Abstract
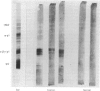
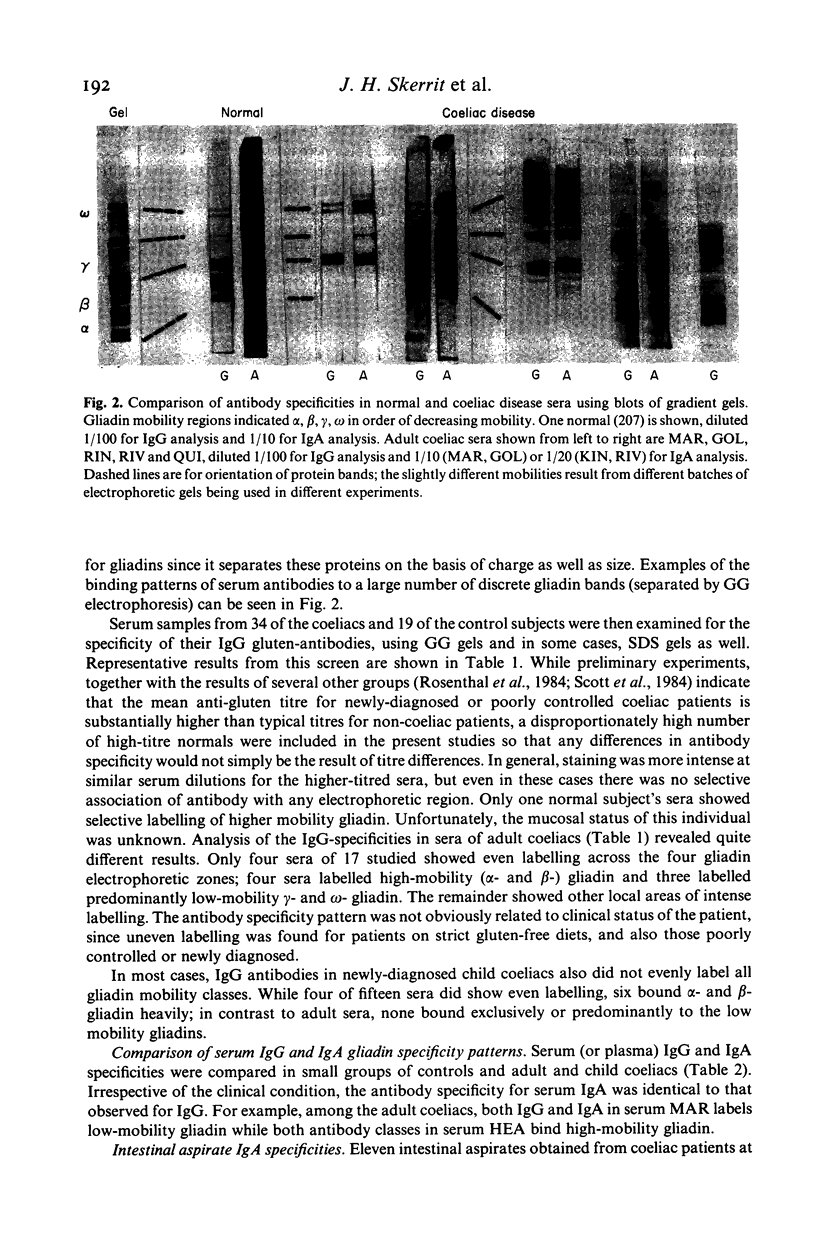
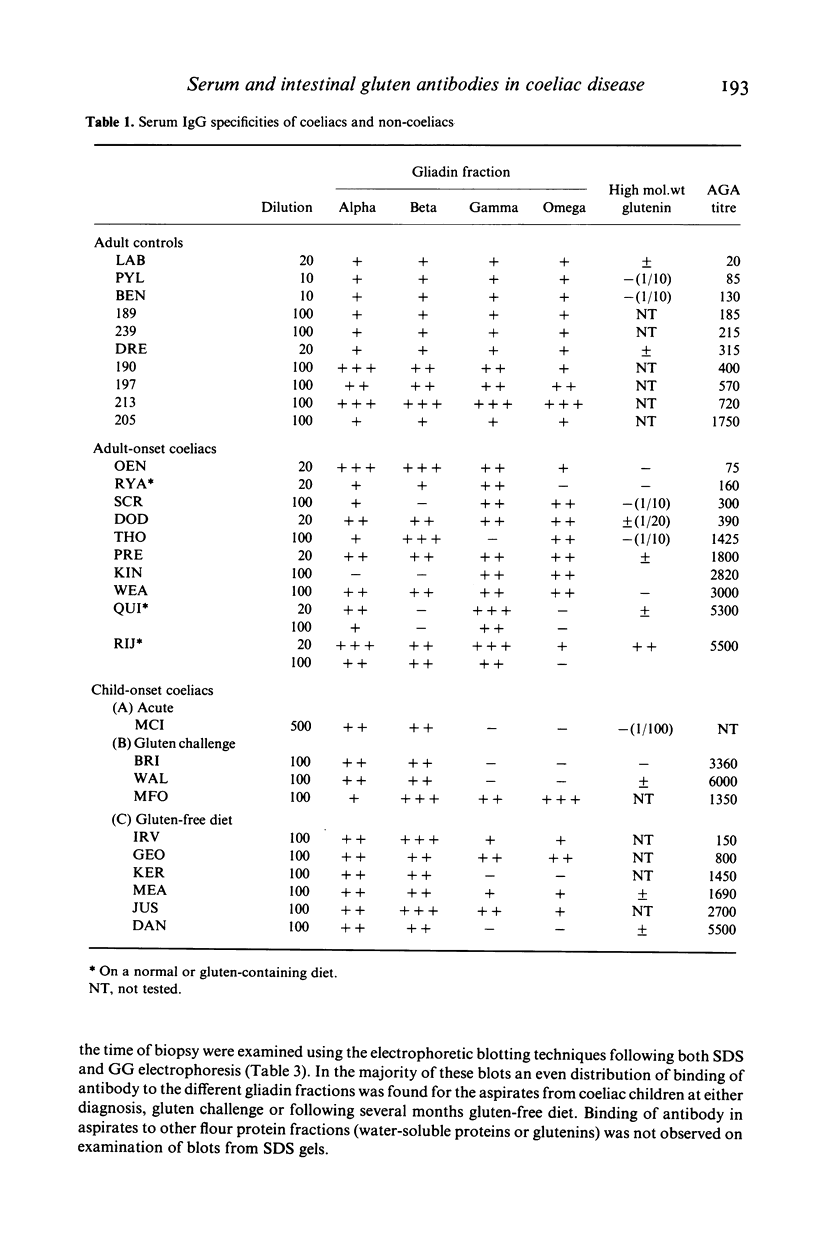
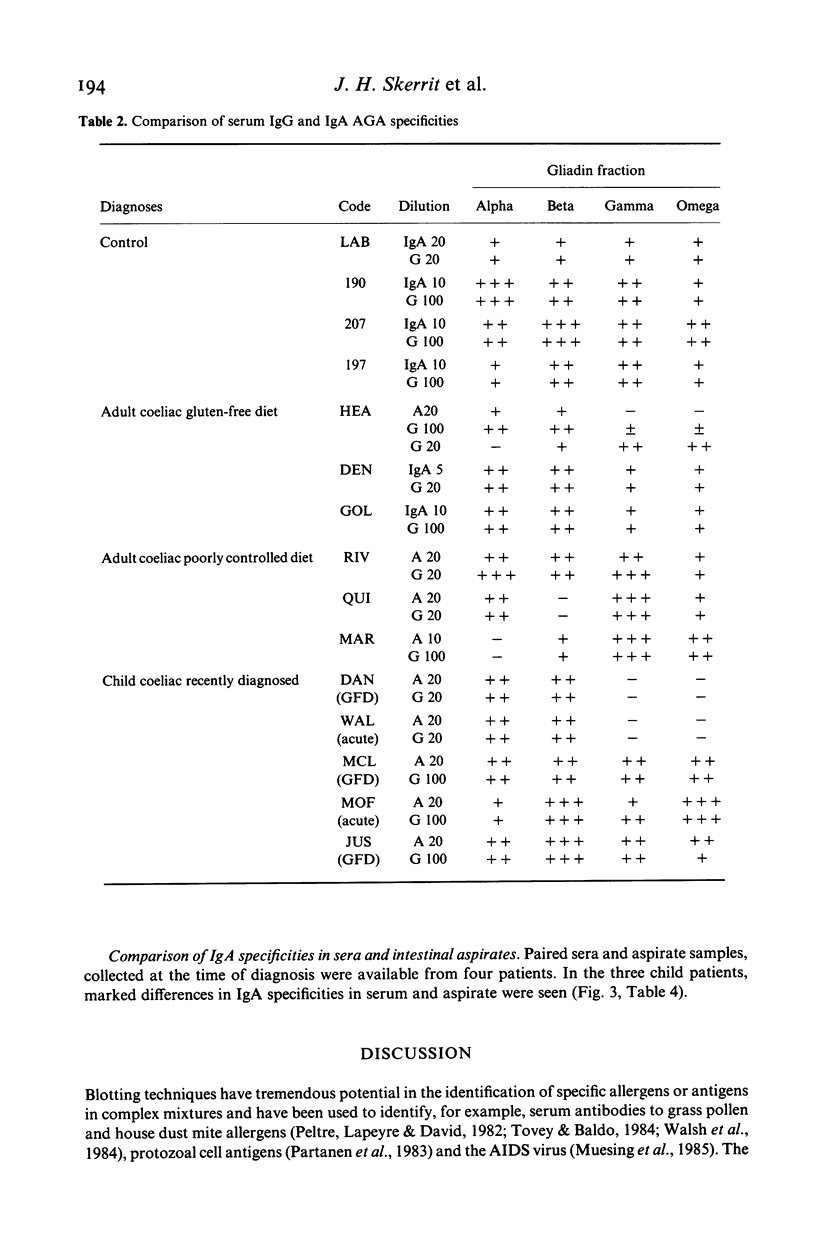
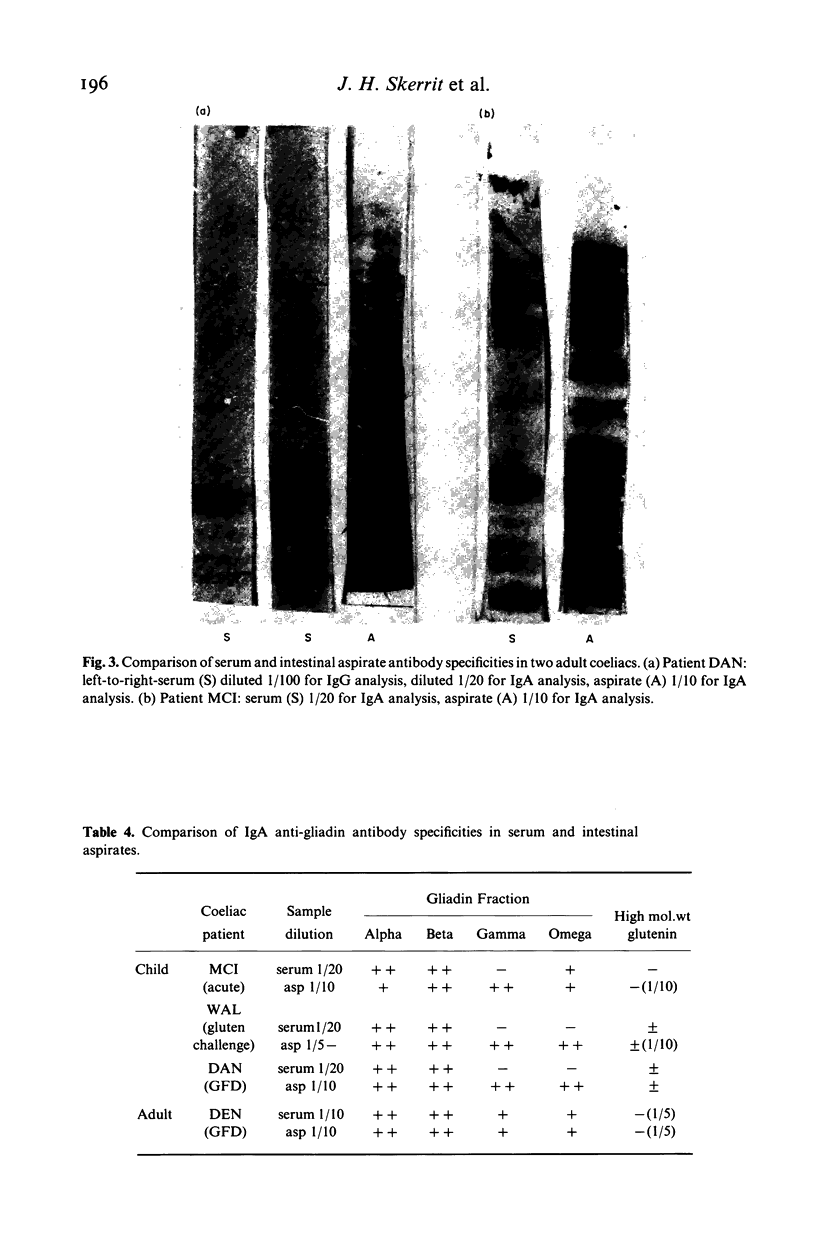
Protein blotting techniques were used to investigate the gluten specificity of IgA and IgG antibodies in sera and intestinal aspirates from patients with coeliac disease and normal controls. Initially, discontinuous SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to separate the flour proteins. All normal and coeliac sera contained antibodies which bound to various of the gliadin proteins. In only a few sera was binding found to the high molecular weight glutenin subunits, while none was detected to the salt-soluble wheat proteins. Polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis was then used to further separate the gliadin proteins. Almost all normal sera examined showed similar gliadin specificity, binding uniformly to all gliadin groups. While approximately a quarter of the coeliac sera showed even binding to all of the gliadin proteins, the majority showed antibody binding intensely to discrete groups of gliadin bands. We were unable to identify any gliadin band(s) which only bound antibodies from coeliac patients in comparison with normal subjects. The specificities of IgG and IgA serum antibodies were identical for each patient examined, but some differences between serum and intestinal IgA specificities were found for certain patients.
