Abstract
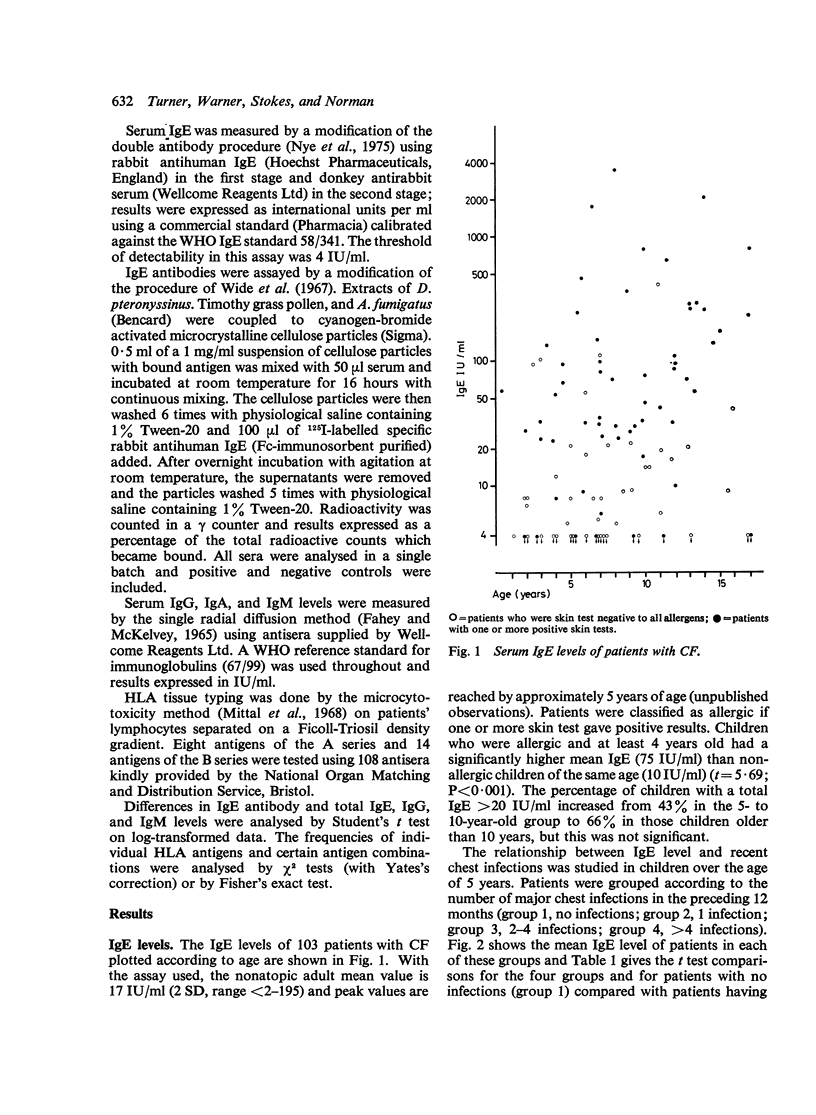
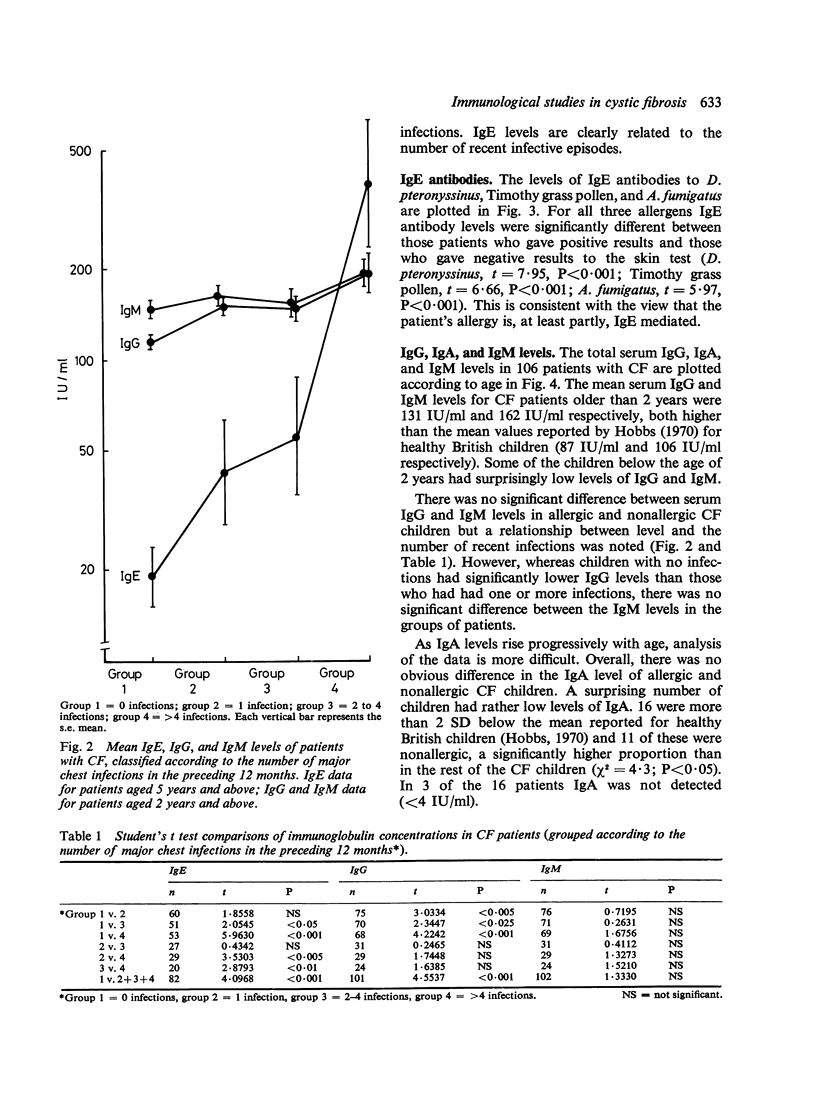
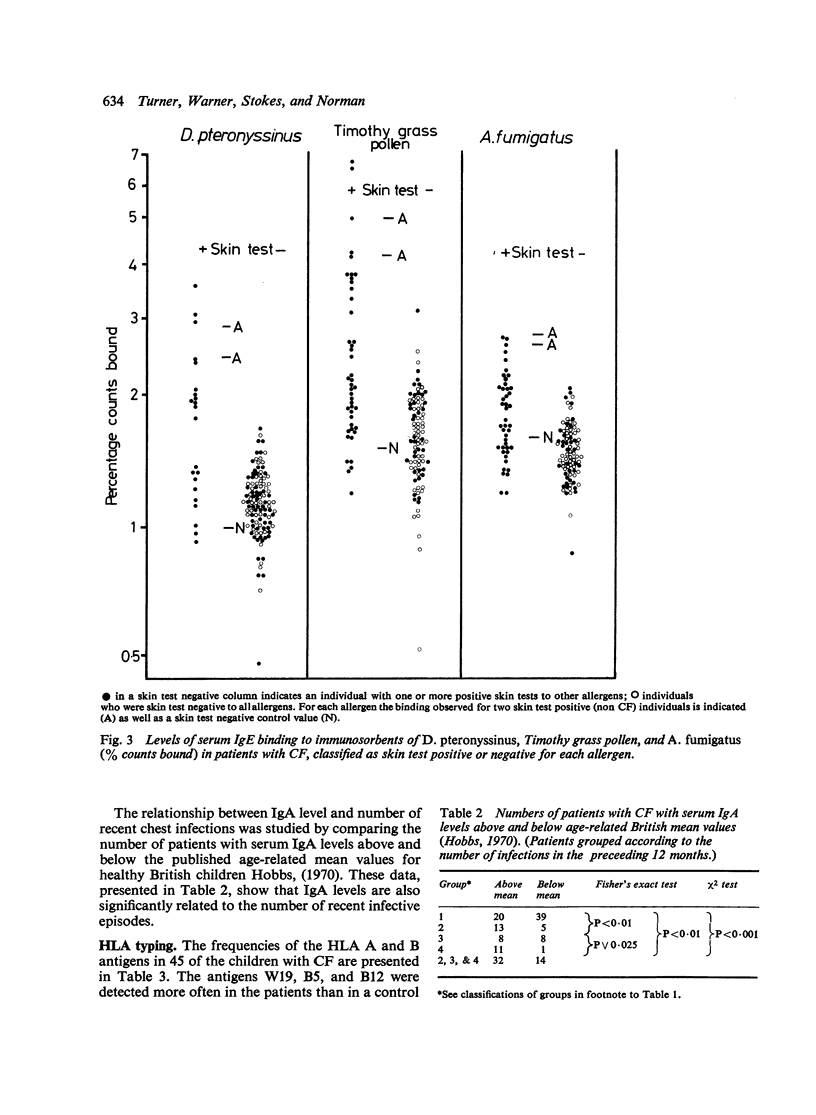
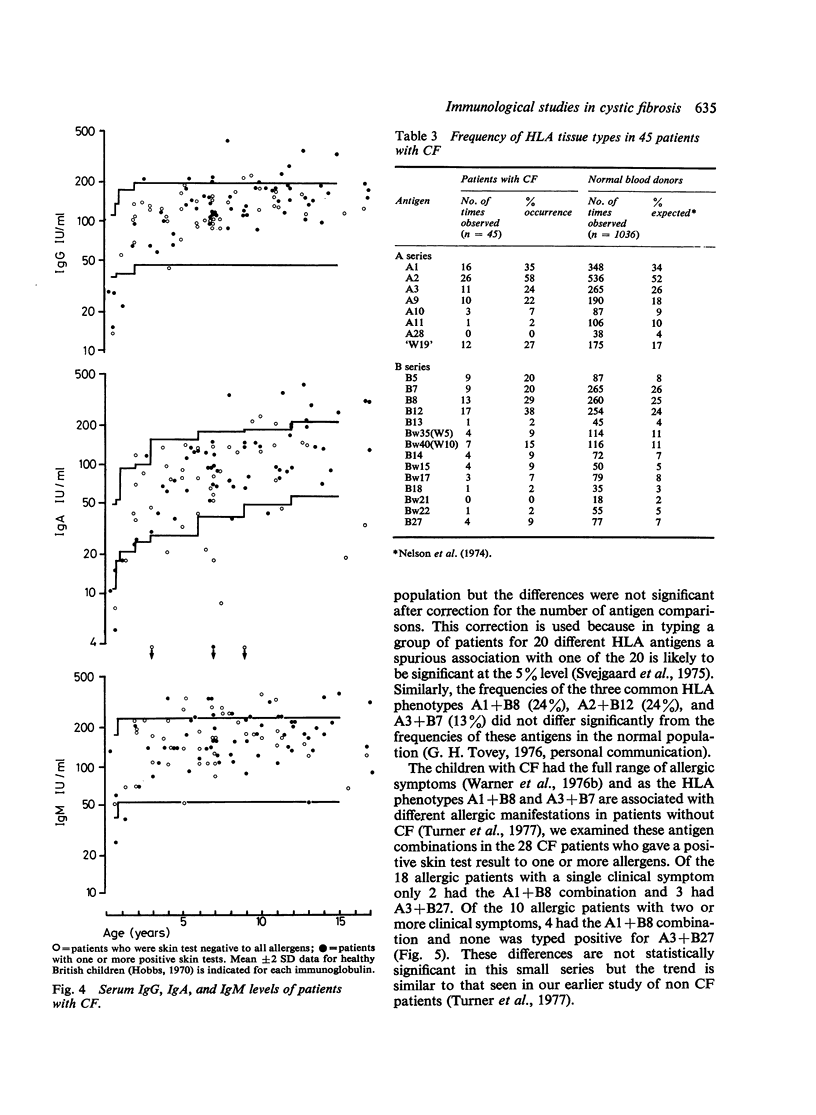
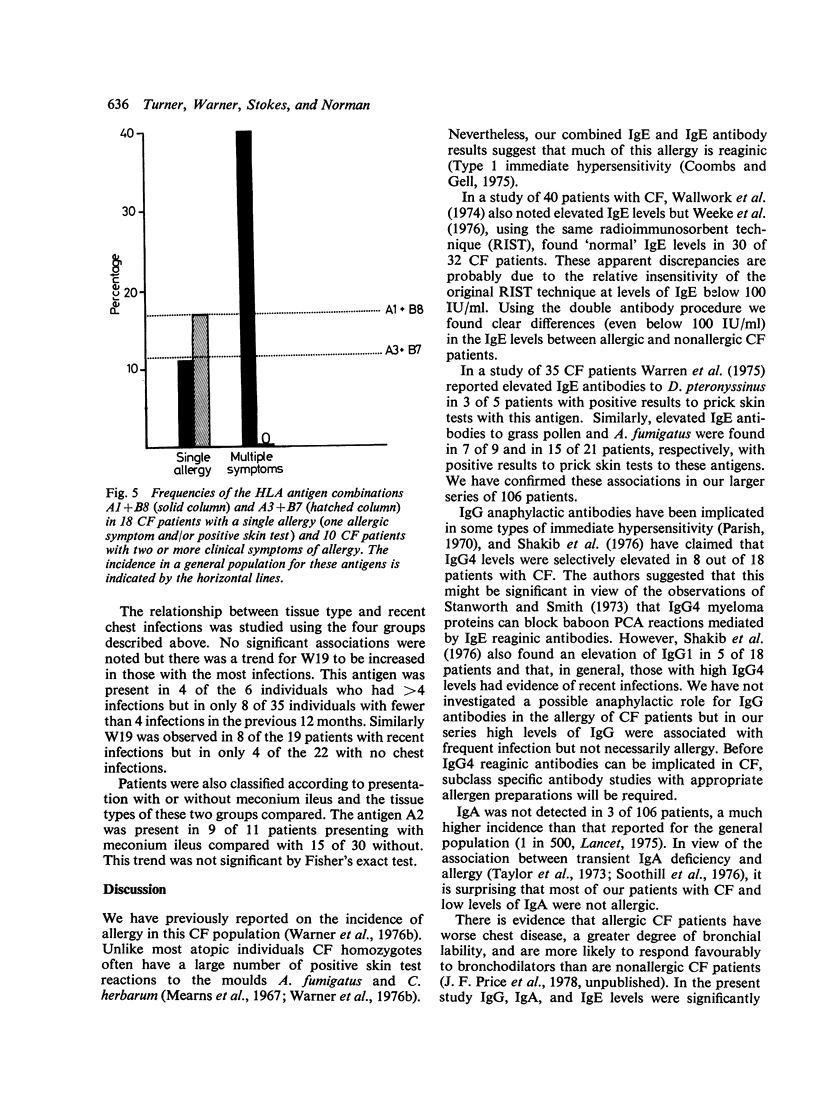
Evidence is presented to support the concept that much of the allergy in cystic fibrosis (CF) is IgE mediated. Total IgE levels were higher in allergic than in nonallergic CF patients. Levels were also higher in those patients who had had the greatest number of chest infections in the preceding 12 months. IgE antibody levels to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Timothy grass pollen, and Aspergillus fumigatus were higher in those with positive results from skin tests to these allergens. The serum IgG, IgM, and IgA levels of allergic and nonallergic CF patients did not differ but the overall mean values for IgG and IgM were higher than those reported for healthy British children. The highest levels tended to be present in patients with the greatest number of recent major chest infections and the difference was significant for IgG. 16 patients had IgA levels 72SD below the reported means for age-matched controls and 11 of these were nonallergic. IgA levels were also higher in patients who had recently experienced major chest infections. 