Abstract
Intravenous treatment with miconazole brought about the recovery of 90% of patients with gastrointestinal or systemic candidosis. Miconazole given by the same route has also been found effective in the treatment of cryptococcosis, coccidioidomycosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. Cryptococcal and coccidioidal meningitis have been cured by combined intravenous and intrathecal instillation, although treatment of aspergillosis has presented difficulty. Oral treatment was effective in curing dermatophyte skin infections and systemic mycoses caused by sensitive organisms such as paracoccidioides, blastomyces and histoplasma. The question of blood levels following oral and intravenous administration is discussed. Side effects of the drug were few, and included chills, dizziness, skin rash, itching and diarrhoea. Thus miconazole can safely be given to seriously ill patients. Its behaviour in the body is not influenced by renal insufficiency and no drug induced resistance has been reported.
Full text
PDF
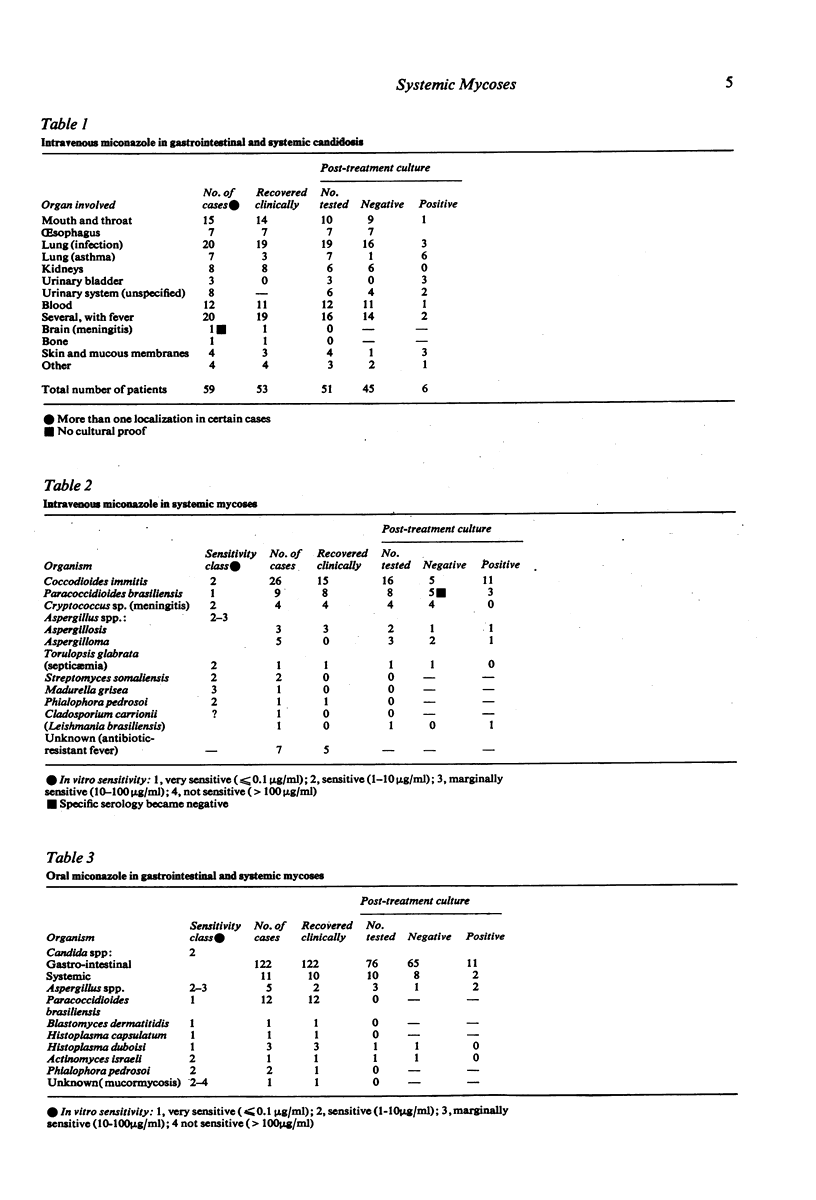




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daneels R., Demeyere R., Eggers L., Lust P., van Landuyt H., Symoens J. Zur Behandlung systemischer Candidiasis mit Miconazol. Med Welt. 1974 Mar 8;25(10):428–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen G., Van Camp K. Les candidoses rénales et urothéliales. Acta Urol Belg. 1974 Oct;42(4):452–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Goldstein E. Miconazole therapy for coccidioidomycosis. JAMA. 1974 Nov 25;230(8):1153–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. J. Recent developments in antimycotic chemotherapy. Infection. 1974;2(2):95–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01642028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijgens P. C., Boeijinga J. K., van der Meer J. Een mogelijk cardiotoxische reactie van miconazol-injectievloeistof. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1975 Oct 4;119(40):1549–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Stevens D. A., Cobb J. M., Gebhardt A. E. Miconazole in coccidioidomycosis. I. Assays of activity in mice and in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):407–414. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer P. R., Brogden R. N., Pinder R. M., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Miconazole: a review of its antifungal activity and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1975;9(6):406–423. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197509060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. A., Levine H. B., Deresinski S. C. Miconazole in coccidiodomycosis. II. Therapeutic and pharmacologic studies in man. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem J. M., Thienpont D. Miconazole, a broad-spectrum antimycotic agent with antibacterial activity. Chemotherapy. 1972;17(6):392–404. doi: 10.1159/000220875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