Full text
PDF

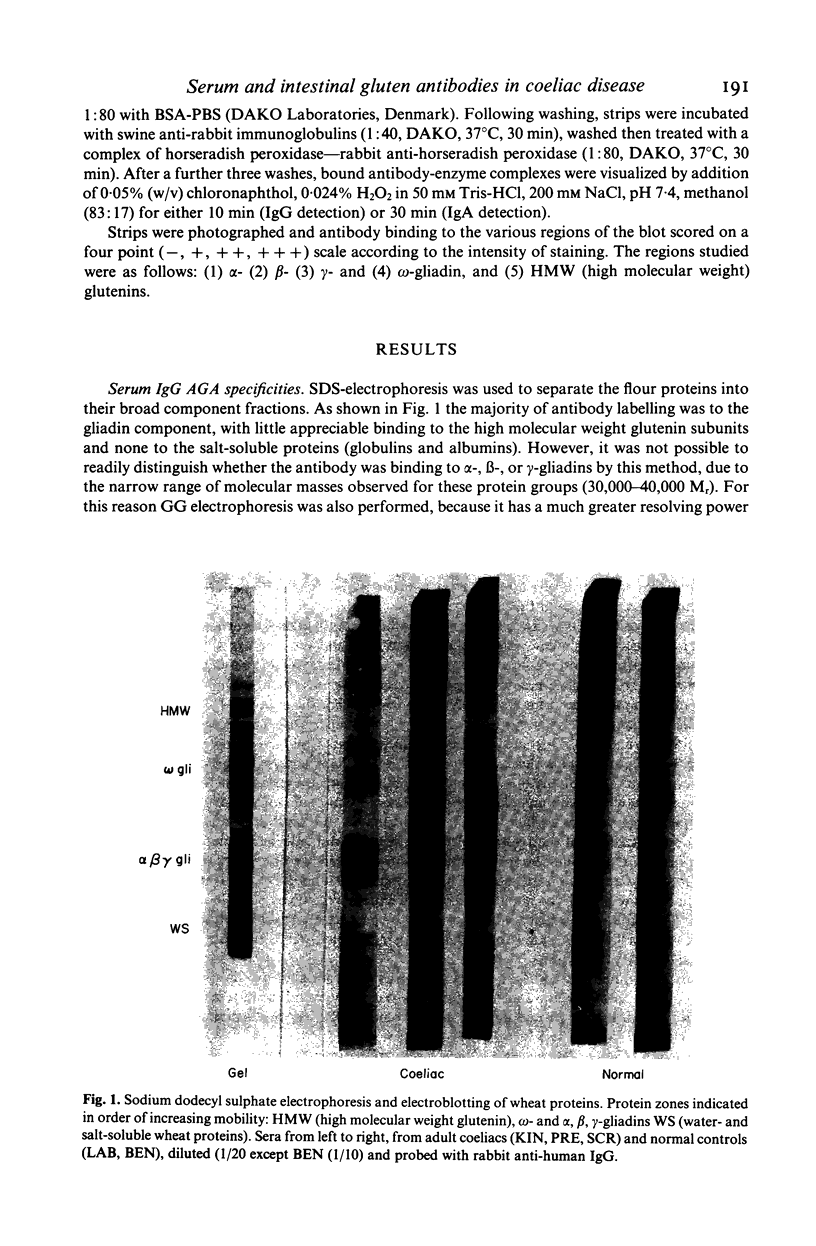




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Veall N. A persistent defect in intestinal permeability in coeliac disease demonstrated by a 51Cr-labelled EDTA absorption test. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell F., Ferguson A. Plasma food antibodies during withdrawal and reintroduction of dietary gluten in coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Aug;48(8):583–586. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.8.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Ellis H. J., Evans D. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for measurement of circulating antibody titres to wheat gliadin and its subfractions in patients with adult coeliac disease. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Aug 26;62(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Evans D. J., Fagg N. L., Lennox E. S., Dowling R. H. Clinical testing of gliadin fractions in coeliac patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Mar;66(3):357–364. doi: 10.1042/cs0660357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Hunter J. O., Lennox E. S. Clinical testing of bread made from nullisomic 6A wheats in coeliac patients. Lancet. 1980 Aug 2;2(8188):234–236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Kieffer M., Fraser D. R., Frazier P. J. Naturally developing antibodies to wheat gliadin fractions and to other cereal antigens in rabbits, rats and guinea pigs on normal laboratory diets. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983 Mar;70(3):200–204. doi: 10.1159/000233323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Carswell F. Precipitins to dietary proteins in serum and upper intestinal secretions of coeliac children. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):75–77. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., LaBrooy J., Davidson G. P., Shearman D. J. Measurement of specific antibodies in human intestinal aspirate: effect of the protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Hubert J. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. Possible role for a human adenovirus in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1544–1557. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Schneider R., Cox P. S., Hawkins C. F. Gluten subfractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer M., Frazier P. J., Daniels N. W., Coombs R. R. Wheat gliadin fractions and other cereal antigens reactive with antibodies in the sera of coeliac patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Dec;50(3):651–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Davidson G. P., Sherman D. J., Rowley D. The antibody response to bacterial gastroenteritis in serum and secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):290–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Shearman D. J., Rowley D. Antibodies in serum and secretions 1 year after salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):551–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson S. D., Austin R. K., Dietler M. D., Kasarda D. D., Kagnoff M. F. Specificity of antigliadin antibody in celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Harms H. K., Rey J., Shmerling D. H., Visakorpi J. K., Walker-Smith J. A. The diagnosis of coeliac disease. A commentary on the current practices of members of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (ESPGAN). Arch Dis Child. 1979 Oct;54(10):783–786. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.10.