Abstract
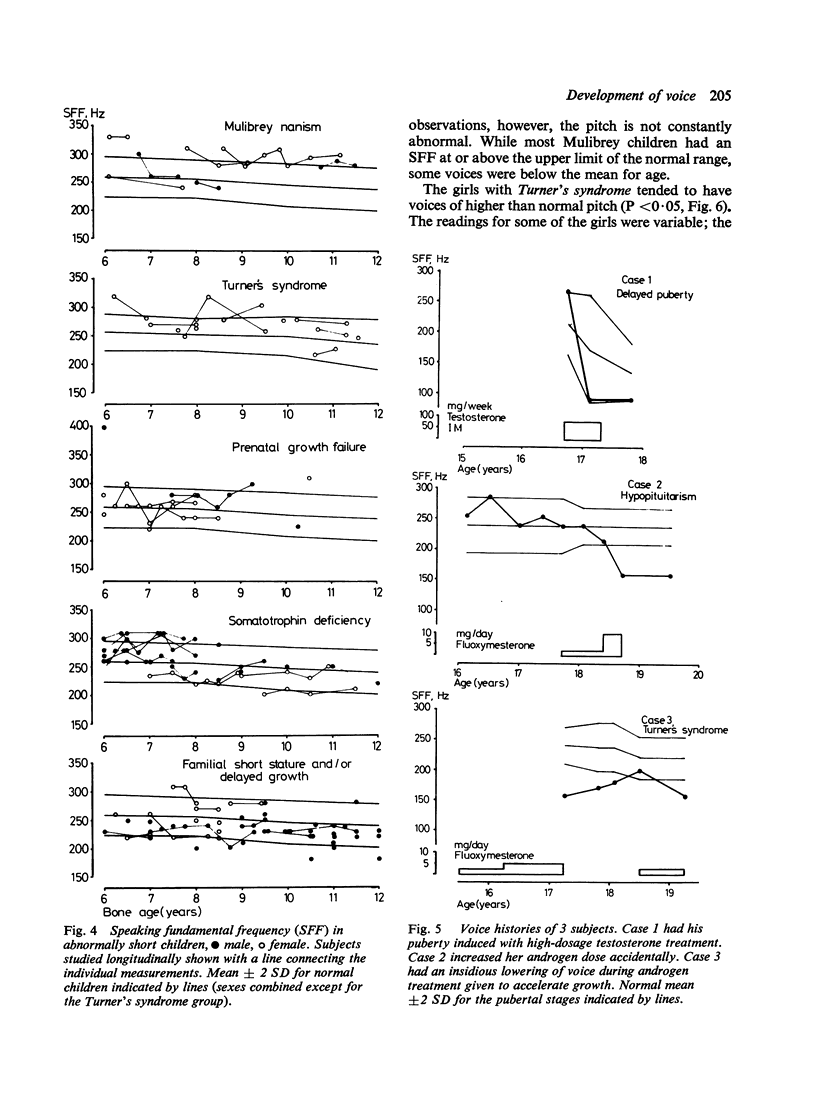
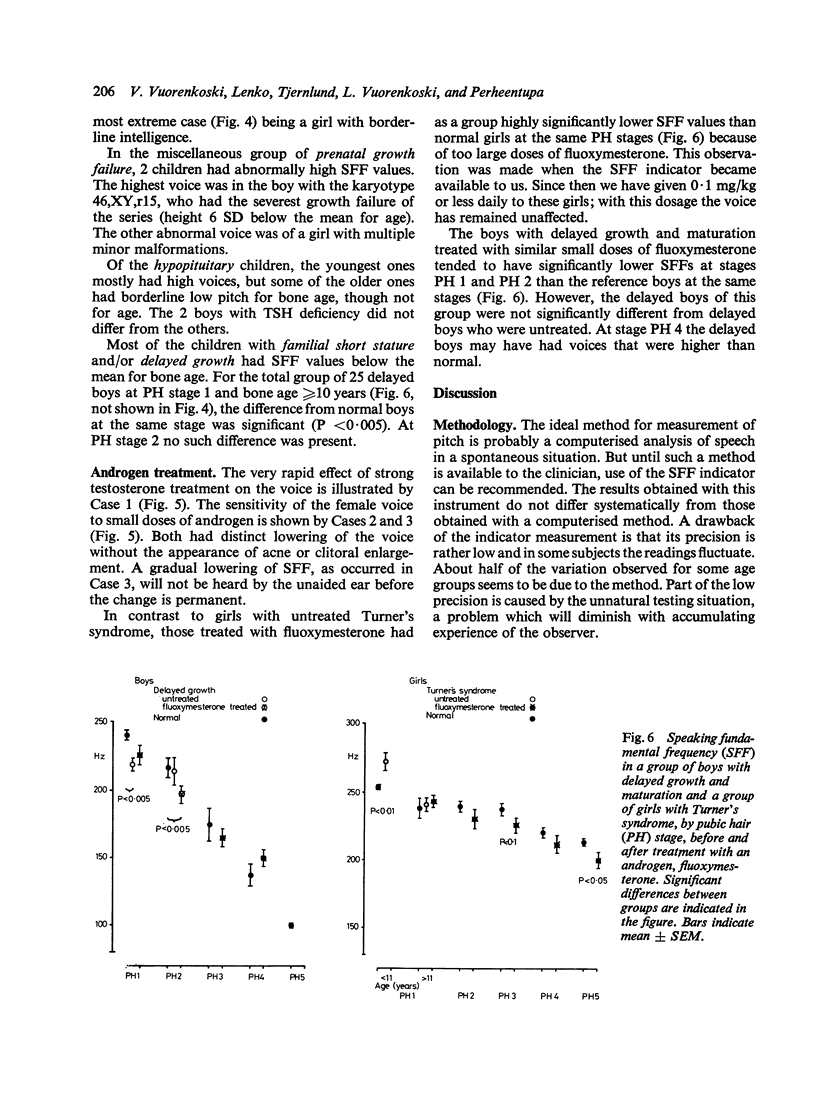
A simple treatment was shown to be suitable for clinical measurement of fundamental voice frequency. Basal frequency (SFF) and lowest frequency (LF) were determined in 374 normal subjects aged 6 years to adulthood. SFF fell between ages 8 and 10 years in boys (from 259 to 247 Hz), but not in girls (253 Hz). LF fell between ages 6 and 10 years in boys (from 234 to 203 Hz) and girls (from 230 to 218 Hz), and a sex difference appeared. In puberty, parallel to pubic hair (PH) development, a gradual fall of SFF and LF occurred in both boys (to 100 and 90 Hz, respectively) and girls (to 213 and 180 Hz). As a group, young hypopituitary children and girls with Turner's syndrome had a high SFF, and prepubertal boys with delayed maturation a low SFF. In some children with prenatal growth failure, SFF was abnormally high. The girls with Turner's syndrome exhibited a high, though individually variable, sensitivity of voice to androgen; their voices became lower before the appearance of any other masculinising effects. The instrument is useful for characterisation of growth failure syndromes and stages of puberty. It is particularly recommended for monitoring an undesirable effect on the voice during androgen treatment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen E. Skeletal maturation of Danish school children in relation to height, sexual development, and social conditions. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1968;(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER H. DIE BEEINFLUSSUNG DER WEIBLICHEN STIMME DURCH ANDROGENE HORMONE. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1963;15:264–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer H. Die Beziehungen der Phoniatrie zur Endokrinologie. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1968;20(6):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrie-Muller C. Etude du fondamental de la voix parlée sur des groupes d'enfants de 3 ans à 5 ans et demi. J Fr Otorhinolaryngol Audiophonol Chir Maxillofac. 1971 Feb;20(2):451–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollien H., Paul P. A second evaluation of the speaking fundamental frequency characteristics of post-adolescent girls. Lang Speech. 