Abstract
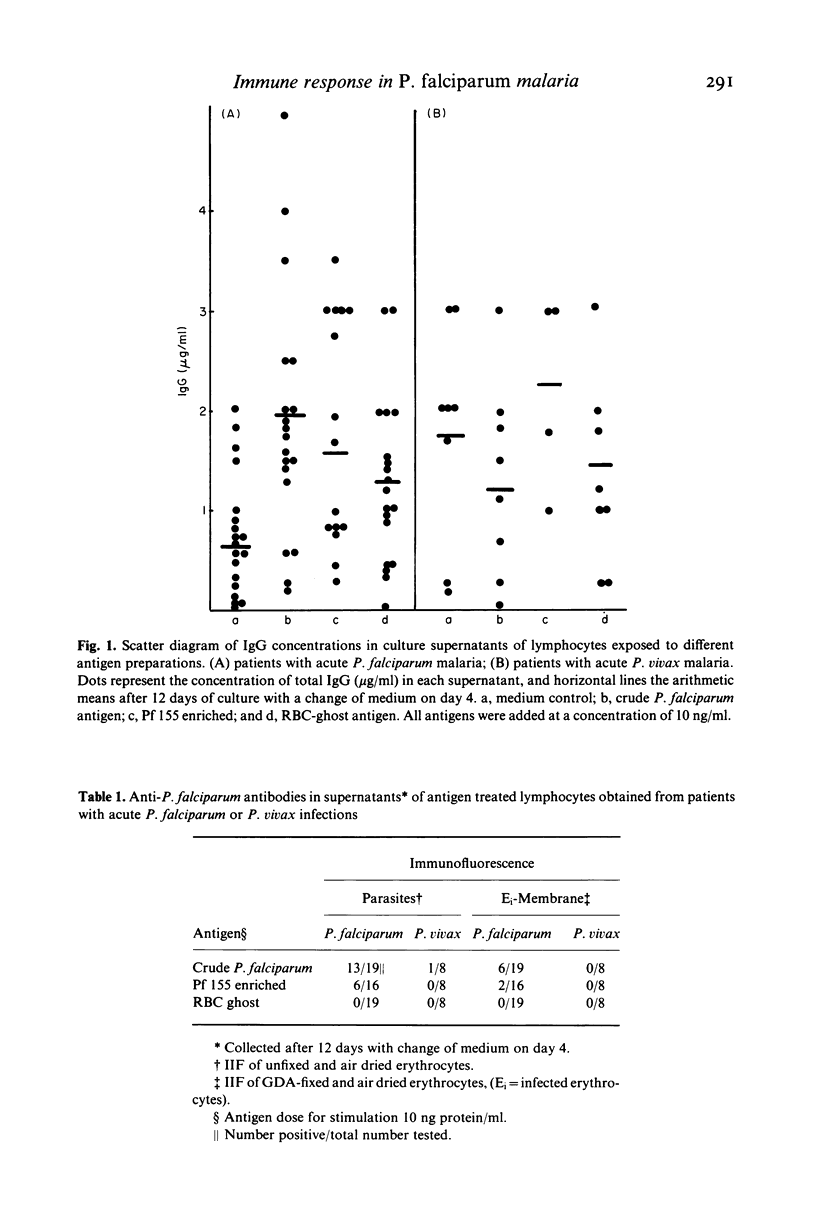
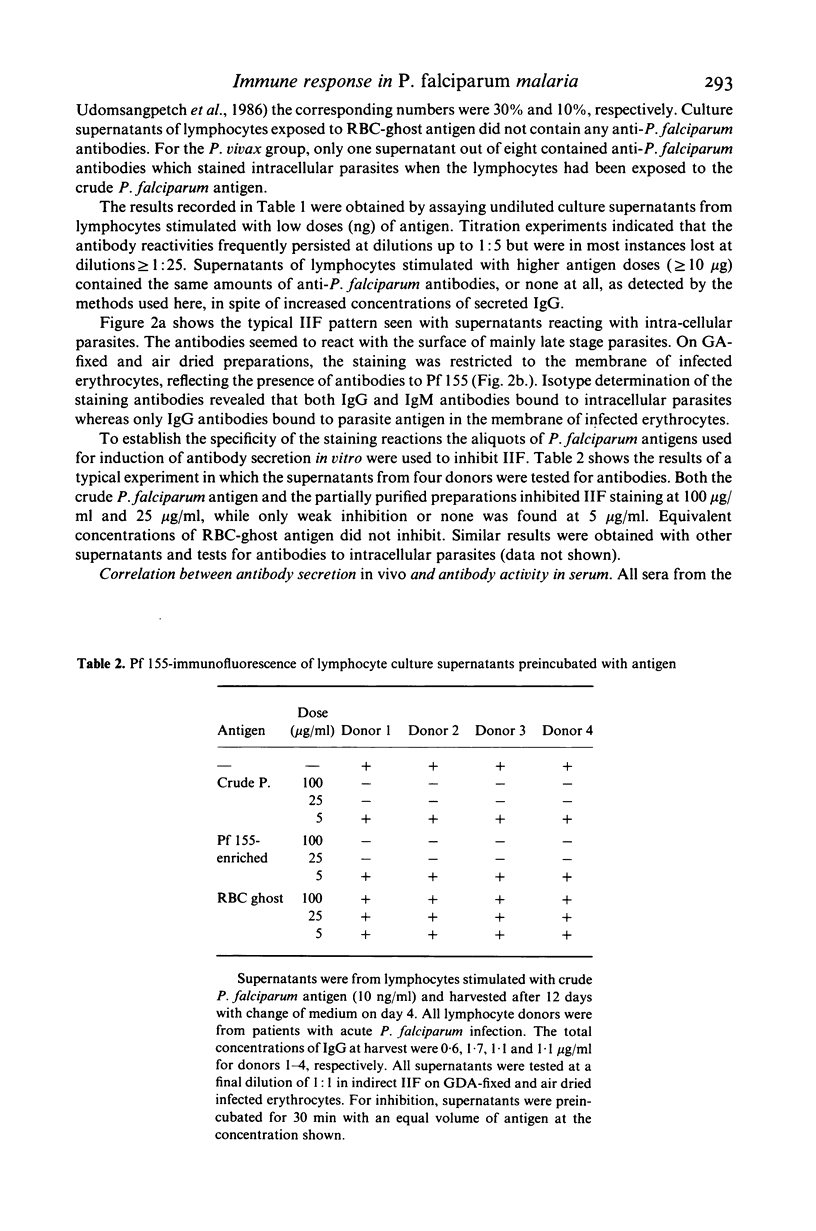
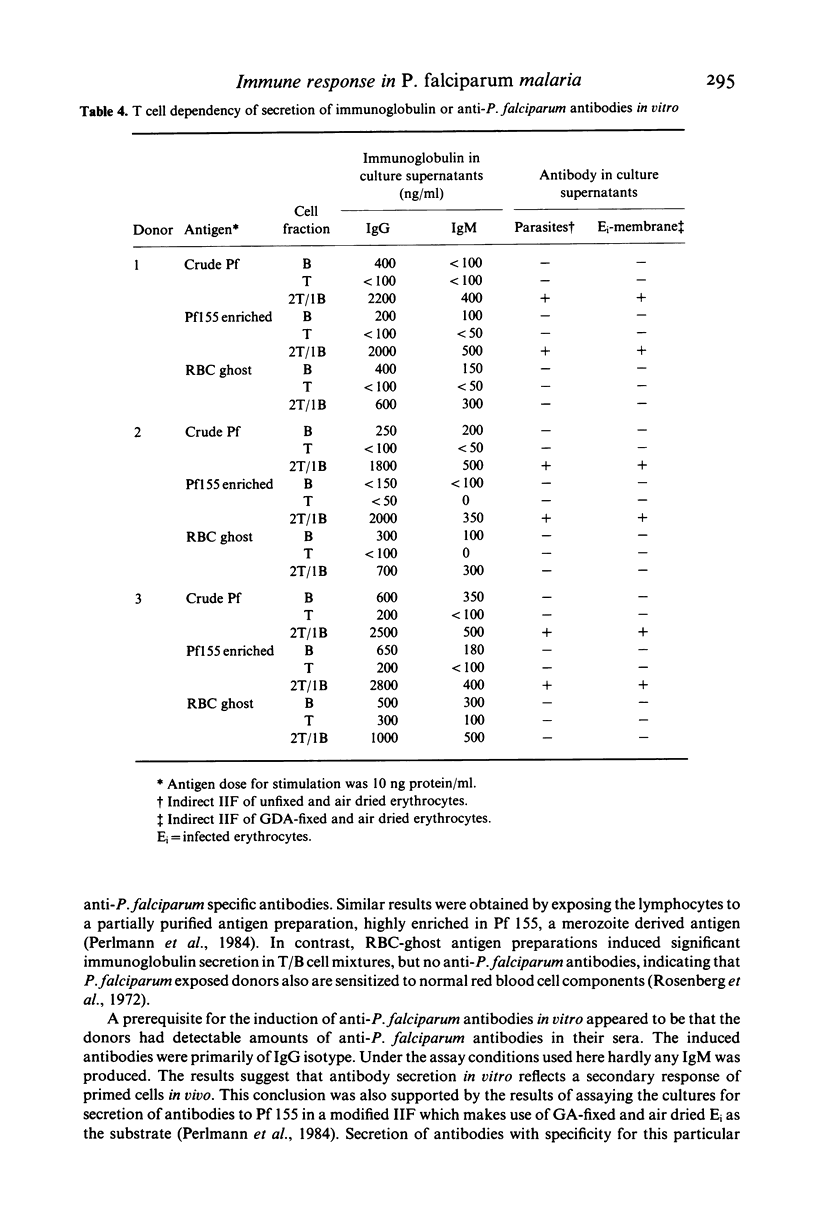
T cells from patients with acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria were investigated for induction of immunoglobulin- or anti-malaria antibody secretion in vitro. Stimulation of autologous T/B cell mixtures (2T:1B) with low concentrations of P. falciparum antigen and cultured for 12 days gave rise to a T-dependent IgG secretion which was significantly elevated over that in medium controls. This was achieved with both a crude P. falciparum antigen and a partially purified preparation enriched in Pf 155, a merozoite-derived antigen deposited in the red cell membrane at invasion (Perlmann et al., 1984). Control antigen (RBC ghosts) induced IgG secretion only when added at high concentrations (greater than 10 micrograms/ml). Neither of the antigens induced IgG secretion at concentrations of less than or equal to 10 micrograms/ml in control cultures of lymphocytes from patients with P. vivax malaria. Supernatants from cultures of P. falciparum patients frequently contained anti-P. falciparum antibodies when nanogram quantities (10-100 ng/ml) of either one of the two malaria antigen preparations was used for stimulation. No anti-P. falciparum antibodies were induced by the control antigen at any concentration. The induced anti-P. falciparum antibodies were directed to intracellular parasites and. at lower frequencies, to Pf 155 as detected on the surface of infected erythrocytes. The induction in vitro of anti-P. falciparum antibodies appeared to be correlated with the presence of such antibodies in the sera of the lymphocyte donors. The lymphocytes of only one out of eight P. vivax patients responded to antigen stimulation by secreting anti-P. falciparum antibodies. However, this donor (but not any of the others), was also P. falciparum seropositive. Taken together, these results indicate that the induction of anti-P. falciparum antibody secretion reflects a secondary response in vitro of cells primed in vivo. The present experimental system should be well suited to map parasite antigen for their capacity to induce T cell dependent responses in P. falciparum malaria.