Abstract
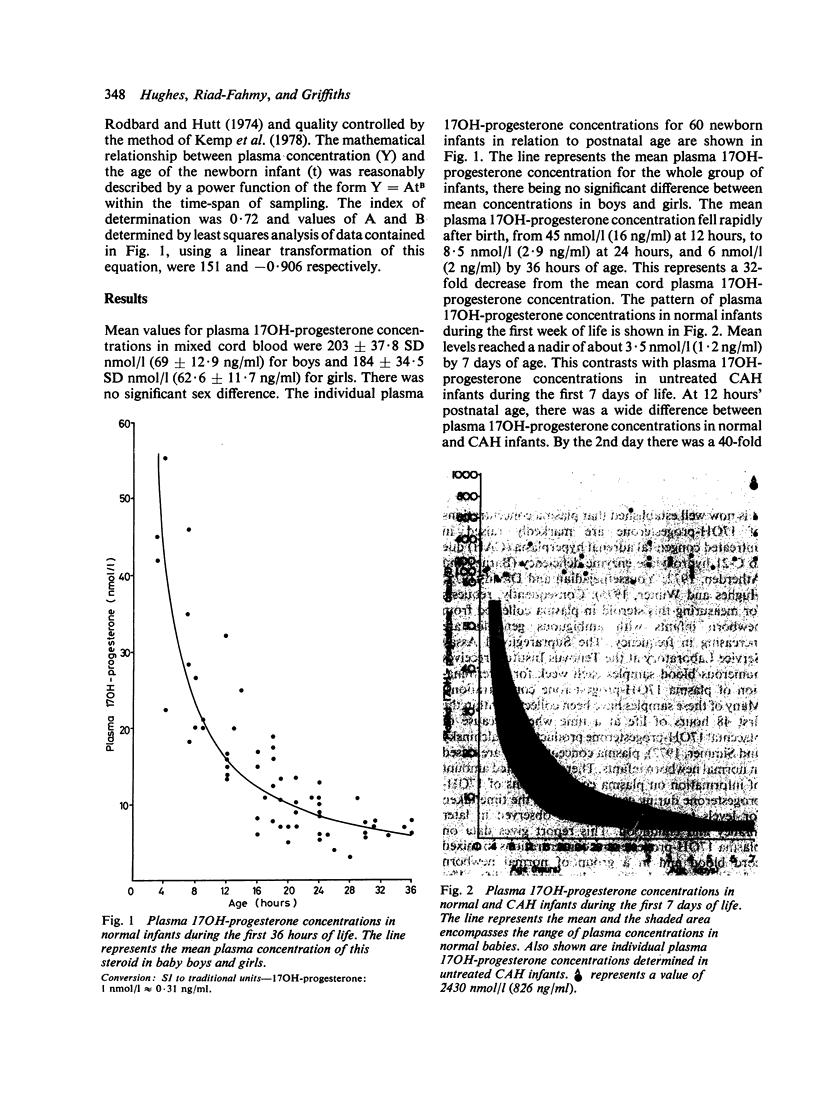
Plasma concentrations of 17OH-progesterone were determined in 60 normal newborn infants aged between 3 and 36 hours. Mean levels decreased rapidly during this time after removal of the placental contribution of this steroid. A further 70 normal infants, studied between ages 2 and 7 days, showed a mean plasma 17OH-progesterone concentration of 3.5 nmol/1 (1.2 ng/ml). By comparison, plasma concentrations in untreated infants with congenital adrenal hyperplasia were markedly raised. At 36 hours of age, there was an obvious difference between plasma levels of this steroid in normal and affected infants. Determination of plasma 17OH-progesterone concentrations are valuable in the evaluation of disorders of sexual differentiation and electrolyte balance in newborn infants, provided due care is given to the timing of sample collections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes N. D., Atherden S. M. Diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia by measurement of plasma 17-hydroxyprogesterone. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Feb;47(251):62–65. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.251.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forest M. G., Cathiard A. M. Ontogenic study of plasma 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone in the human. I. Postnatal period: evidence for a transient ovarian activity in infancy. Pediatr Res. 1978 Jan;12(1):6–11. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197801000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I. A., Winter J. S. Early diagnosis of salt-losing congenital adrenal hyperplasia in a newborn boy. Can Med Assoc J. 1977 Aug 20;117(4):363–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I. A., Winter J. S. The application of a serum 17OH-progesterone radioimmunoassay to the diagnosis and management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1976 May;88(5):766–773. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp K. W., Nix A. B., Wilson D. W., Griffiths K. Internal quality control of radioimmunoassays. J Endocrinol. 1978 Feb;76(2):203–210. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0760203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippe B. M., LaFranchi S. H., Lavin N., Parlow A., Coyotupa J., Kaplan S. A. Serum 17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone, progesterone, estradiol, and testosterone in the diagnosis and management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1974 Dec;85(6):782–787. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippell W. G., Becker H., Versmold H. T., Bidlingmaier F., Knorr D. Longitudinal studies of plasma aldosterone, corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone, progesterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, cortisol, and cortisone determined simultaneously in mother and child at birth and during the early neonatal period. I. Spontaneous delivery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Jun;46(6):971–985. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-6-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulchinsky D., Simmer H. H. Sources of plasma 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone in human pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Dec;35(6):799–808. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-6-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J. S., Hughes I. A., Reyes F. I., Faiman C. Pituitary-gonadal relations in infancy: 2. Patterns of serum gonadal steroid concentrations in man from birth to two years of age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Apr;42(4):679–686. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-4-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssefnejadian E., David R. Early diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia by measurement of 17-hydroxyprogesterone. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1975 Jul;4(4):451–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1975.tb01553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


