Abstract
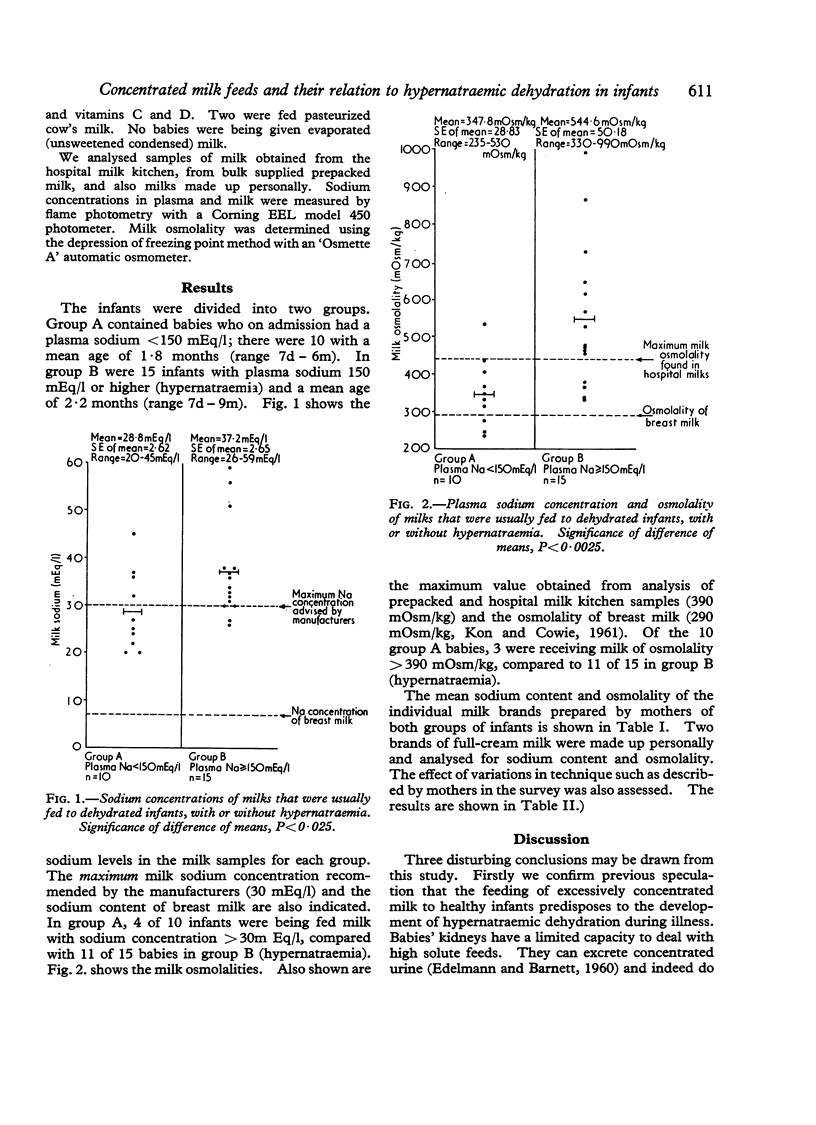
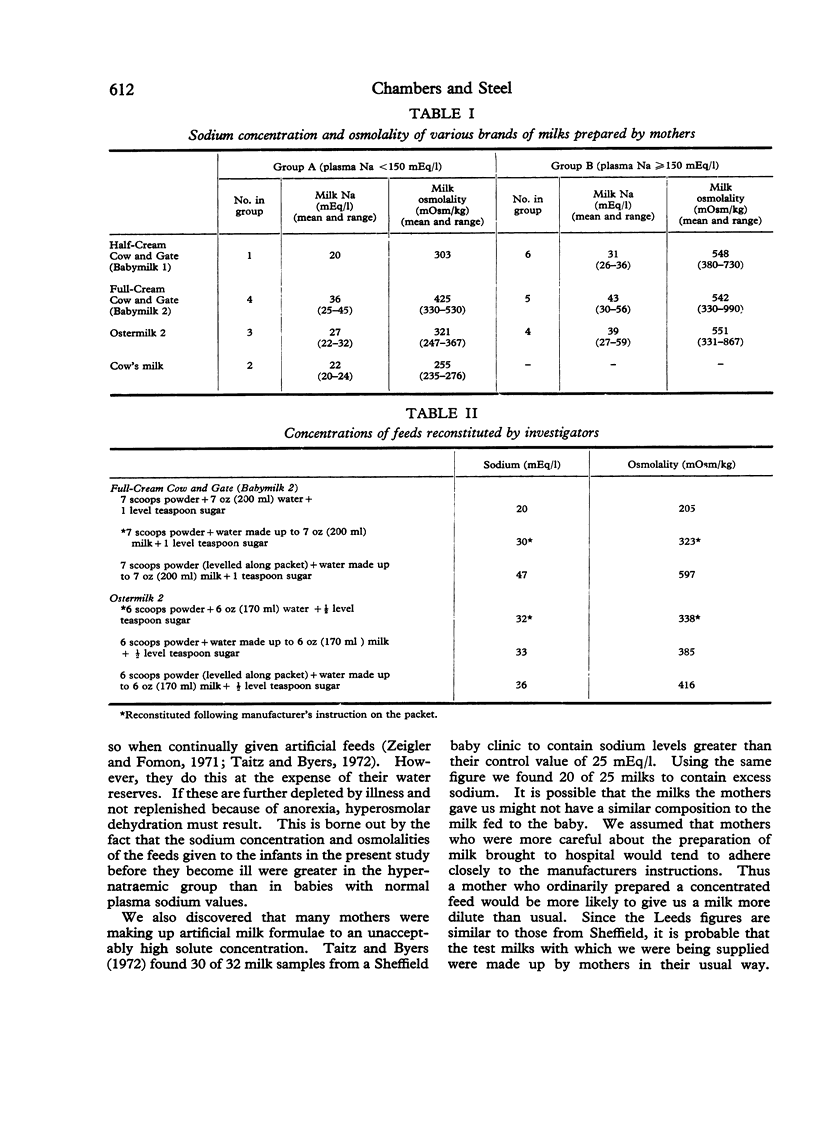
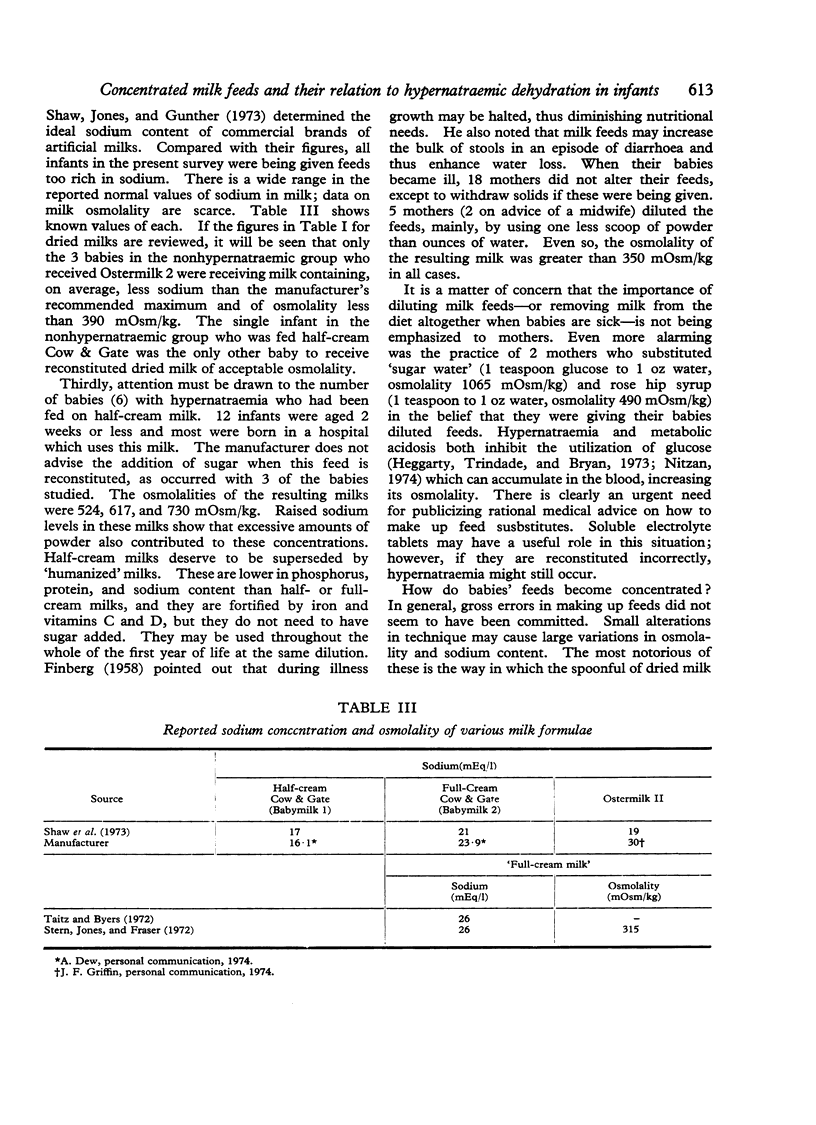
The composition of milks usually fed to 25 infants admitted to hospital with a dehydrating illness was studied. 15 hypernatraemic babies had been given feeds of greater sodium concentration and osmolality than those fed to the 10 infants whose plasma sodium was below 150 mEq/l. Hypernatraemic dehydration may be followed by death or permanent brain damage. Most infants in the survey were receiving milk with a sodium content greater than that advised by the manufacturers. Suggestions are made for reducing the sources of error commonly made in the reconstitution of dried milk formulae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLLE E., AYOUB E., RAILE R. Hypertonic dehydration (hypernatremia): the role of feedings high in solutes. Pediatrics. 1958 Jul;22(1 Pt 1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. P. Plasma osmolality and feeding practices of healthy infants in first three months of life. Br Med J. 1973 May 12;2(5862):340–342. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5862.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMANN C. M., Jr, BARNETT H. L. Role of the kidney in water metabolism in young infants: physiologic and clinical considerations. J Pediatr. 1960 Feb;56:154–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery J. L., Swift P. G., Worthy E. Hypernatraemia and uraemia in unexpected death in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Sep;49(9):686–692. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.9.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L., HARRISON H. E. Hypernatremia in infants; an evaluation of the clinical and biochemical findings accompanying this state. Pediatrics. 1955 Jul;16(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L. The possible role of the physician in causing hypernatremia in infants dehydrated from diarrhea. Pediatrics. 1958 Jul;22(1 Pt 1):2–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggarty H., Trindade P., Bryan E. M. Hyperglycaemia in hyperosmolar dehydration. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Sep;48(9):740–741. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.9.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay D., Watson M. Hypernatraemia in infants as a cause of brain damage. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Oct;42(225):485–491. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.225.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris-Jones P. H., Houston I. B., Evans R. C. Prognosis of the neurological complications of acute hypernatraemia. Lancet. 1967 Dec 30;2(7531):1385–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)93022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitzan M. Letter: Hyperglycaemia and uraemia in hyperosmolar dehydration. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jun;49(6):500–501. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.6.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates R. K. Infant-feeding practices. Br Med J. 1973 Jun 30;2(5869):762–764. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5869.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla A., Forsyth H. A., Anderson C. M., Marwah S. M. Infantile overnutrition in the first year of life: a field study in Dudley, Worcestershire. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 2;4(5839):507–515. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5839.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern G. M., Jones R. B., Fraser A. C. Hyperosmolar dehydration in infancy due to faulty feeding. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Jun;47(253):468–469. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.253.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taitz L. S., Byers H. D. High calorie-osmolar feeding and hypertonic dehydration. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Apr;47(252):257–260. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.252.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. W., Noble T. C., Gray G., Spence O. Inaccuracies in measurement of dried milk powders. Br Med J. 1973 Apr 7;2(5857):15–17. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5857.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. E., Fomon S. J. Fluid intake, renal solute load, and water balance in infancy. J Pediatr. 1971 Apr;78(4):561–568. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