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Eugui E. M. The role of cell-mediated immune responses in resistance to malaria, with special reference to oxidant stress. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:361–392. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballet J. J., Druilhe P., Querleux M. A., Schmitt C., Agrapart M. Parasite-derived mitogenic activity for human T cells in Plasmodium falciparum continuous cultures. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):758–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.758-762.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzins K., Perlmann H., Udomsangpetch R., Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Troye-Blomberg M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Perlmann P. Pf 155, a candidate for a blood stage vaccine in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;62:99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur P., Agrapart M., Ballet J. J., Druilhe P., Warrell M. J., Tharavanij S. Impaired cell-mediated immunity in Plasmodium falciparum-infected patients with high-parasitemia and cerebral malaria. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):38–50. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. Immunity to malaria. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Jan 15;203(1153):323–345. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Principato M. A., Thompson G. S., Teichman F. Antigen-specific and polyclonal immunoglobulin production induced by a cloned tetanus toxoid-specific T cell line. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1164–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Oduloju A. J., Platts-Mills T. A. Partial characterization of a malaria mitogen. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström U., Sylvan S., Lundbergh P. Regulatory functions of T- and accessory-cells for hepatitis B surface antigen induced specific antibody production and proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes, in vitro. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1985 Apr;16(4):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jónsdóttir I., Dillner-Centerlind M. L., Perlmann H., Perlmann P. Antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity and mitogen responsiveness of human peripheral blood lymphocytes differing in avidity for sheep erythrocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(6):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataaha P. K., Facer C. A., Mortazavi-Milani S. M., Stierle H., Holborow E. J. Stimulation of autoantibody production in normal blood lymphocytes by malaria culture supernatants. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Sep;6(5):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum L. G., Culbertson N. J. The induction and suppression of in vitro IgG anti-tetanus toxoid antibody synthesis by human lymphocytes stimulated with tetanus toxoid in the absence of in vivo booster immunizations. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., David P. H., Hadley T. J. Perspectives for malaria vaccination. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Nov 13;307(1131):99–115. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Development of a sporozoite vaccine. Parasitol Today. 1985 Dec;1(6):150–152. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. E. Surface proteins of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites binding to the erythrocyte receptor, glycophorin. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):788–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Perlmann P., Pape G. R., Halldén G. Purification, fractionation and assay of antibody-dependent lymphocytic effector cells (K cells) in human blood. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E. B., Strickland G. T., Yang S. L., Whalen G. E. IgM antibodies to red cells and autoimmune anemia in patients with malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Mar;22(2):146–152. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. L., Booth R. J., Prestidge R. L., Watson J. D., Dower S. K., Gillis S. Induction of antibody responses to influenza virus in human lymphocyte cultures. I. Role of interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2128–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targett G. A., Sinden R. E. Transmission blocking vaccines. Parasitol Today. 