Abstract
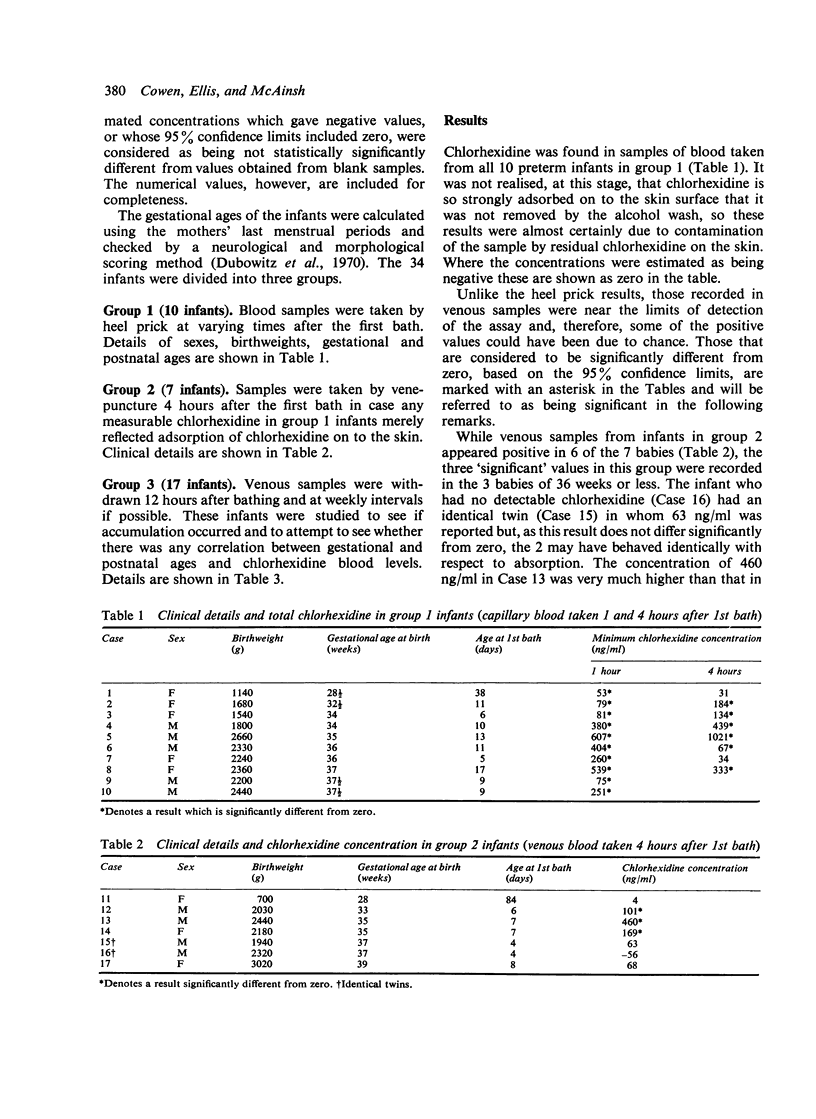
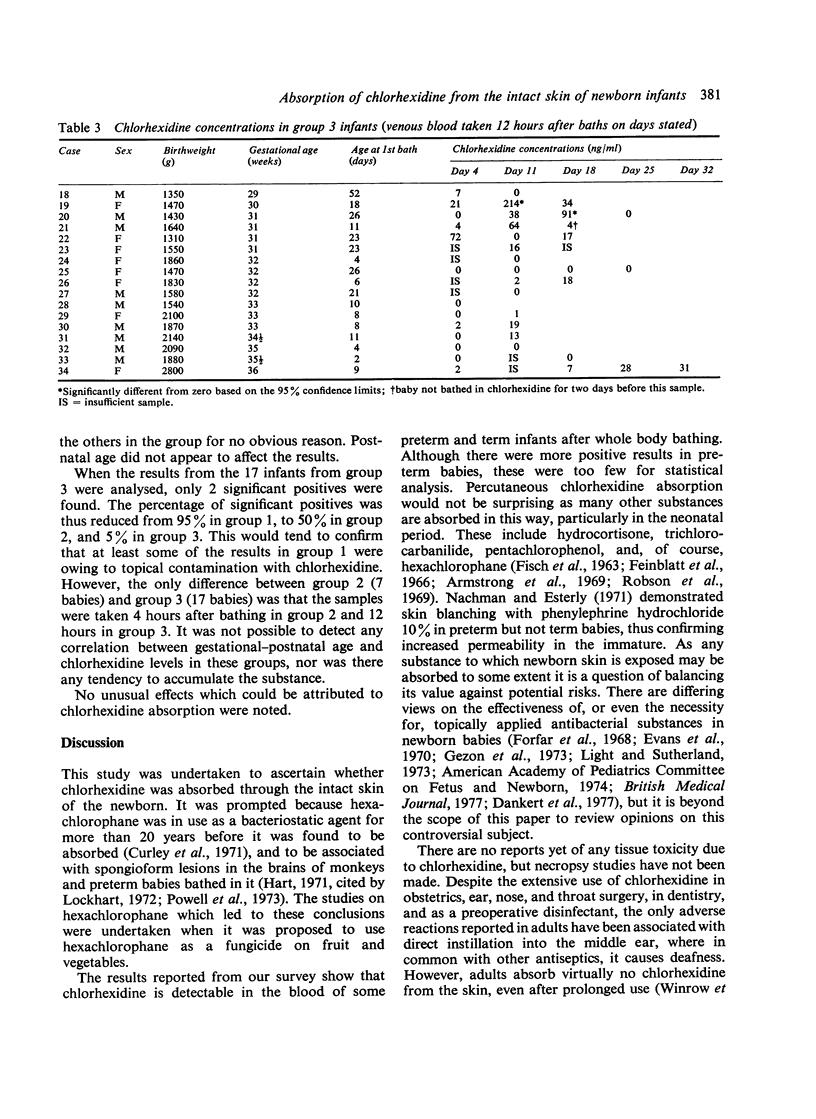
34 newborn infants who had been bathed in a standard manner with Hibiscrub were studied to find out whether it was absorbed percutaneously. Low levels of chlorhexidine were found in the blood of all 10 babies sampled by heel prick, and 5 of 24 from whom venous blood was taken. The detection of chlorhexidine varied greatly with the method and timing of sampling, and no correlation was found between gestational or postnatal age and chlorhexidine levels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. W., Eichner E. R., Klein D. E., Barthel W. F., Bennett J. V., Jonsson V., Bruce H., Loveless L. E. Pentachlorophenol poisoning in a nursery for newborn infants. II. Epidemiologic and toxicologic studies. J Pediatr. 1969 Aug;75(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen F., Bleeg H. S., Jensen J. E. The effect of chlorhexidine on some biochemical parameters of rat liver mitochondria. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975 Jan;36(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb00766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen F., Jensen J. E. The effect of chlorhexidine on some biochemical parameters of rat liver microsomes. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 Jul;35(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curley A., Kimbrough R. D., Hawk R. E., Nathenson G., Finberg L. Dermal absorption of hexochlorophane in infants. Lancet. 1971 Aug 7;2(7719):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. E., Akpata S. O., Baki A. Factors influencing the establishment of the neonatal bacterial flora. II. The role of environmental factors. Arch Environ Health. 1970 Nov;21(5):643–648. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1970.10667309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHARSON C. D., PENNY S. F., EDWARDS H. E., BARR E. The control of staphylococcal skin infections in the nursery. Can Med Assoc J. 1952 Sep;67(3):247–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCH R. O., BERGLUND E. B., BRIDGE A. G., FINLEY P. R., QUIE P. G., RAILE R. METHEMOGLOBINEMIA IN A HOSPITAL NURSERY: A SEARCH FOR CAUSATIVE FACTORS. JAMA. 1963 Sep 7;185:760–763. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03060100040014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinblatt B. I., Aceto T., Jr, Beckhorn G., Bruck E. Percutaneous absorption of hydrocortisone in children. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Sep;112(3):218–224. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090120086008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forfar J. O., Gould J. C., Maccabe A. F. Effect of hexachlorophane on incidence of staphylococcal and gram-negative infection in the newborn. Lancet. 1968 Jul 27;2(7561):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92618-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gezon H. M., Thompson D. J., Rogers K. D., Hatch T. F., Rycheck R. R., Yee R. B. Control of staphylococcal infections and disease in the newborn through the use of hexachlorophene bathing. Pediatrics. 