1969 Apr-Jun;12(2):119–124. doi: 10.1177/002383096901200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIDR J., ZBORIL M., SEVCIK K. DIE PUBERTALEN VERAENDERUNGEN DER STIMME BEI JUNGEN IM VERLAUF VON 5 JAHREN. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1965;17:1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perheentupa J., Autio S., Leisti S., Raitta C. Mulibrey-nanism: dwarfism with muscle, liver, brain and eye involvement. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1970;206(Suppl):74+–74+. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1970.tb14591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perheentupa J., Autio S., Leisti S., Raitta C., Tuuteri L. Mulibrey nanism, an autosomal recessive syndrome with pericardial constriction. Lancet. 1973 Aug 18;2(7825):351–355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perheentupa J., Autio S., Leisti S., Raitta C., Tuuteri L. Mulibrey nanism: review of 23 cases of a new autosomal recessive syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):3–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfalz R. Veränderungen an Hals, Nase und Ohr durch endokrine Erkrankungen. HNO. 1967 Mar;15(3):88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruszewicz A., Obrebowski A., Jassem W., Kubzdela H. Ausgeprägte akustische Merkmale virilisierter Mädchenstimmen. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1973;25(5):331–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz-Coulon H. J., Arndt H. J. Tonhöhenschreibung in der phoniatrischen Praxis. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1972;24(4):241–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN OORDTH, DROST H. A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE FREQUENCY RANGE OF THE VOICE IN CHILDREN. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1963;15:289–298. doi: 10.1159/000262974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorenkoski V., Lind J., Partanen T. J., Lejeune J., Lafourcade J., Wasz-Höckert O. Spectrographic analysis of cries from children with maladie du cri du chat. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1966;12(3):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg B., Zlatin M. Speaking fundamental frequency characteristics of five- and six-year-old children with mongolism. J Speech Hear Res. 1970 Jun;13(2):418–425. doi: 10.1044/jshr.1302.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]