Abstract
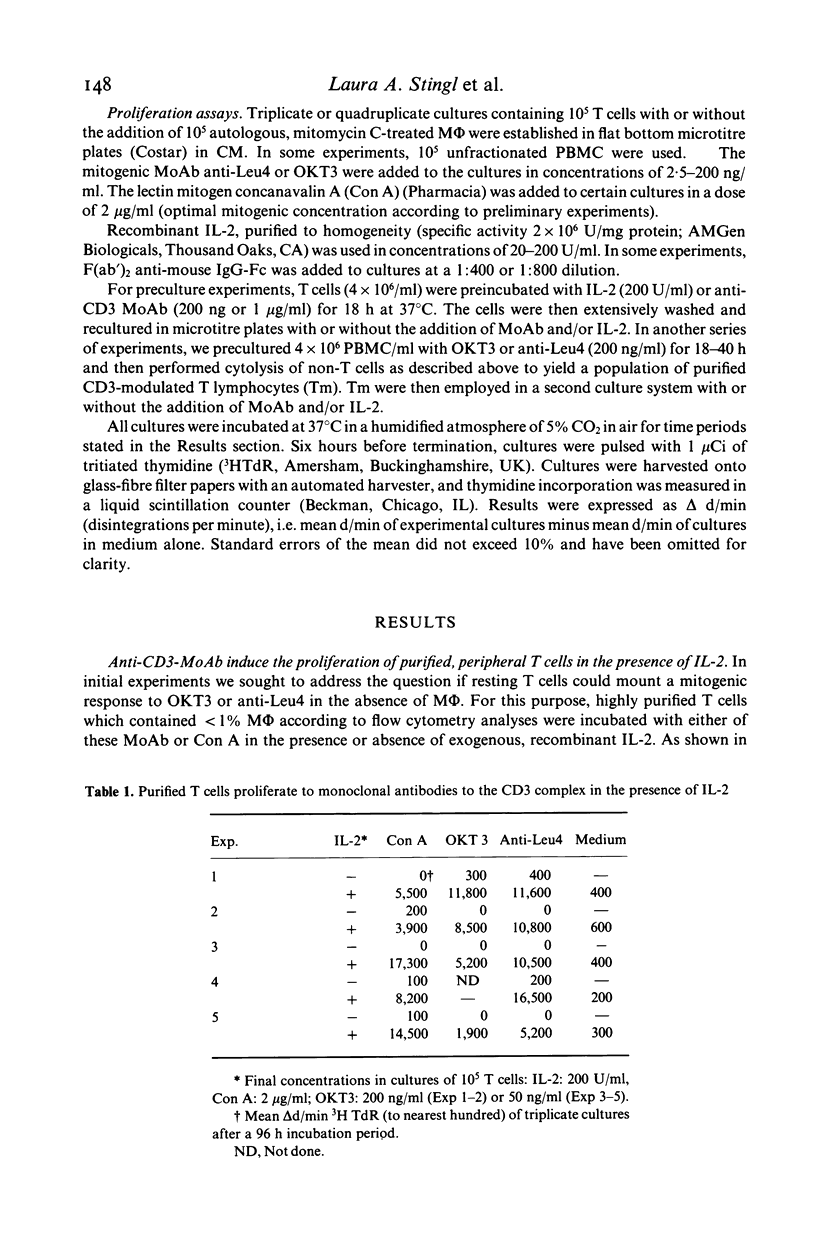
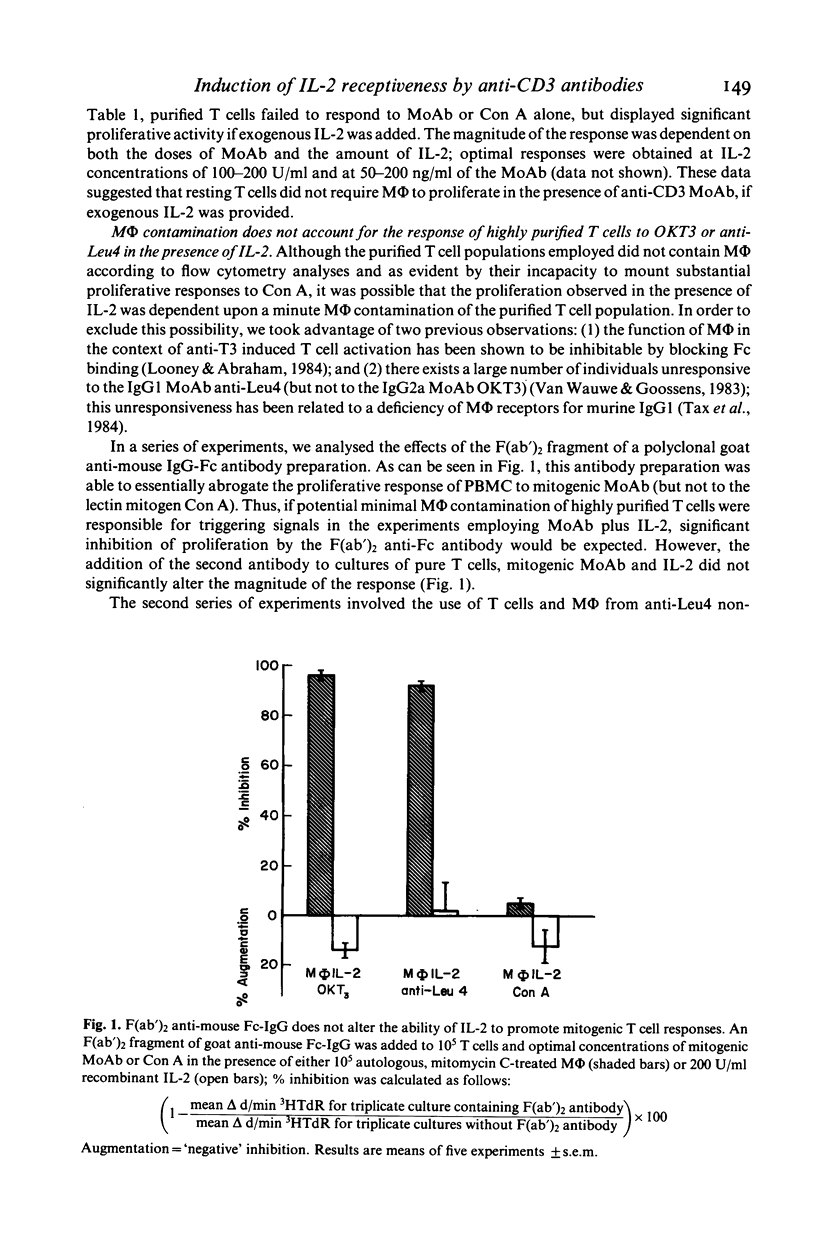
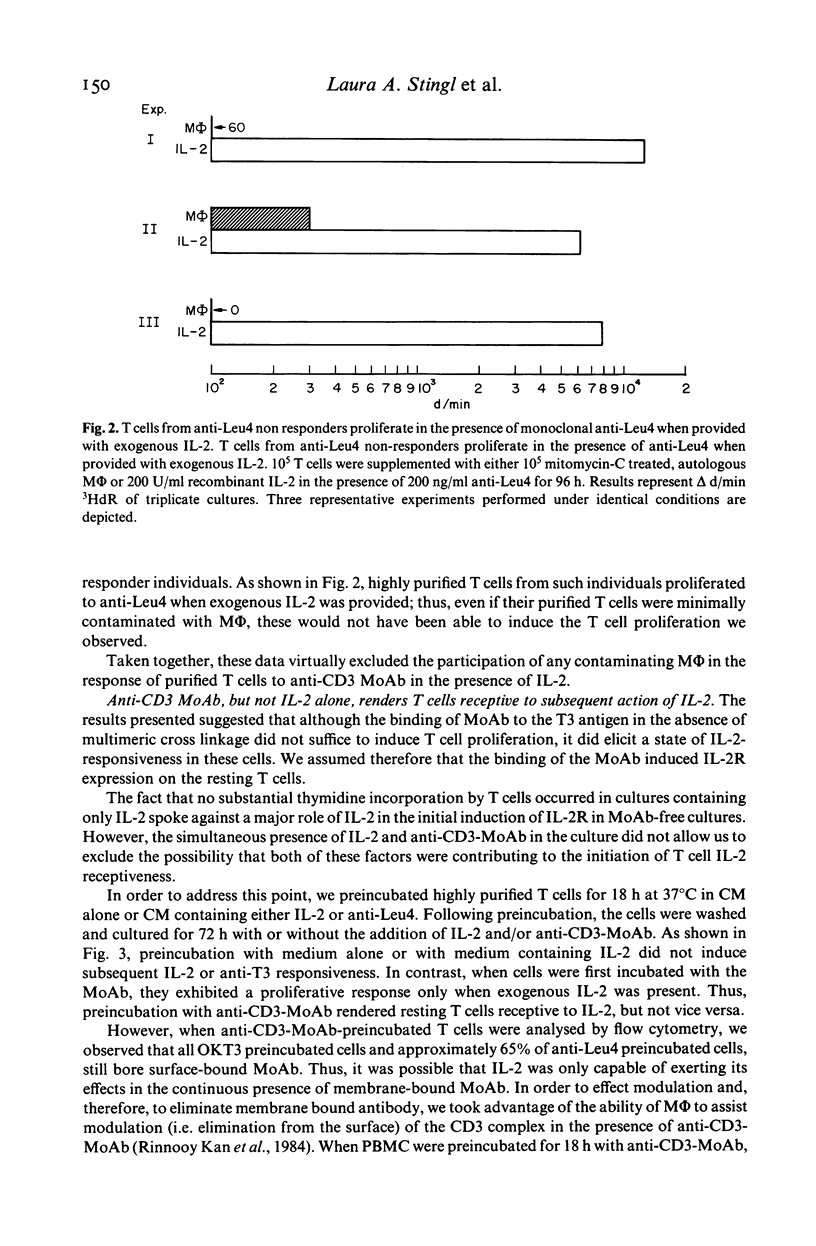
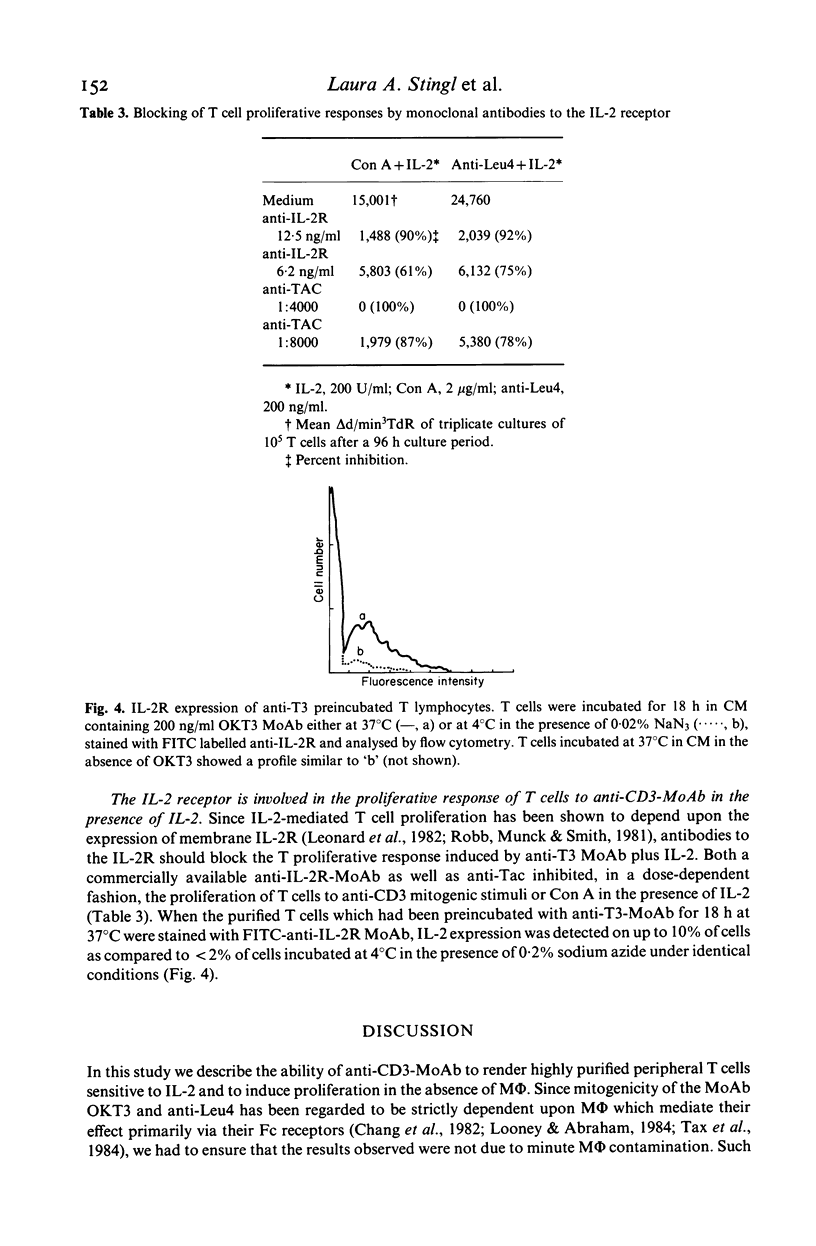
In this study, we sought to elucidate the sequence of events by which mitogenic monoclonal anti-CD3 antibodies (anti-CD3-MoAb) initiate T cell activation. In cultures of monocyte-depleted resting T cells, two anti-CD3-MoAb, OKT3 and anti-Leu 4, induced a state of interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptiveness which culminated in T lymphocyte proliferation when recombinant IL-2 was provided. Evidence that Fc-receptor mediation by monocytes did not contribute to this mitogenesis was supported by studies showing that polyclonal F(ab')2 anti-mouse IgG Fc antibody did not alter the magnitude of the IL-2 driven T cell proliferative response, and by the use of T cells from donors whose monocytes were unable to assist in the induction of anti-Leu 4 (IgG1 subclass) initiated proliferation. Anti-CD3-MoAb, in the absence of IL-2, induced IL-2 receptor expression on purified T cells, and anti-IL 2 receptor antibodies inhibited T cell proliferation in the presence of this growth factor. Furthermore, following modulation of the CD3 molecular complex in the presence of monocytes, depletion of accessory cells rendered the modulated T cells mitogenically dependent on exogenous IL-2. IL-2 itself did not suffice to promote T cell proliferation in the absence of anti-CD3-MoAb. These results indicate that the binding of monoclonal antibody to CD3 is capable of initiating, in an accessory cell-independent manner, premitotic alterations in T cells which can culminate in proliferation when exogenous IL-2 is provided.