1973 Feb;51(2):331–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. DISINFECTION OF HANDS: REMOVAL OF TRANSIENT ORGANISMS. Br Med J. 1964 Jul 25;2(5403):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5403.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light I. J., Sutherland J. M. What is the evidence that hexachlorophene is not effective? Pediatrics. 1973 Feb;51(2):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart J. D. How toxic is hexachlorophene? Pediatrics. 1972 Aug;50(2):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Ayliffe G. A. Preoperative disinfection of surgeons' hands: use of alcoholic solutions and effects of gloves on skin flora. Br Med J. 1974 Nov 16;4(5941):369–372. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5941.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntoni S. Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by biguanides: implications for metabolic physiopathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1974;12(0):311–377. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024912-1.50014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Esterly N. B. Increased skin permeability in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1971 Oct;79(4):628–632. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell H., Swarner O., Gluck L., Lampert P. Hexachlorophene myelinopathy in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):976–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson A. M., Kissane J. M., Elvick N. H., Pundavela L. Pentachlorophenol poisoning in a nursery for newborn infants. I. Clinical features and treatment. J Pediatr. 1969 Aug;75(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman R. M., Leech R. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Neurotoxicity of hexachlorophene in humans. II. A clinicopathological study of 46 premature infants. Arch Neurol. 1975 May;32(5):320–325. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490470064009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman R. M., Leech R. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Neurotoxicity of hexachlorophene in the human: I. A clinicopathologic study of 248 children. Pediatrics. 1974 Dec;54(6):689–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrala E. E., Hillman L. S., Hillman R. E., Dodson W. E. Clinical pharmacology of hexachlorophene in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1977 Sep;91(3):481–486. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Snyder M. J., Gutberlet R. L. Group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal colonization. Acquisition, persistence, and effect of umbilical cord treatment with triple dye. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Feb;131(2):178–180. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120150060011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. P., Oliver T. K., Jr Nursery routines and staphylococcal colonization of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1969 Nov;44(5):640–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


