Abstract
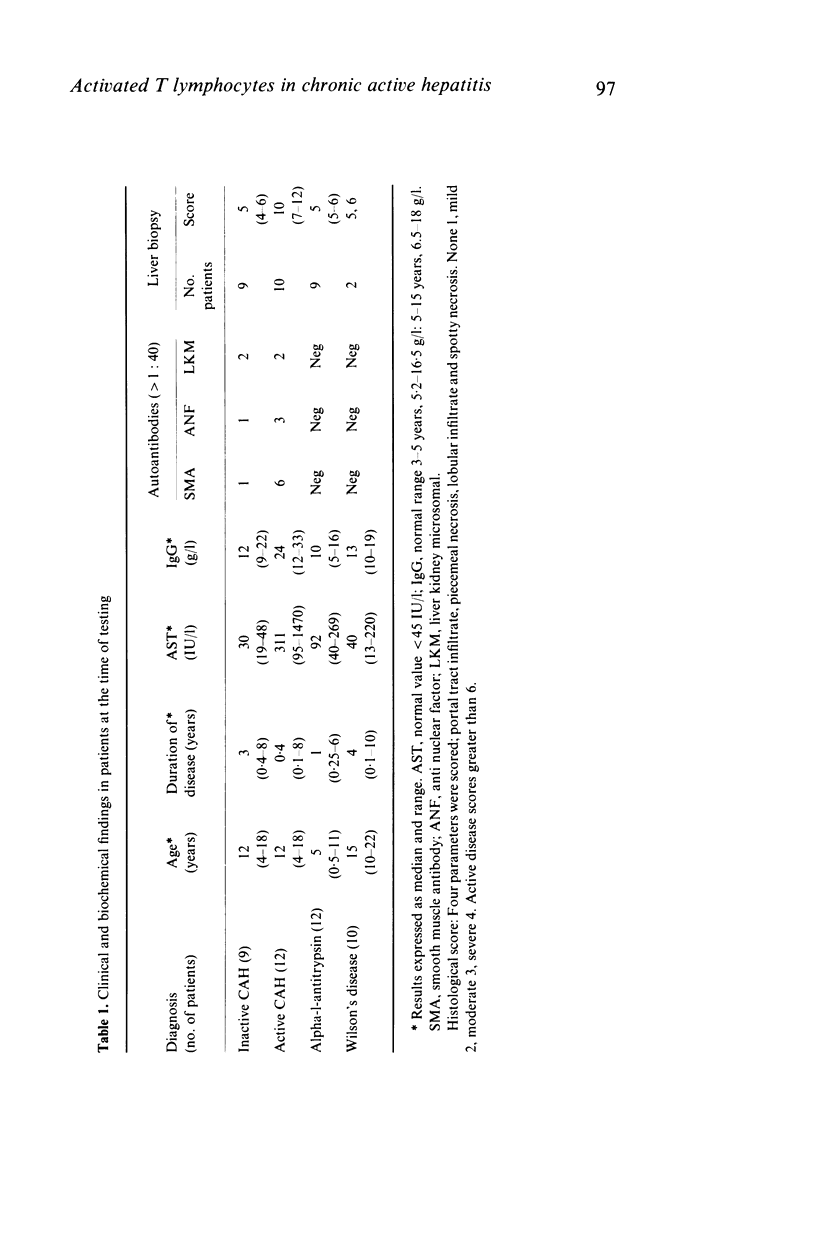
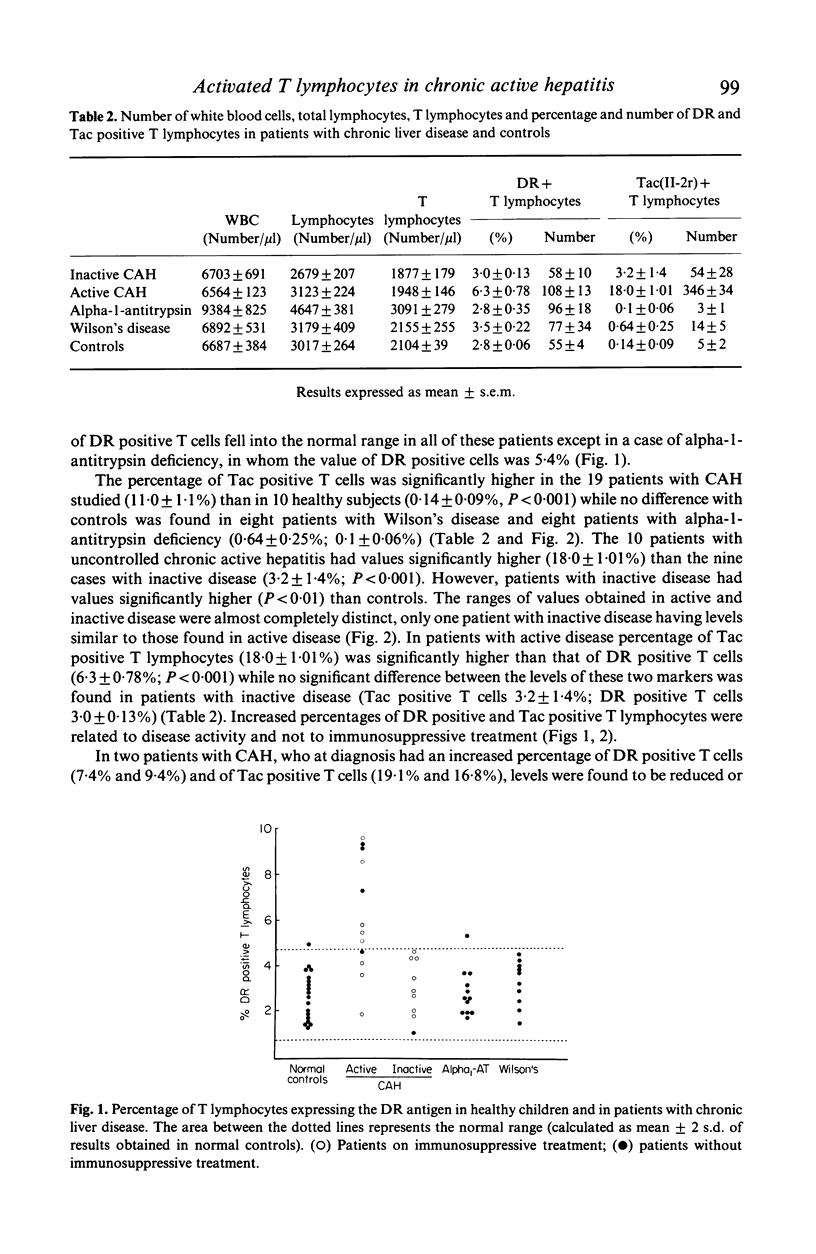
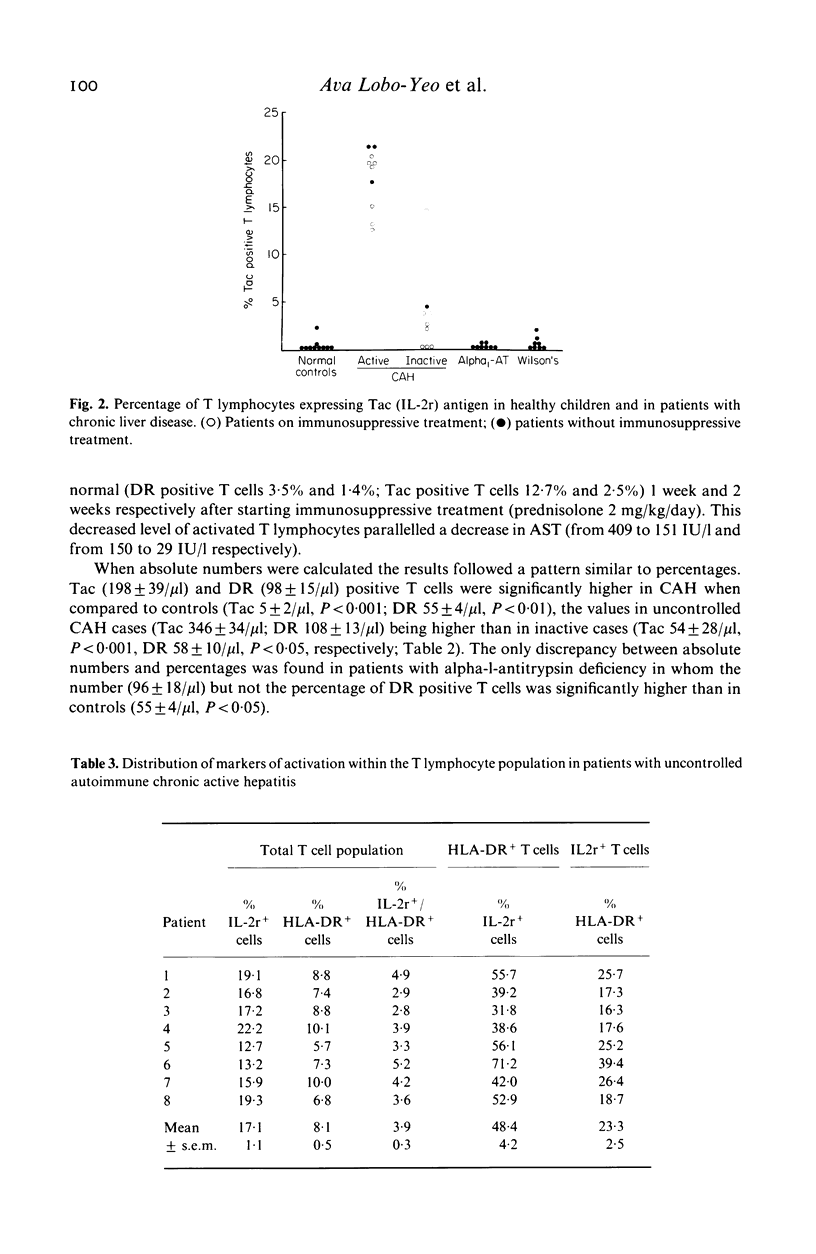
We found a significant increase of activated circulating T lymphocytes expressing interleukin 2 receptor (IL-2r) (mean +/- s.e.m. 11.0 +/- 1.1%) or DR antigen (5.0 +/- 0.49%) in patients with autoimmune chronic active hepatitis (CAH) starting in childhood when compared to healthy controls (0.14 +/- 0.09%, P less than 0.001 and 2.8 +/- 0.06%, P less than 0.01). Patients with liver disorders due to Wilson's disease (IL-2r 0.64 +/- 0.25%, DR 3.5 +/- 0.22%) or alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency (IL-2r 0.1 +/- 0.06%, DR 2.8 +/- 0.35%) had levels similar to controls. Levels of both IL-2r and DR positive T lymphocytes were higher in patients with uncontrolled CAH (IL-2r 18.0 +/- 1.01%; DR 6.3 +/- 0.78%) than in patients with inactive disease (IL-2r 3.2 +/- 1.4%, P less than 0.001; DR 3.0 +/- 0.13%, P less than 0.01). In patients with active disease levels of IL-2r positive cells were higher than DR positive cells (P less than 0.001). Only 21% of activated T cells coexpressed the two markers of activation. Sixty-seven percent of IL-2r positive T lymphocytes were helper/inducer and 25% suppressor/cytotoxic, while 66% of the DR positive T cells were suppressor/cytotoxic and 31% helper/inducer. The finding that the highest levels of activated T lymphocytes are present in patients with uncontrolled CAH suggests that these cells are involved in its pathogenesis. The preferential increase of activated helper/inducer cells might explain the enhanced immune reactivity characteristic of autoimmune CAH.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alviggi L., Johnston C., Hoskins P. J., Tee D. E., Pyke D. A., Leslie R. D., Vergani D. Pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes: a role for activated T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1984 Jul 7;2(8393):4–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91994-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Yu D. T., Irani A. M., Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J. Ia+ T cells in synovial fluid