Abstract
The effect of iron-overload on cell-mediated immunity was examined in C57 mice. Two methods of iron-loading were used: (i) dietary carbonyl iron which produced iron-loading primarily of parenchymal cells or (ii) intraperitoneal administration of iron-dextran which produced iron-loading predominantly of Kupffer cells. Both methods of iron-loading resulted in a diminished capacity of spleen cells to generate an allo-specific cytotoxic response in the absence of exogenous interleukin 2 (IL-2). Exogenous IL-2, however, restored the ability of spleen cells from iron-loaded mice to generate allo-specific cytotoxicity in bulk culture. Clonal assays for the precursor cells of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL-P), performed in the presence of added IL-2, demonstrated that iron-loaded mice contained normal numbers of CTL-P. However, cultures of spleen cells from carbonyl iron-loaded mice generated less IL-2 following Concanavalin A stimulation, apparently as a result of a reduction in the number of IL-2-secreting cells amongst the spleen cell population. This work presents further evidence that iron-overload is associated with defective immunoregulatory control.
Full text
PDF


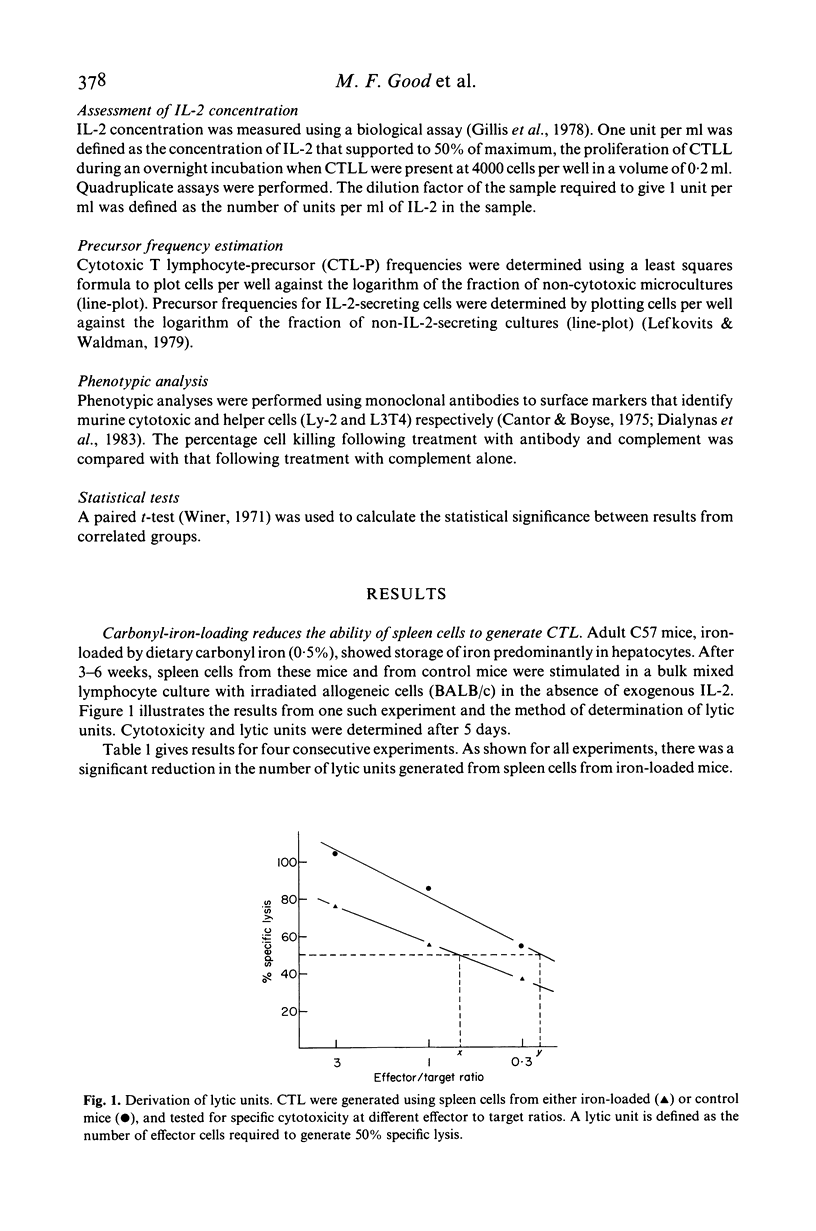


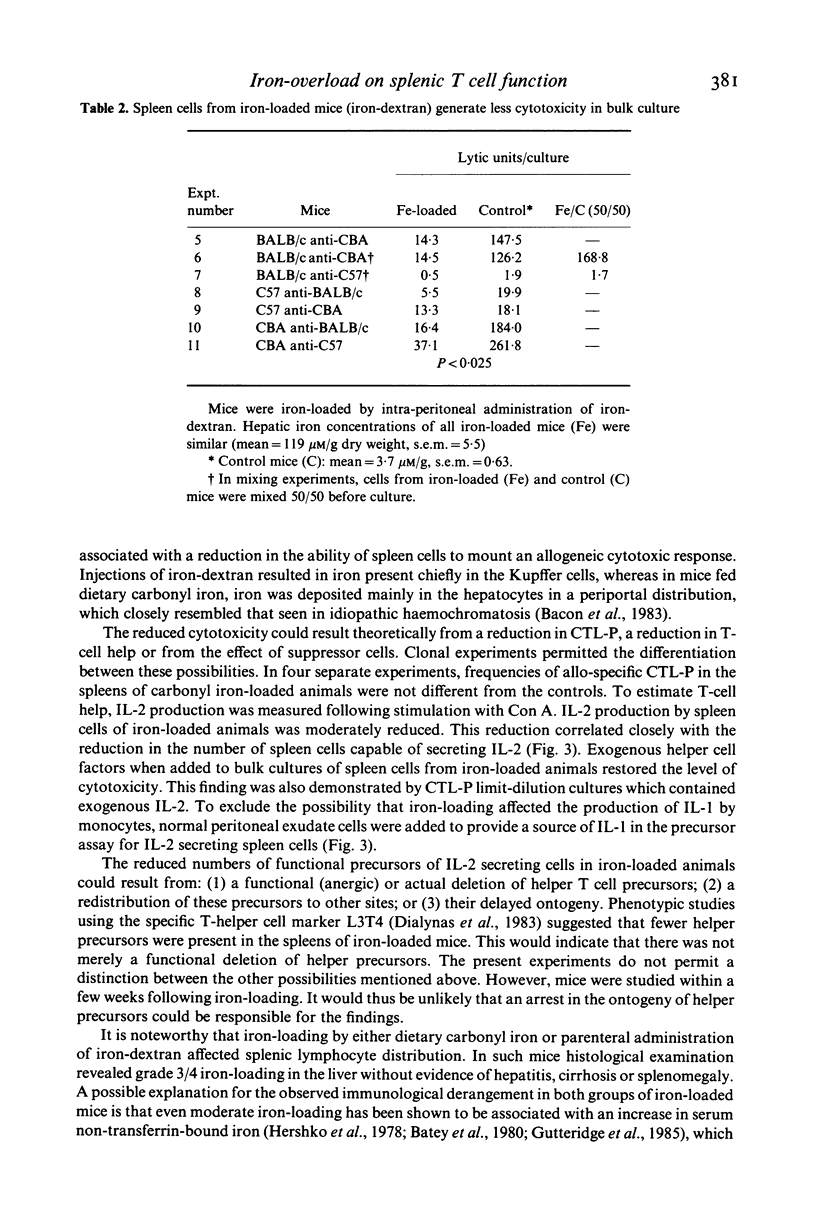


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthoine D., Braun P., Cervoni P., Schwartz P., Lamy P. Le cancer bronchique des mineurs de fer de Lorraine peut-il être considéré comme une maladie professionnelle? A propos de 270 nouveaux cas observés de 1964 à 1978. Rev Fr Mal Respir. 1979 Jan-Feb;7(1):63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN C. Primary carcinoma of the liver. Adv Cancer Res. 1958;5:55–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon B. R., Tavill A. S., Brittenham G. M., Park C. H., Recknagel R. O. Hepatic lipid peroxidation in vivo in rats with chronic iron overload. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):429–439. doi: 10.1172/JCI110787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batey R. G., Lai Chung Fong P., Shamir S., Sherlock S. A non-transferrin-bound serum iron in idiopathic hemochromatosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 May;25(5):340–346. doi: 10.1007/BF01308057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron R. J., Streiff R. R., Elliott G. T. Influence of iron on in vivo proliferation and lethality of L1210 cells. J Nutr. 1985 Mar;115(3):369–374. doi: 10.1093/jn/115.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boemi G., Chiesa C., Di Lorenzo M., Patti G., Marrocco G., Midulla M. Yersinia enterocolitica peritonitis. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):927–928. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouza E., Dominguez A., Meseguer M., Buzon L., Boixeda D., Revillo M. J., de Rafael L., Martinez-Beltran J. Yersinia enterocolitica Septicemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Oct;74(4):404–409. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.4.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbear R. A., Bain C., Siskind V., Schofield F. D., Webb S., Axelsen E. M., Halliday J. W., Bassett M. L., Powell L. W. Cohort study of internal malignancy in genetic hemochromatosis and other chronic nonalcoholic liver diseases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Jul;75(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. F., Nishiya K., Pollack M. S., Dupont B., de Sousa M. Differential inhibition of the MLR by iron: association with HLA phenotype. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01561656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron J. P., Capron-Chivrac D., Tossou H., Delamarre J., Eb F. Spontaneous Yersinia enterocolitica peritonitis in idiopathic hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1372–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa M., Nishiya K. Inhibition of E-rosette formation by two iron salts. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jun;38(1):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Nossal G. J. Characteristics of tolerance induction among adult hapten-specific T lymphocyte precursors revealed by clonal analysis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M., Rowley D. A., Griffiths E., Halliwell B. Low-molecular-weight iron complexes and oxygen radical reactions in idiopathic haemochromatosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):463–467. doi: 10.1042/cs0680463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Dower S. K., Henney C. S., Gillis S. Limiting dilution analysis of interleukin 2 and colony-stimulating factor producer cells in normal and autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1863–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko C., Graham G., Bates G. W., Rachmilewitz E. A. Non-specific serum iron in thalassaemia: an abnormal serum iron fraction of potential toxicity. Br J Haematol. 1978 Oct;40(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keown P., Descamps-Latscha B. In vitro suppression of cell-mediated immunity by ferroproteins and ferric salts. Cell Immunol. 1983 Sep;80(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzner Y., Hershko C., Polliack A., Konijn A. M., Izak G. Suppressive effect of ferritin on in vitro lymphocyte function. Br J Haematol. 