Abstract
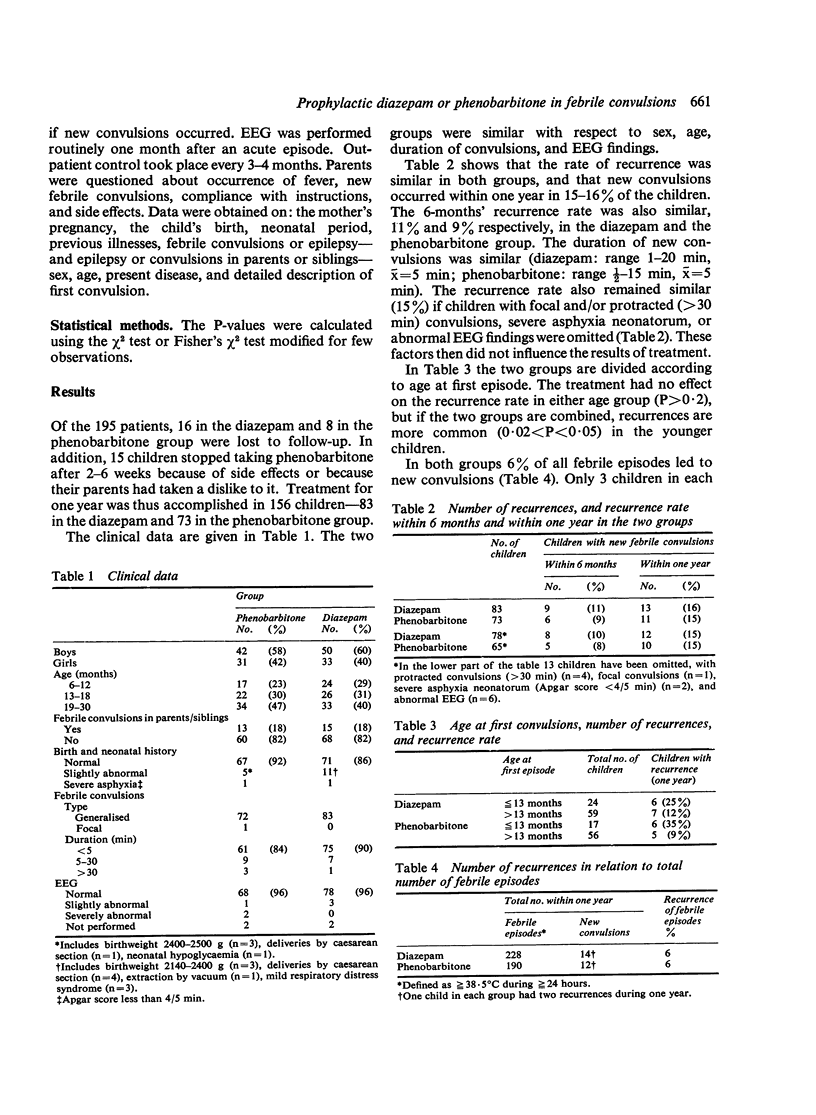
After their first episode of febrile convulsions, 195 previously healthy children, aged 6--30 months, were given either diazepam or phenobarbitone for a year. Each child was assigned at random to one of the two medications: children admitted on even days were given a suppository containing 5 mg diazepam every 8 hours when the rectal temperature was greater than or equal to 38.5 degree C. Children admitted on odd days were given treatment with phenobarbitone, 3.5 +/- 1 mg/kg per day. 156 children completed treatment and outpatient control for a year, 83 in the diazepam and 73 in the phenobarbitone group. The rate of recurrence was independent of the prophylactic and 15--16 % of the children in both groups had new febrile convulsions within a year. The recurrence rate after 6 months was also similar, 11% in the diazepam group and 9% in the phenobarbitone group. New convulsions were of similar duration and severity in both groups. In both groups 6% of all febrile episodes led to new convulsions. Long-term treatment with phenobarbitone thus offered no advantage over intermittent diazepam.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agurell S., Berlin A., Ferngren H., Hellström B. Plasma levels of diazepam after parenteral and rectal administration in children. Epilepsia. 1975 Jun;16(2):277–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb06058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faero O., Kastrup K. W., Lykkegaard Nielsen E., Melchior J. C., Thorn I. Successful prophylaxis of febrile convulsions with phenobarbital. Epilepsia. 1972 Apr;13(2):279–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1972.tb05262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantzen E., Lennox-Buchthal M., Nygaard A. Longitudinal EEG and clinical study of children with febrile convulsions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(68)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantzen E., Lennox-Buchthal M., Nygaard A., Stene J. A genetic study of febrile convulsions. Neurology. 1970 Sep;20(9):909–917. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.9.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmatt J. Z., Houston A. B., Clow D. J., Strephenson J. B., Dodd K. L., Lealman G. T., Logan R. W. Failure of phenobarbitone to prevent febrile convulsions. Br Med J. 1976 Mar 6;1(6009):559–561. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6009.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen F. U. Plasma-diazepam in infants after rectal administration in solution and by suppository. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Sep;66(5):563–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. E., Naestoft J., Hvidberg E. Rapid routine determination of some anti-epileptic drugs in serum by gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Aug;40(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette E. M. The child who convulses with fever. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1974 May;21(2):467–481. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn I. A controlled study of profylactic long-term treatment of febrile convulsions with phenobarbital. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1975;60:67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1975.tb01392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. J. Recurrence of febrile convulsions. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Oct;49(10):763–765. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.10.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. M., Carr A., Davis D. C., Davidson S., Dale E. P., Forsythe A., Goldenberg E. D., Hanson R., Lulejian G. A., Nelson M. A. The value of phenobarbital in the child who has had a single febrile seizure: a controlled prospective study. Pediatrics. 1977 Mar;59(3):378–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


