Abstract
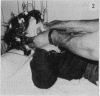
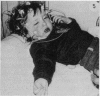
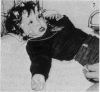
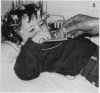
From clinical history 58 children were diagnosed as having reflex anoxic seizures secondary to provoked cardioinhibition (also known as white breath-holding attacks). Before referral, these seizures were commonly misdiagnosed as epileptic either because the provocation was ignored, not recognised, or was a febrile illness, or because there was no crying, no obvious breath-holding, little cyanosis, and often no pallor to suggest syncope and cerebral ischaemia. The duration of cardiac asystole after ocular compression was measured in these children and in 60 additional children with other paroxysmal disorders. In 45 (78%) of the 58 with reflex anoxic seizures asystole was 2 seconds or over, and in 32 (55%) it was 4 seconds or greater, an abnormal response. Review of the literature supports the concept that these seizures result from vagal-mediated reflex cardiac arrest which can if necessary be prevented by atropine. The simple name 'vagal attack' is proposed. Ocular compression under EEG and ECG control supports the clinical diagnosis if asystole and/or an anoxic seizure is induced; the procedure described is safe and should be routine in seizure or syncope evaluation, when a meticulous history still leaves room for doubt.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apivor D., Ravi P. K. Ketamine and the oculocardiac reflex. Dysrhythmia in pediatric strabismus surgery: the role of intravenous atropine. Anaesthesia. 1976 Jan-Feb;31(1):18–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1976.tb11740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster F. M. The classification and conditioning treatment of the reflex epilepsies. Int J Neurol. 1972;9(1):73–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis M. L., Lund M. Stress convulsions. Arch Neurol. 1974 Sep;31(3):155–159. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490390037002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H., FISCHER-WILLIAMS M. Electro-encephalographic study of syncope; its differentiation from epilepsy. Lancet. 1957 Nov 23;273(7004):1018–1025. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H., GASTAUT Y. Electroencephalographic and clinical study of anoxic convulsions in children; their location within the group of infantile convulsions and their differenciation from epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Nov;10(4):607–620. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H., GASTAUT Y. Syncopes et convulsions; à propos de la nature syncopale de certains spasmes du sanglot et de certaines convulsions essentielles hyperthermiques ou à froid. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1957 Feb;96(2):158–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUK E. W., KIDD L., PRICHARD J. S. Mechanism of seizures associated with breath-holding spells. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jun 27;268:1436–1441. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196306272682603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastaut H., Tassinari C. A. Triggering mechanisms in epilepsy. The electroclinical point of view. Epilepsia. 1966 Jun;7(2):85–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.1966.tb06262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Ariagno R., Souquet M., Dement W. C. Abnormal polygraphic findings in near-miss sudden infant death. Lancet. 1976 Jun 19;1(7973):1326–1327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92656-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLOWACH J., THURSTON D. L. Breath-holding spells and anemia. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jan 3;268:21–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196301032680105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havland T., Frithz G. A hazard of apple-eating. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 11;2(6036):643–643. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6036.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton B. R., Southall E., Rutter N., Anderson R. H., Shinebourne E. A., Southall D. P. Cardiac conduction disorders in six infants with "near-miss" sudden infant deaths. Br Med J. 1977 Sep 3;2(6087):600–601. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6087.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keipert J. A. A new form of sensory precipitation epilepsy: epilepsy precipitated by undressing. Med J Aust. 1972 Nov 11;2(20):1124–1126. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb103758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN M. E., EHRENFELD I. Ventricular fibrillation following eyeball pressure in a case of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Am Heart J. 1952 May;43(5):791–795. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(52)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso C. T., Lerman P. Breathholding spells (cyanotic and pallid infantile syncope). Pediatrics. 1967 Apr;39(4):563–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALLINSON F. B., COOMBES S. K. A hazard of anaesthesia in ophthalmic surgery. Lancet. 1960 Mar 12;1(7124):574–575. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92780-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOFENSON H. C., WEYMULLER C. A., GREENSHER J. EPILEPSY DUE TO WATER IMMERSION: AN UNUSUAL CASE OF REFLEX SENSORY EPILEPSY. JAMA. 1965 Feb 15;191:600–601. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080070084019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J., Papp C., Evans W. THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM OF THE STOKES-ADAMS ATTACK. Br Heart J. 1941 Jul;3(3):171–199. doi: 10.1136/hrt.3.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. M. Epilepsy and drowning in childhood. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 11;1(6075):1510–1511. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6075.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford D. J., Izukawa T., Rowe R. D. Evaluation of children with ventricular arrhythmias. Arch Dis Child. 1977 May;52(5):345–353. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson P. Shuffling, hitching, scooting or sliding: some observations in 30 otherwise normal children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1970 Oct;12(5):608–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1970.tb01970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPEY-SCHAFER E. P. Syncope. Br Med J. 1956 Mar 3;1(4965):506–509. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4965.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORENSON E. J., GILMORE J. E. Cardiac arrest during strabismus surgery; a preliminary report. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 May;41(5):748–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(56)91767-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz P. J. Cardiac sympathetic innervation and the sudden infant death syndrome. A possible pathogenetic link. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90425-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott O., Macartney F. J., Deverall P. B. Sick sinus syndrome in children. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Feb;51(2):100–105. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]