1985 Dec;1(6):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theander T. G., Bygbjerg I. C., Andersen B. J., Jepsen S., Kharazmi A., Odum N. Suppression of parasite-specific response in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. A longitudinal study of blood mononuclear cell proliferation and subset composition. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Jul;24(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Perlmann H., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Regulation of the immune response in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. II. Antigen specific proliferative responses in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):345–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Björkman A., Perlmann P. Regulation of the immune response in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. III. Proliferative response to antigen in vitro and subset composition of T cells from patients with acute infection or from immune donors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):380–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udomsangpetch R., Lundgren K., Berzins K., Wåhlin B., Perlmann H., Troye-Blomberg M., Carlsson J., Wahlgren M., Perlmann P., Björkman A. Human monoclonal antibodies to Pf 155, a major antigen of malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):57–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3510452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Allyn S. P., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced in vitro antibody production in humans: tetanus toxoid-specific antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Larsson A., Ljungström I., Patarroy M. E., Perlmann P. Characterization of the humoral immune response in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. III. Factors influencing the coexpression of antibody isotypes (IgM and IgG-1 to 4). Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Feb;63(2):343–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidanz W. P., Grun J. L. Antibody-independent mechanisms in the development of acquired immunity to malaria. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;162:409–423. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4481-0_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]