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Kelly J., Hekkens W., Bradley B., Thompson A., Feighery C., Weir D. G. Alpha gliadin antibody levels: a serological test for coeliac disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jun 25;286(6383):2007–2010. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6383.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R., Forsblom E., Suni J., Leinikki P. O. Identification of antigenic components of Toxoplasma gondii by an immunoblotting technique. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 25;158(2):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80589-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltre G., Lapeyre J., David B. Heterogeneity of grass pollen allergens (Dactylis glomerata) recognized by IgE antibodies in human patients sera by a new nitrocellulose immunoprint technique. Immunol Lett. 1982 Sep;5(3):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E., Golan D. T., Benderly A., Shmuel Z., Levy J. Immunofluorescent antigluten antibody test. Titer and profile of gluten antibodies in celiac disease. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Jul;138(7):659–662. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140450041012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Viander M., Perkkiö M., Vainio E., Kalimo K., Reunala T. IgA antigliadin antibodies: a marker of mucosal damage in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):320–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Fausa O., Ek J., Brandtzaeg P. Immune response patterns in coeliac disease. Serum antibodies to dietary antigens measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):25–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M., Fischer K., Grüttner R. Immunofluorescent serum gliadin antibodies in children with coeliac disease and various malabsorptive disorders. II. Specificity of Gliadin antibodies: immunoglobulin classes, immunogenic properties of wheat protein fractions, and pathogenic significance of food antibodies in coeliac disease. Eur J Pediatr. 1979 Mar 1;130(3):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00455262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Wrigley C. W., Baldo B. A. Detection of IgE- and IgG-binding proteins after electrophoretic transfer from polyacrylamide gels. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jul 30;52(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey E. R., Baldo B. A. Standardization of allergens. Qualitative definition of house dust mite extracts following electroblotting and detection of components with antibody and lectin probes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;75(4):322–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Kieffer M., Holborow E. J., Coombs R. R., Walker-Smith J. A. IgA anti-gliadin antibodies in coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Nov;46(2):286–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh B. J., Sutton R., Wrigley C. W., Baldo B. A. Allergen discs prepared from nitrocellulose: detection of IgE binding to soluble and insoluble allergens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Oct 12;73(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley C. W. Protein mapping by combined gel electrofocusing and electrophoresis: application to the study of genotypic variations in wheat gliadins. Biochem Genet. 1970 Aug;4(4):509–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00486601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]