and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1370–1376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci G., Colombo M., Del Ninno E., Paronetto F. In situ characterization by monoclonal antibodies of the mononuclear cell infiltrate in chronic active hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Nov;85(5):1138–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waele M., Thielemans C., Van Camp B. K. Characterization of immunoregulatory T cells in EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis by monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 19;304(8):460–462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102193040804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggink H. F., Houthoff H. J., Huitema S., Gips C. H., Poppema S. Cellular and humoral immune reactions in chronic active liver disease. I. Lymphocyte subsets in liver biopsies of patients with untreated idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis, chronic active hepatitis B and primary biliary cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):17–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Kakumu S., Murakami H., Kuriki J., Yoshioka K., Sakamoto N. Increased peripheral blood Ia positive T cells and their effect on autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in chronic active liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):90–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby P. A., Kotzin B. L., Kansas G. S., Engleman E. G. Immunoglobulin secretion in the human autologous mixed leukocyte reaction. Definition of a suppressor-amplifier circuit using monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):55–67. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Manning M. E., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. In vivo activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Brenner M. B., McLean J. M., Strominger J. L. Antigenic stimulation regulates the level of expression of interleukin 2 receptor on human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Wormser G. P., Schooley R. T., Ho D. D., Felsenstein D., Hopkins C. C., Joline C., Duncanson F., Sarngadharan M. G., Saxinger C. Risk of nosocomial infection with human T-cell lymphotropic virus III (HTLV-III). N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 3;312(1):1–4. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501033120101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Morris M. A., Haynes B. F., Eisenbarth G. S. Increased circulating Ia-antigen-bearing T cells in type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 1;306(13):785–788. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204013061305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Farrar W. L. The role of a gamma interferon-like lymphokine in the activation of T cells for expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Wood G. S., Fishwild D. M., Engleman E. G. Functional characterization of human T lymphocyte subsets distinguished by monoclonal anti-leu-8. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2995–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashio T., Hotta R., Kakumu S. Lymphocyte suppressor cell activity in acute and chronic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):459–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Gartland G. L., Clement L. T. Characterization of a phenotypically distinct subpopulation of Leu-2+ cells that suppresses T cell proliferative responses. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2757–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Tait B. D. HLA associations with autoimmune-type chronic active hepatitis: identification of B8-DRw3 haplotype by family studies. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan D., Mathur U., Enlow R. W., Romain P. L., Winchester R. J., Colp C., Singman H., Adelsberg B. R., Spigland I. Opportunistic infections and immune deficiency in homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):700–704. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri-Aria K. T., Lobo-Yeo A., Vergani D., Mieli-Vergani G., Eddleston A. L., Mowat A. P. T suppressor cell function and number in children with liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Aug;61(2):283–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Kermani-Arab V., Fahey J. L. Depressed interleukin 2 receptor expression in acquired immune deficiency and lymphadenopathy syndromes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1313–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Ia determinants on human T-cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibody. Activation stimuli required for expression. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1472–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Morimoto C., Penta A. C., Schlossman S. F. Subpopulations of the T4+ inducer T cell subset in man: evidence for an amplifier population preferentially expressing Ia antigen upon activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Parkman R., Rappeport J., Rosen F. S., Schlossman S. F. Aberrations of suppressor T cells in human graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 10;300(19):1061–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905103001901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain P. L., Schlossman S. F. Human T lymphocyte subsets. Functional heterogeneity and surface recognition structures. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1559–1565. doi: 10.1172/JCI111571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer P. J. Chronic hepatitis: a problem for the pathologist. Histopathology. 1977 Jan;1(1):5–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1977.tb01640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi N., Miyawaki T., Yachie A., Ikuta N., Ohzeki S. Kinetics of expression of T-cell "activation" antigens on in vivo- and in vitro-stimulated T cells. Diagn Immunol. 1983;1(3):104–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin L., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces enhanced expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on B lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachie A., Miyawaki T., Uwadana N., Ohzeki S., Taniguchi N. Sequential expression of T cell activation (Tac) antigen and Ia determinants on circulating human T cells after immunization with tetanus toxoid. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Gibofsky A., Ko H. S., Kunkel H. G. Peripheral blood Ia-positive T cells. Increases in certain diseases and after immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):91–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


