Abstract
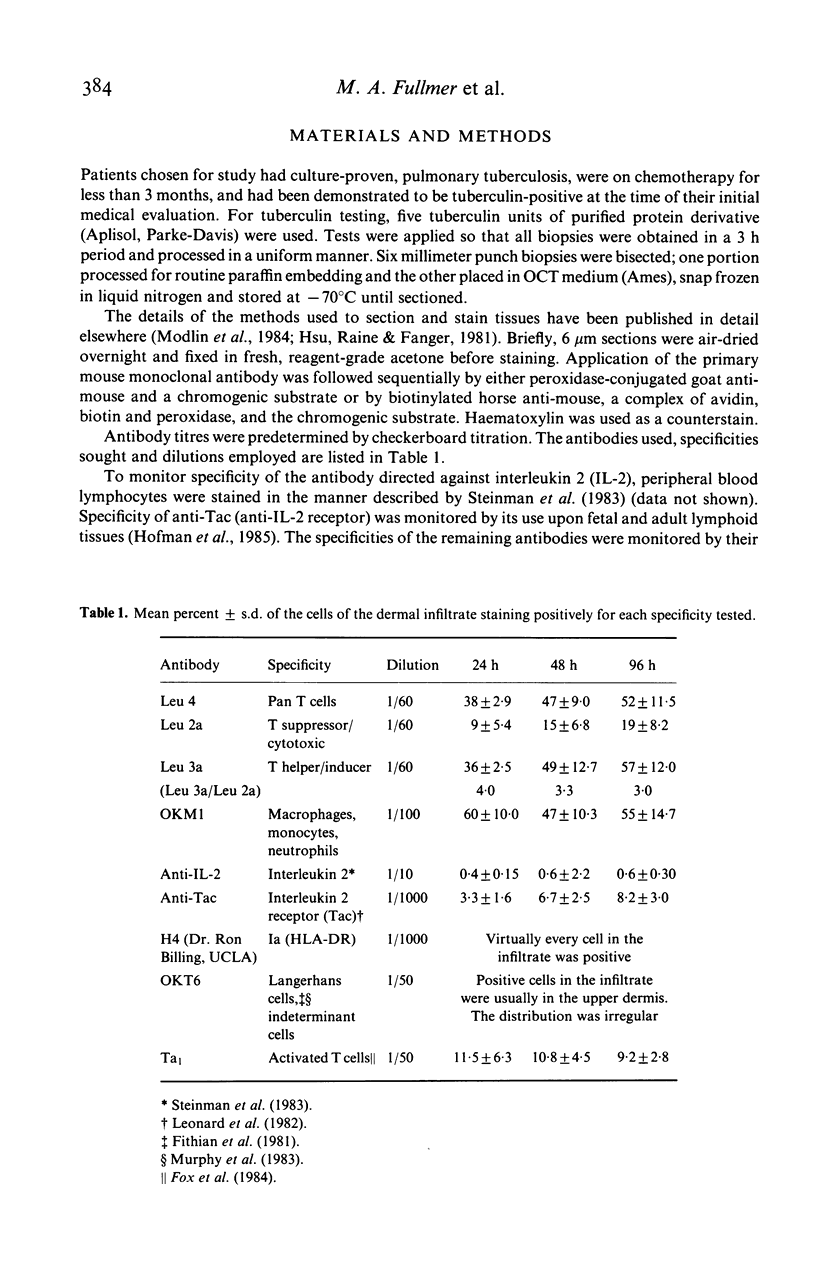
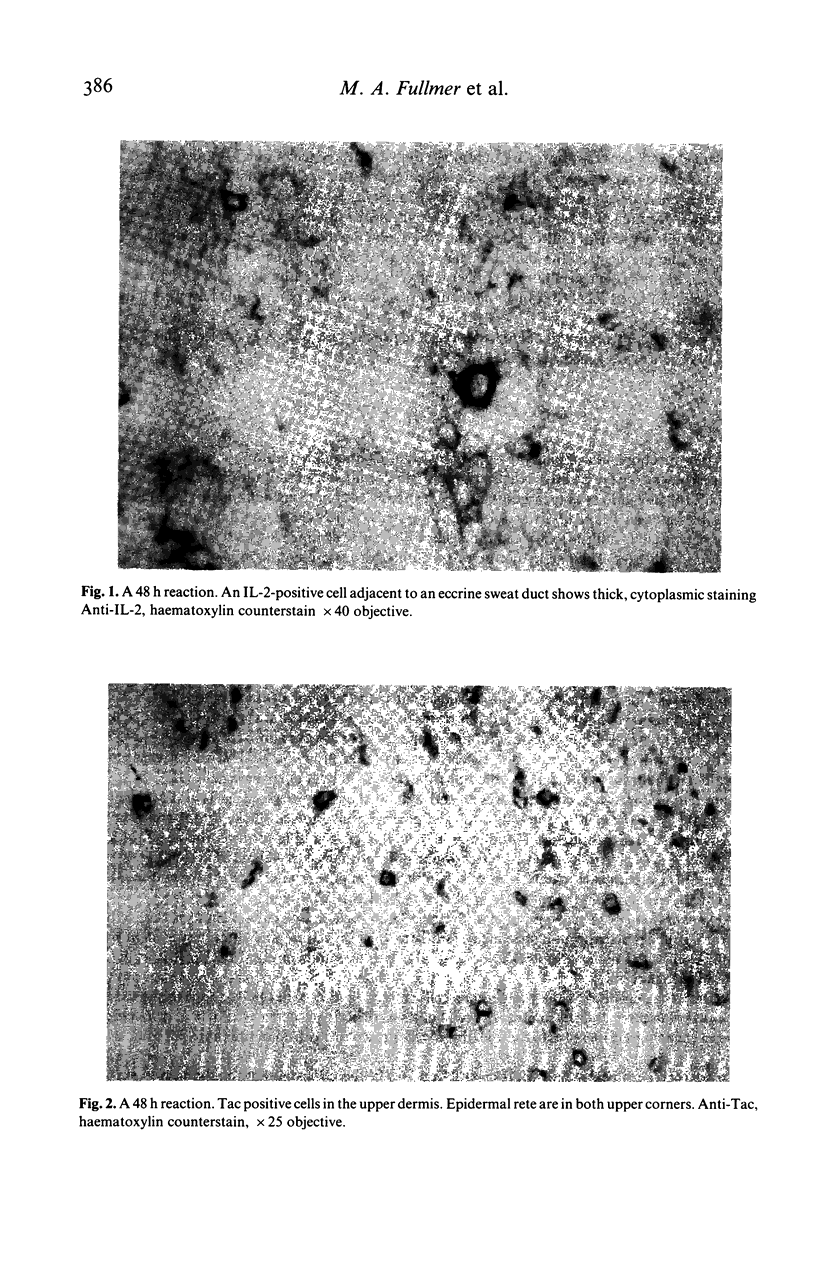
Evidence of lymphokine elaboration and lymphocyte activation was sought in tuberculin skin test reactions at 24 and 48, or 48 and 96 h in patients with active, culture-proven, pulmonary tuberculosis. Through the use of frozen sections, immunoperoxidase techniques and monoclonal antibodies, anti-interleukin 2 positive cells were found to constitute 0.4% to 0.6% of the dermal infiltrate, and keratinocyte Ia expression at 96 h was consistent with a marker for interferon-gamma production. Cells bearing the interleukin 2 receptor more than doubled in prevalence from 24 to 48 or 96 h but cells staining with Ta1, an antibody identifying activated lymphocytes, were 10% of the cells of the infiltrate at all three times. One-half of the cells of the infiltrate were OKM1-positive, presumably macrophages, perhaps reflecting the presence of active tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basham T. Y., Nickoloff B. J., Merigan T. C., Morhenn V. B. Recombinant gamma interferon induces HLA-DR expression on cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Aug;83(2):88–90. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12262597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Acuto O., Poole C., Palley L., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Ta1, a novel 105 KD human T cell activation antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1250–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. H., Ferguson J., Brown R. A., Kenicer K. J., Potts R. C., Coghill G., Swanson Beck J. Histometric study of the localisation of lymphocyte subsets and accessory cells in human Mantoux reactions. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Nov;37(11):1227–1234. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.11.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Witmer M. D., Nath I., Steinman R. M., Laal S., Prasad H. K., Sarno E. N., Elvers U., Cohn Z. A. Influence of delayed immune reactions on human epidermal keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Bergroth V., Visa-Tolvanen K., Reitamo S., Förström L. Cellular infiltrate in situ and response kinetics of human intradermal and epicutaneous tuberculin reactions. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Sep;28(3):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley J., Haregewoin A., Yemaneberhan T., Warndorff van Diepen T., Nsibami J., Knowles D., Smith K. A., Godal T. In vivo responses to Mycobacterium leprae: antigen presentation, interleukin-2 production, and immune cell phenotypes in naturally occurring leprosy lesions. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1985 Sep;53(3):385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKie R. M., Turbitt M. L. Quantitation of dendritic cells in normal and abnormal human epidermis using monoclonal antibodies directed against Ia and HTA antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Sep;81(3):216–220. