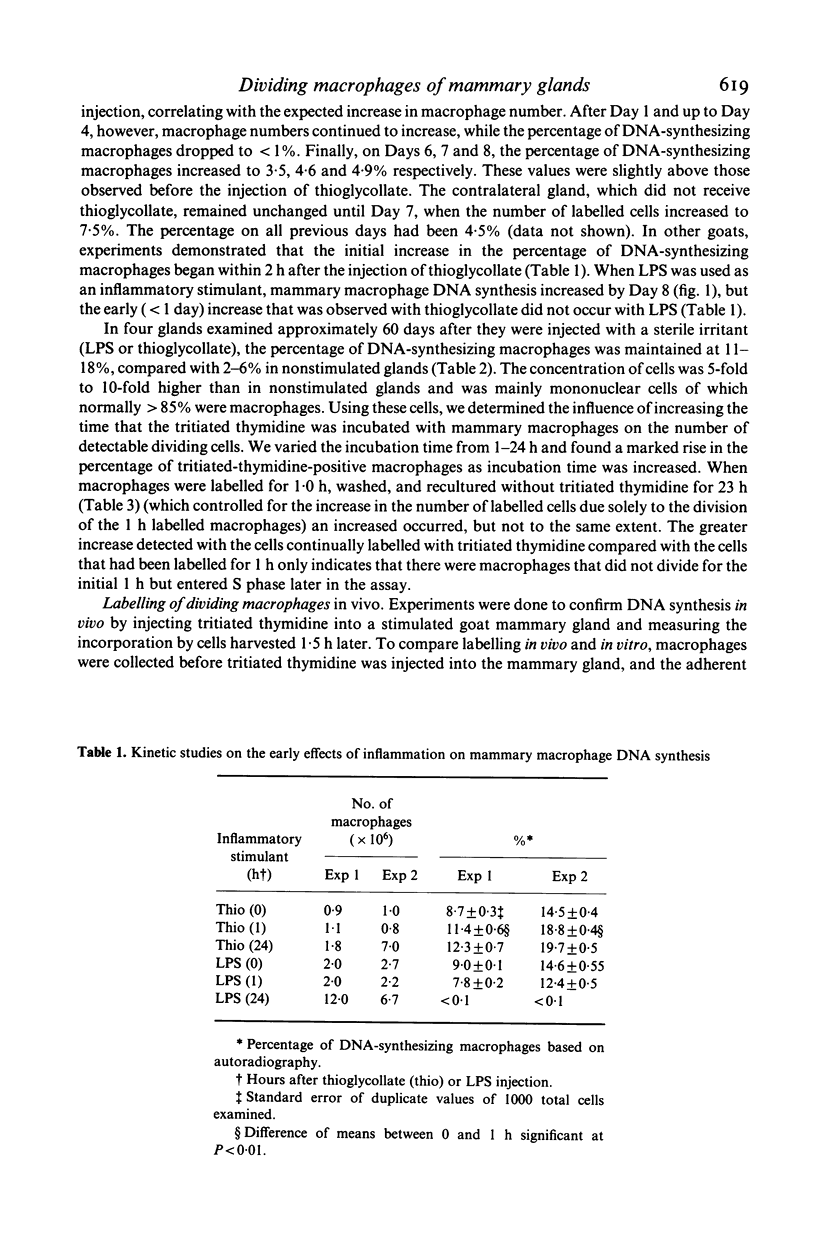
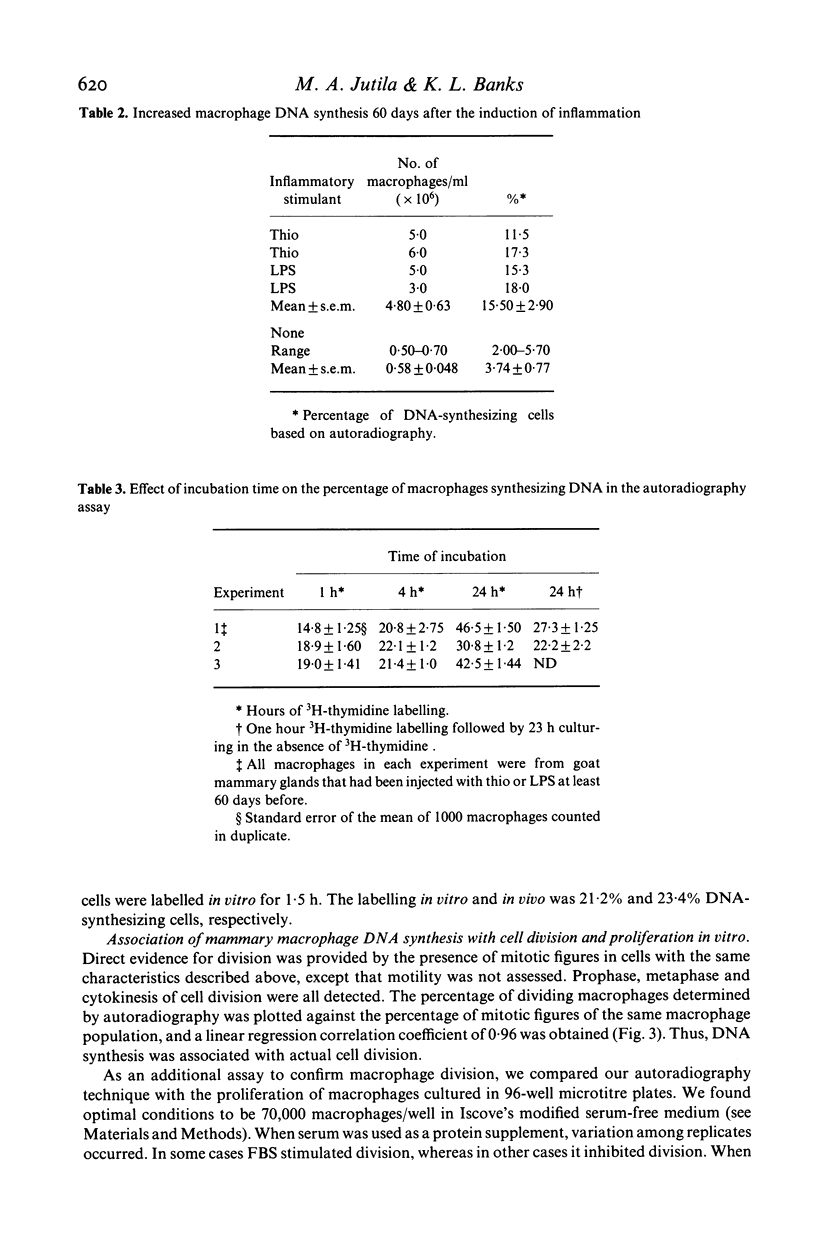
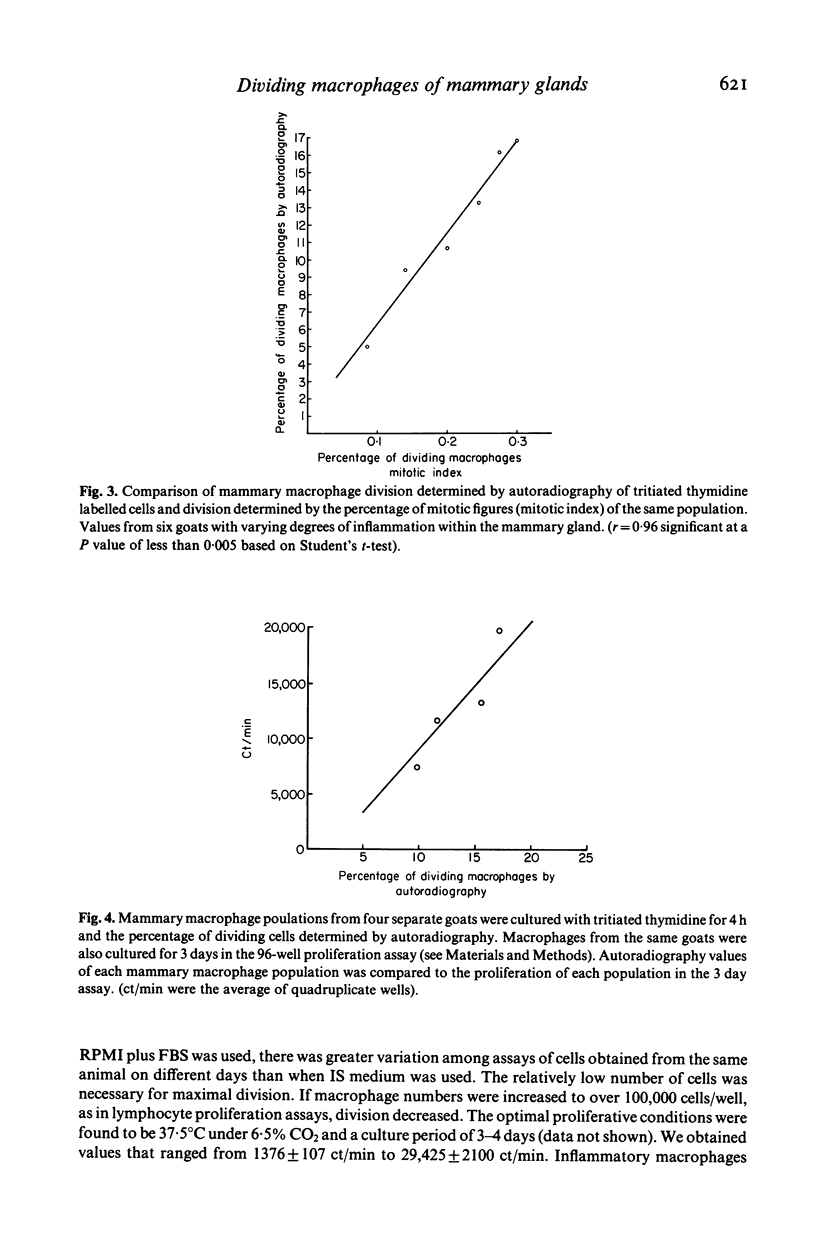



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolphe M., Fontagné J., Pelletier M., Giroud J. P., Timsit J., Lechat P. Induction of DNA synthesis in rat peritoneal macrophages in culture by a pleural inflammatory exudate. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):114–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01972194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. W., Banks K. L. Collection and cultivation in vitro of equine mammary macrophages. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1956–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks K. L., Greenlee A. Lymphocyte subpopulations of the goat: isolation and identification. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):314–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Kumar V. 89Sr-induced bone marrow aplasia: effects on seed (stem cells) and soil (inductive microenvironment). Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):235–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blussé van Oud Alblas A., Mattie H., van Furth R. A quantitative evaluation of pulmonary macrophage kinetics. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1983 May;16(3):211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggle J. E., Tarling J. D. The proliferation kinetics of pulmonary alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Mar;35(3):317–327. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Auerbach H. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Tissue-specific pretranslational regulation of complement production in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2610–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Schneeberger E. E., Lichtenberg N. A., Colten H. R. Complement biosynthesis in human breast-milk macrophages and blood monocytes. Immunology. 1982 Jun;46(2):429–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven N. Generation of neutrophil chemoattractants by phagocytosing bovine mammary macrophages. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Nov;35(3):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Henahan M., Armstrong B. Cell types and morphogenesis in the mammary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES I. J. INDUCTION OF MITOSIS IN MACROPHAGES BY ENDOTOXIN. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:37–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. L., Eberhart R. J. Macrophages in bovine milk. Am J Vet Res. 1975 May;36(5):619–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Outteridge P. M. The identification and ultrastructure of macrophages from the mammary gland of the ewe. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Feb;54(1):43–55. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon B., Cole P., Brown J. Etiology of human breast cancer: a review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jan;50(1):21–42. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J., Keller H. U., Dürig P., Hagmann J., Cornioley D. M., Reinhard J., Ruchti C., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Nonspecific esterase in human lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;64(4):410–421. doi: 10.1159/000232721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A. Inhibition of macrophage DNA synthesis by immunomodulators. I. Suppression of [3H]thymidine incorporation into macrophages by MDP and LPS. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(4):377–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann C., Sorg C. Regulation of plasminogen activator secretion, interferon induction and proliferation in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):143–147. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paape M. J., Wergin W. P., Guidry A. J., Schultze W. D. Phagocytic defense of the ruminant mammary gland. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:555–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patierno S. R., Costa M., Lewis V. M., Peavy D. L. Inhibition of LPS toxicity for macrophages by metallothionein-inducing agents. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1924–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler E., Raedler A. Local proliferation of brain macrophages in central nervous system tissue cultures. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Sep;43(5):531–540. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198409000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Strausbauch P. H., Volkman A. Resident macrophage proliferation in mice depleted of blood monocytes by strontium-89. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Axelrod B. J. Mouse peritoneal macrophages: tritiated thymidine labeling and cell kinetics. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Jan;21(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. C., Roguinsky M. Mastitis and other diseases of the goat's udder. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Dec 15;171(12):1241–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian J. J., Campbell S. G. Interaction between caprine macrophages and corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: an electron microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Apr;44(4):690–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., van Furth R. The effect of glucocorticosteroids on the kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):429–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Furth R., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. C., Mattie H. Quantitative study on the production and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes during an acute inflammatory reaction. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1314–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman A. Disparity in origin of mononuclear phagocyte populations. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Apr;19(4):249–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Sebunya T. K. In vitro phagocytosis and killing of coliforms by bovine mammary leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1941–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Cellular biology of pulmonary macrophages. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76 (Suppl 1):21–27. doi: 10.1159/000233731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):415–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. M. Dual origin of mouse spleen macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1273–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