45 of the patients were tissue types for HLA A and B antigens but no significant clinical associations with single antigens were observed. The antigen phenotype A1 + B8 was more common in datients with multiple allergic symptoms than in those with a single allergy or merely a positive result from a skin test Nonsignificant increases of W19 in patients with frequent infections and of A2 in patients presenting with meconium ileus were also noted. The data presented do not permit a choice to be made between the alternative concepts of allergy as a primary abnormality in CF, and allergy arising secondary to infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. D., Moss A. D., Wallwork J. C., McFarlane H. Immediate hypersensitivity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Allergy. 1975 Sep;5(3):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard R. L., Katz S. I., Marks J., Shuster S., Trapani R. J. HL-A antigen type and small-intestinal disease in dermatitis herpetiformis. Lancet. 1973 Oct 6;2(7832):760–762. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Morris P. J. Association of autoimmune active chronic hepatitis with HL-A1,8. Lancet. 1972 Oct 14;2(7781):793–795. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Nelson R., Mackintosh P. H-LA 1 and 8 in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1973 Mar 24;1(7804):668–668. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearns M., Longbottom J., Batten J. Precipitating antibodies to aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1967 Mar 11;1(7489):538–539. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickey M. R., Kreisler M., Albert E. D., Tanaka N., Terasaki P. I. Analysis of HL-A incompatibility in human renal transplants. Tissue Antigens. 1971;1(2):57–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1971.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. D., Darke C., Tovey G. H. HL-A antigen frequencies in normal blood donors, kidney donors and prospective kidney recipients. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):361–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1974.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye L., Merrett T. G., Landon J., White R. J. A detailed investigation of circulating IgE levels in a normal population. Clin Allergy. 1975 Mar;5(1):13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish W. E. Short-term anaphylactic IgG antibodies in human sera. Lancet. 1970 Sep 19;2(7673):591–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirskanen R., Tiilikainen A., Hokkanen E. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens associated with myasthenia gravis. A preliminary report. Ann Clin Res. 1972 Oct;4(5):304–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymenidis Z., Ludwig H., Götz M. Letter: Cystic fibrosis and HL-A antigens. Lancet. 