Abstract
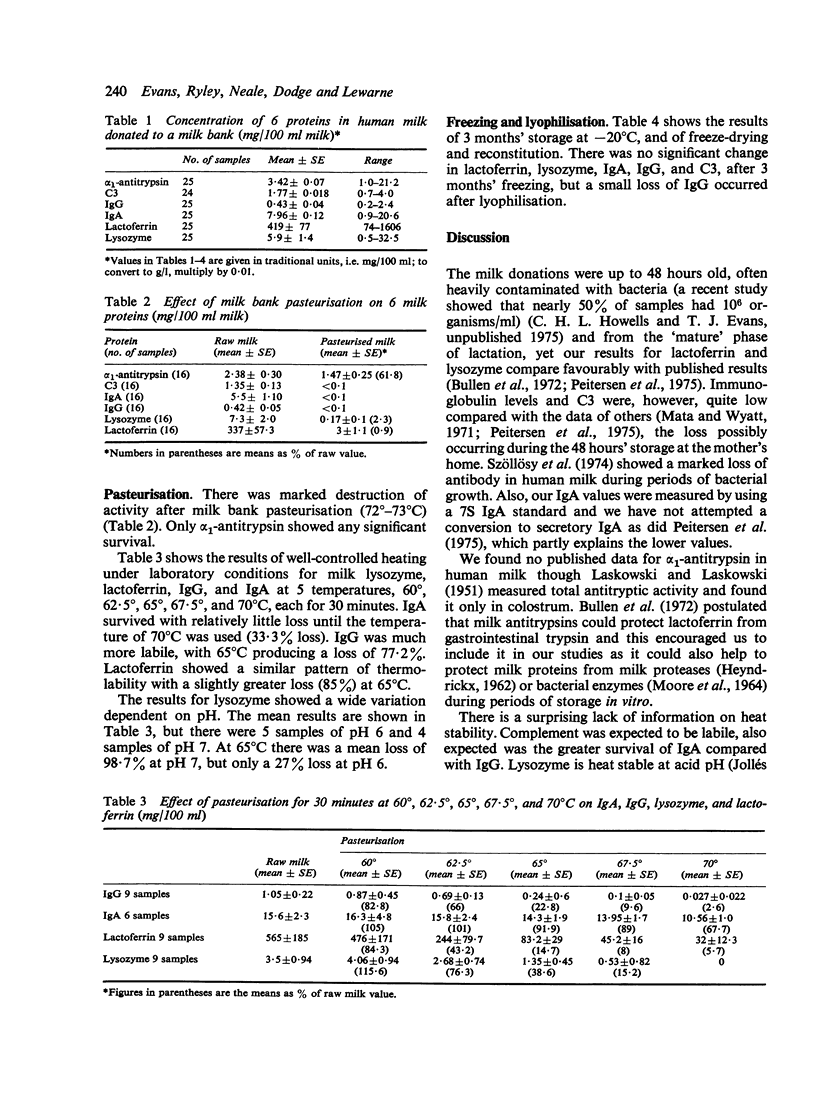
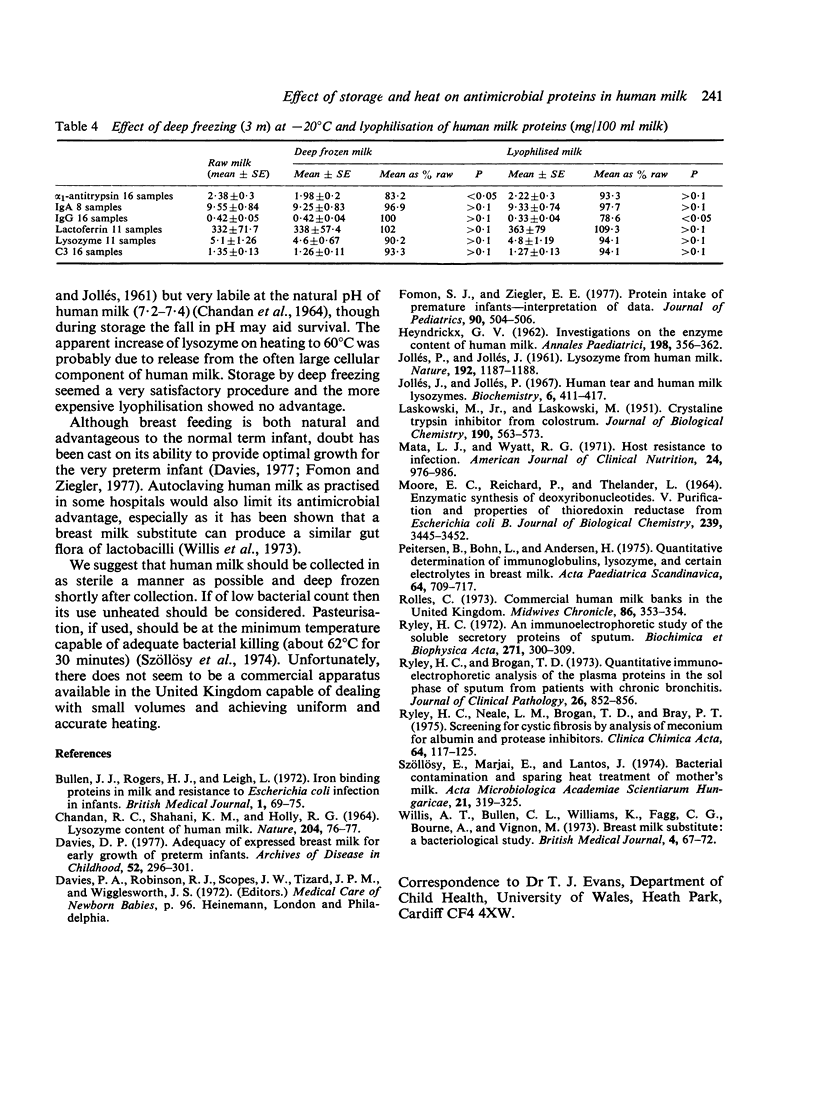
Human milk, after storage and pasteurisation at 73 degrees C for 30 minutes at a milk bank, was found to have little surviving IgA, IgG, lactoferrin, lysozyme, and C3 complement. Accurate pasteurisation at 62.5 degrees C produced a loss of 23.7% of the lysozyme, 56.8% of the lactoferrin 34% of the IgG, but no loss of IgA. Storage by deep freezing at -20 degrees C for 3 months produced no appreciabile loss of lactoferrin, lysozyme, IgG, IgA, or C3.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Leigh L. Iron-binding proteins in milk and resistance to Escherichia coli infection in infants. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):69–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANDAN R. C., SHAHANI K. M., HOLLY R. G. LYSOZYME CONTENT OF HUMAN MILK. Nature. 1964 Oct 3;204:76–77. doi: 10.1038/204076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. P. Adequacy of expressed breast milk for early growth of preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr;52(4):296–301. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.4.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomon S. J. Protein intake of premature infants: interpretation of data. J Pediatr. 1977 Mar;90(3):504–506. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80750-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYNDRICKX G. V. Investigations on the enzymes in human milk. Ann Paediatr. 1962;198:356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., Jr, LASKOWSKI M. Crystalline trypsin inhibitor from colostrum. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):563–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE E. C., REICHARD P., THELANDER L. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDES.V. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THIOREDOXIN REDUCTASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI B. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3445–3452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Wyatt R. G. The uniqueness of human milk. Host resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Aug;24(8):976–986. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.8.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitersen B., Bohn L., Andersen H. Quantitative determination of immunoglobulins, lysozyme, and certain electrolytes in breast milk during the entire period of lactation, during a 24-hour period, and in milk from the individual mammary gland. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Sep;64(5):709–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolles C. Commercial human mild banks in the United Kingdom. Midwives Chron. 1973 Nov;86(30):353–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryler H. C. An immunoelectrophoretic study of the soluble secretory proteins of sputum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 21;271(2):300–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley H. C., Brogan T. D. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of the plasma proteins in the sol phase of sputum from patients with chronic bronchitis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Nov;26(11):852–856. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.11.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley H. C., Neale L. M., Brogan T. D., Bray P. T. Screening for cystic fibrosis by analysis of meconium for albumin and protease inhibitors. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Oct 15;64(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szöllösy E., Marjai E., Lantos J. Bacterial contamination and sparing heat treatment of mother's milk. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1974;21(3-4):319–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. T., Bullen C. L., Williams K., Fagg C. G., Bourne A., Vignon M. Breast milk substitute: a bacteriological study. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 13;4(5884):67–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5884.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


