Abstract
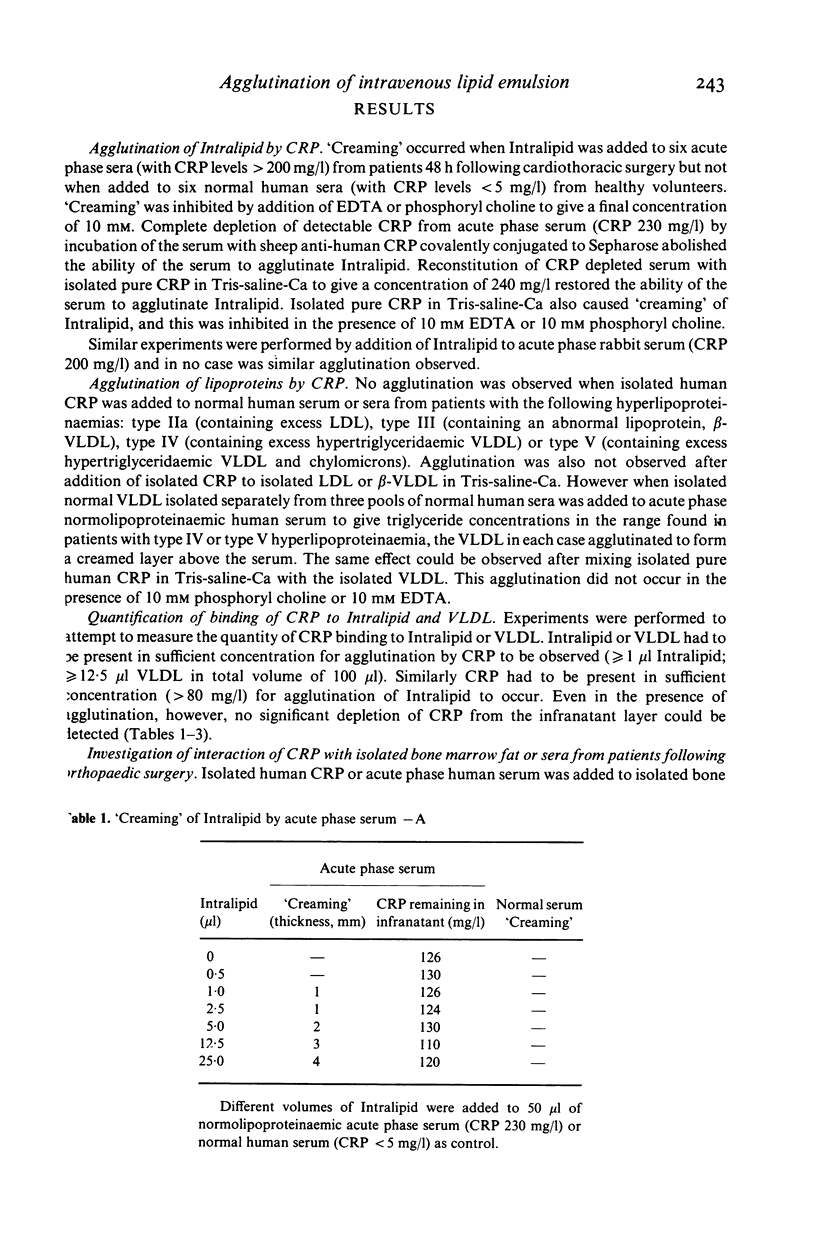
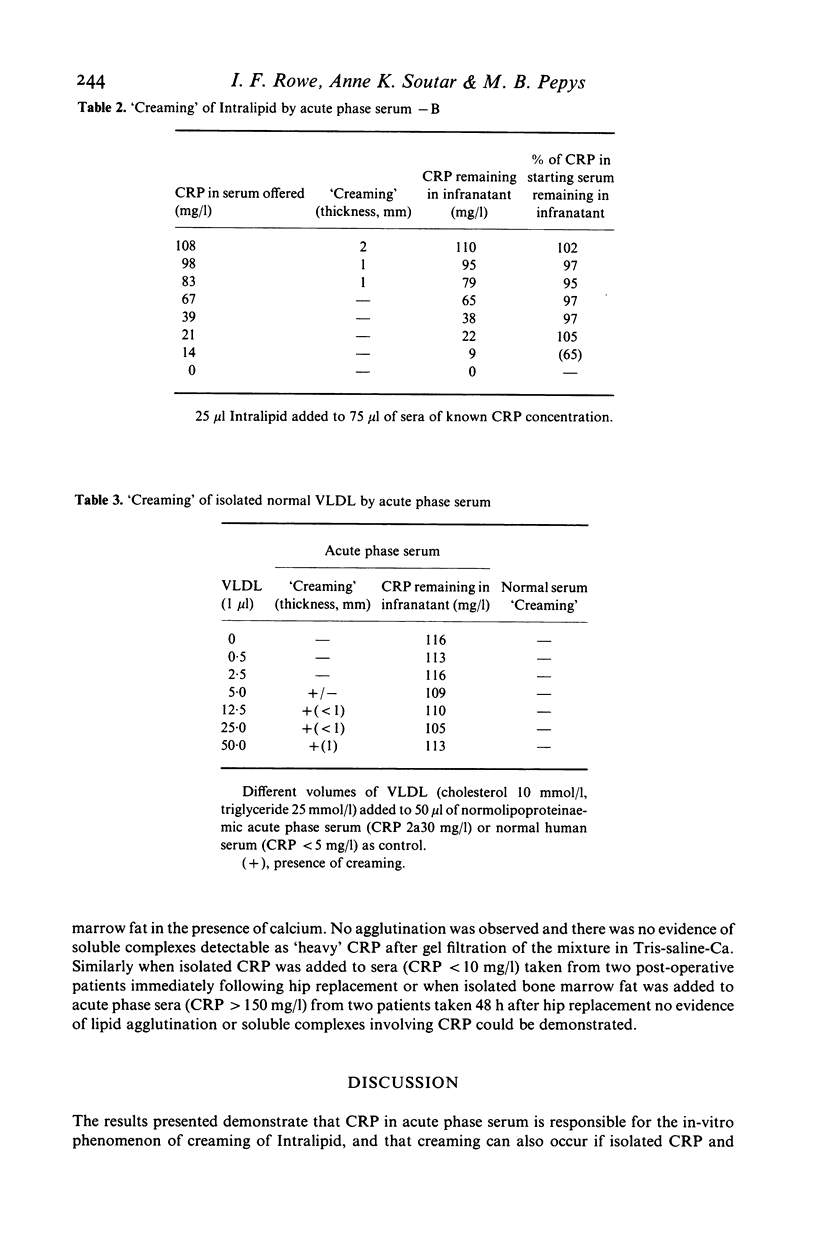
Isolated human C-reactive protein (CRP), or CRP in acute phase serum, produced in-vitro agglutination ('creaming') of the intravenously administered lipid suspension 'Intralipid'. CRP also produced similar agglutination of isolated normal very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). Agglutination in both cases was calcium-dependent and inhibitable by phosphoryl choline. These findings have important implications for patients receiving intravenous lipid suspensions and may be relevant to the pathogenesis of the fat embolism syndrome following trauma.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombes E. J., Shakespeare P. G., Batstone G. F. Lipoprotein changes after burn injury in man. J Trauma. 1980 Nov;20(11):971–975. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198011000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Shine B., Pepys M. B. Radiometric ligand binding assay for C-reactive protein. Complexed C-reactive protein is not detectable in acute phase serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchsig P., Brücke P., Blümel G., Gottlob R. A new clinical and experimental concept on fat embolism. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 25;276(21):1192–1193. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705252762107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Brown F. B., Gotto A. M., Jr, Bradley W. A. Receptor-mediated uptake of hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins by normal human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):984–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossling H. R., Pellegrini V. D., Jr Fat embolism syndrome: a review of the pathophysiology and physiological basis of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 May;(165):68–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Oliveira E. Binding of C-reactive protein to C-carbohydrate and PC-substituted protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd A. R., Wilson R. I. The fat embolism syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974 Aug;56B(3):408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. W., LeQuire V. S. Lipid metabolism and fat embolism after trauma: the contribution of serum lipoproteins to embolic fat. Surg Forum. 1968;19:465–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulman G., Fraser I., Pearson H. J., Bell P. R. Agglutination of intralipid by sera of acutely ill patients. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1426–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulman G., Pearson H. J., Fraser I., Bell P. R. Agglutination of intralipid by serum. Lancet. 1983 Apr 30;1(8331):985–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Broder M. L., Karp D. Control of the acute phase response. Serum C-reactive protein kinetics after acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):235–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI108932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Comparative studies on the binding properties of human and rabbit C-reactive proteins. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Markham R. E., Thomas H. C., Williams B. D., Petrie A. Comparative clinical study of protein SAP (amyloid P component) and C-reactive protein in serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Rowe I. F., Baltz M. L. C-reactive protein: binding to lipids and lipoproteins. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1985;27:83–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Soutar A. K., Trayner I. M., Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Walker L., Bowyer D., Herbert J., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Rabbit and rat C-reactive proteins bind apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Soutar A. K., Trayner I. M., Thompson G. R., Pepys M. B. Circulating human C-reactive protein binds very low density lipoproteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):237–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treiman N., Waisbrod V., Waisbrod H. Lipoprotein electrophoresis in fat embolism: a preliminary report. Injury. 1981 Sep;13(2):108–110. doi: 10.1016/0020-1383(81)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Kaplan M. H. Specificity of C-reactive protein for choline phosphate residues of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):612–614. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. M., Nguyen N. Y., Yonaha K., Robey F., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of rabbit C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13610–13615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer F. C., Soutar A. K., Baltz M. L., Trayner I. M., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein are selectively bound by aggregated C-reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):230–242. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