1973 Dec 22;2(7843):1452–1452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92856-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R., Smalley C. A., Brown G. A. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Allergy. 1976 May;6(3):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Stokes C. R., Turner M. W., Norman A. P., Taylor B. Predisposing factors and the development of reaginic allergy in infancy. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jul;6(4):305–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Smith A. K. Inhibition of reagin-mediated PCA reactions in baboons by the human IgG4 sub-class. Clin Allergy. 1973 Mar;3(1):37–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M. HL-A and disease associations--a survey. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:3–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B., Norman A. P., Orgel H. A., Stokes C. R., Turner M. W., Soothill J. F. Transient IgA deficiency and pathogenesis of infantile atopy. Lancet. 1973 Jul 21;2(7821):111–113. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Brostoff T. J., Wells R. S., Stokes C. R., Soothill J. F. HLA in eczema and hay fever. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):43–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallwork J. C., Brenchley P., McCarthy J., Allan J. D., Moss D., Ward A. M., Holzel A., Williams R. F., McFarlane H. Some aspects of immunity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):303–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. O., Norman A. P., Soothill J. F. Cystic fibrosis heterozygosity in the pathogenesis of allergy. Lancet. 1976 May 8;1(7967):990–991. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91862-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. O., Taylor B. W., Norman A. P., Soothill J. F. Association of cystic fibrosis with allergy. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Jul;51(7):507–511. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.7.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. P., Tai E., Batten J. C., Hutchcroft B. J., Pepys J. Cystic fibrosis--immunological reactions to A. fumigatus and common allergens. Clin Allergy. 1975 Mar;5(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B., Flensborg E. W., Jacobsen L., Jorgensen B. A., Lykkegaard E., Hoiby N. Immunochemical quantitation of 18 proteins in sera from patients with cystic fibrosis: concentrations correlated to class of fibroblast metachromasia, clinical and radiological lung symptoms. Dan Med Bull. 1976 Jun;23(3):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wide L., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Diagnosis of allergy by an in-vitro test for allergen antibodies. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1105–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