1979 Jul;42(3):345–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzner Y., Konijn A. M., Shlomai Z., Ben-Bassat H. Differential effect of isolated placental isoferritins on in vitro T-lymphocyte function. Br J Haematol. 1985 Mar;59(3):443–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettesheim P., Creasia D. A., Mitchell T. J. Carcinogenic and cocarcinogenic effects of inhaled synthetic smog and ferric oxide particles. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jul;55(1):159–169. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Fischer R., Sonnenberg A., Stremmel W., Trampisch H. J., Strohmeyer G. Survival and causes of death in cirrhotic and in noncirrhotic patients with primary hemochromatosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 14;313(20):1256–1262. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511143132004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Müllbacher A. Automated colorimetric assay for T cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 11;58(1-2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. W., Mortimer R., Harris O. D. Cirrhosis of the liver. A comparative study of the four major aetiological groups. Med J Aust. 1971 May 1;1(18):941–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND H. G. Induction of sarcoma in the rat by iron-dextran complex. Br Med J. 1959 Apr 11;1(5127):947–949. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5127.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. R., Hallett A. F., Koornhof H. J. Generalized Yersinia enterocolitica infection. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):447–451. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. R., Koornhof H. J. Yersinia enterocolitica infections in South Africa. S Afr Med J. 1972 Jun 10;46(24):798–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron, infection, and neoplasia. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1986;4(1):50–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbren K., Salm R., Greenberg G. Intramuscular injections of iron compounds and oncogenesis in man. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):683–685. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asbeck B. S., Verbrugh H. A., van Oost B. A., Marx J. J., Imhof H. W., Verhoef J. Listeria monocytogenes meningitis and decreased phagocytosis associated with iron overload. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Feb 20;284(6315):542–544. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6315.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