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang T. W., Testa D., Kung P. C., Perry L., Dreskin H. J., Goldstein G. Cellular origin and interactions involved in gamma-interferon production induced by OKt3 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Anderson W. B. Interleukin-2 stimulates association of protein kinase C with plasma membrane. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):233–235. doi: 10.1038/315233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. I. Monocyte-independent activation and proliferation induced by anti-T3 monoclonal antibodies in the presence of tumor promoter 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13 acetate. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holter W., Majdic O., Stockinger H., Knapp W. Analysis of T cell activation with a non-mitogenic anti CD3 antibody and the phorbol ester TPA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):600–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U., Ramstedt U., Axberg I., Ullberg M., Jondal M., Wigzell H. Selective inhibition of human T cell cytotoxicity at levels of target recognition or initiation of lysis by monoclonal OKT3 and Leu-2a antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1579–1584. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Abraham G. N. The Fc portion of intact IgG blocks stimulation of human PBMC by anti-T3. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):154–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Evidence for the T3-associated 90K heterodimer as the T-cell antigen receptor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):808–810. doi: 10.1038/303808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Antigen-like effects of monoclonal antibodies directed at receptors on human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):988–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. T cell receptor triggering induces responsiveness to interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 but does not lead to T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4106–4112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Interleukin 2 regulates expression of its receptor and synthesis of gamma interferon by human T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):429–430. doi: 10.1126/science.6429853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinnooy Kan E. A., Platzer E., Welte K., Wang C. Y. Modulation induction of the T3 antigen by OKT3 antibody is monocyte dependent. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2979–2985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Cantrell D. A. Interleukin 2 regulates its own receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Luger T. A., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. Responder cells in the human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1601–1604. doi: 10.1172/JCI110416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Sharrow S. O., Steinberg A. D. Characterization of autologous rosette-forming cells: a nonrestricted phenomenon. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Hermes F. F., Willems R. W., Capel P. J., Koene R. A. Fc receptors for mouse IgG1 on human monocytes: polymorphism and role in antibody-induced T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1185–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Carson D. A., Fong S., Vaughan J. H. Molecular interactions in human T cell-mediated cytotoxicity to EBV II. Monoclonal antibody OKT3 inhibits a post-killer-target recognition/adhesion step. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1421–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Landgraf B., Bentin J., Valentine M., Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Activation of resting T lymphocytes by anti-CD3 (T3) antibodies in the absence of monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., Goossens J. G. The mitogenic activity of OKT3 and anti-Leu 4 monoclonal antibodies: a comparative study. Cell Immunol. 1983 Apr 1;77(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., Goossens J., Van Nyen G. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by monoclonal antibody directed against the T3 antigen on human T cells. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jul;86(2):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Deloria D., Hansen J. A., Dinarello C. A., Loertscher R., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B. The events of primary T cell activation can be staged by use of Sepharose-bound anti-T3 (64.1) monoclonal antibody and purified interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2249–2255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