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12517998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Horwitz D. A., Husmann L. A., Gillis S., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ identification of cells in human leprosy granulomas with monoclonal antibodies to interleukin 2 and its receptor. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Tapia F. J., Bloom B. R., Gallinoto M. E., Castes M., Rondon A. J., Rea T. H., Convit J. In situ characterization of the cellular immune response in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Harrist T. J., Mihm M. C., Jr In situ identification of T6-positive cells in normal human dermis by immunoelectron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Apr;108(4):423–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb04594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Grant B. W., Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Immune cell populations in cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Seymour G. J., Duke O., Janossy G., Panayi G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell Immunol. 1982 Dec;74(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Klareskog L., Forsum U. In situ identification of T lymphocyte subsets and HLA-DR expressing cells in the human skin tuberculin reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):325–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Tjernlund U. Human keratinocytes express HLA-DR antigens in the tuberculin reaction. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Feb;19(2):141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann G., Conlon P., Hefeneider S., Gillis S. Serological visualization of interleukin 2. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1188–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6344215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suitters A. J., Lampert I. A. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes is a consequence of cellular immunity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Apr;63(2):207–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Rudner E. J., Heather C. J. A histochemical analysis of mononuclear cell infiltrates of the skin. II. Delayed hypersensitivity in the human. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;30(3):248–256. doi: 10.1159/000229810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volc-Platzer B., Leibl H., Luger T., Zahn G., Stingl G. Human epidermal cells synthesize HLA-DR alloantigens in vitro upon stimulation with gamma-interferon. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jul;85(1):16–19. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]