Abstract
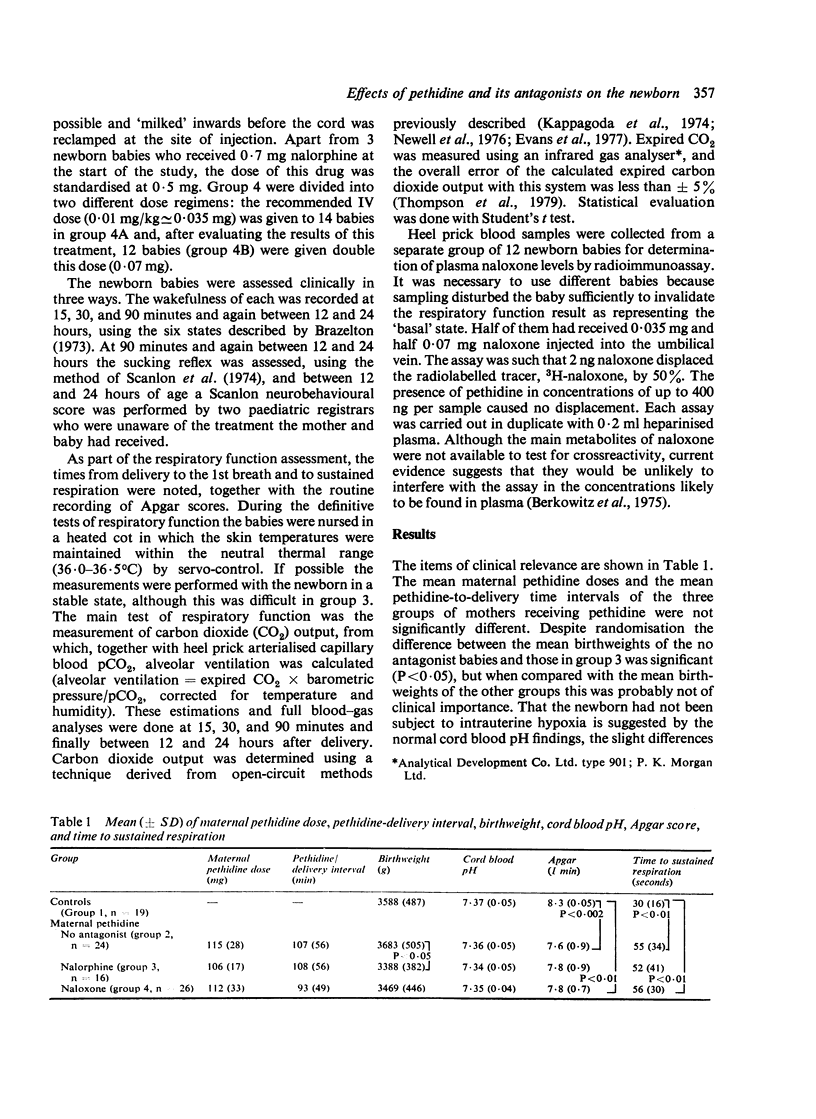
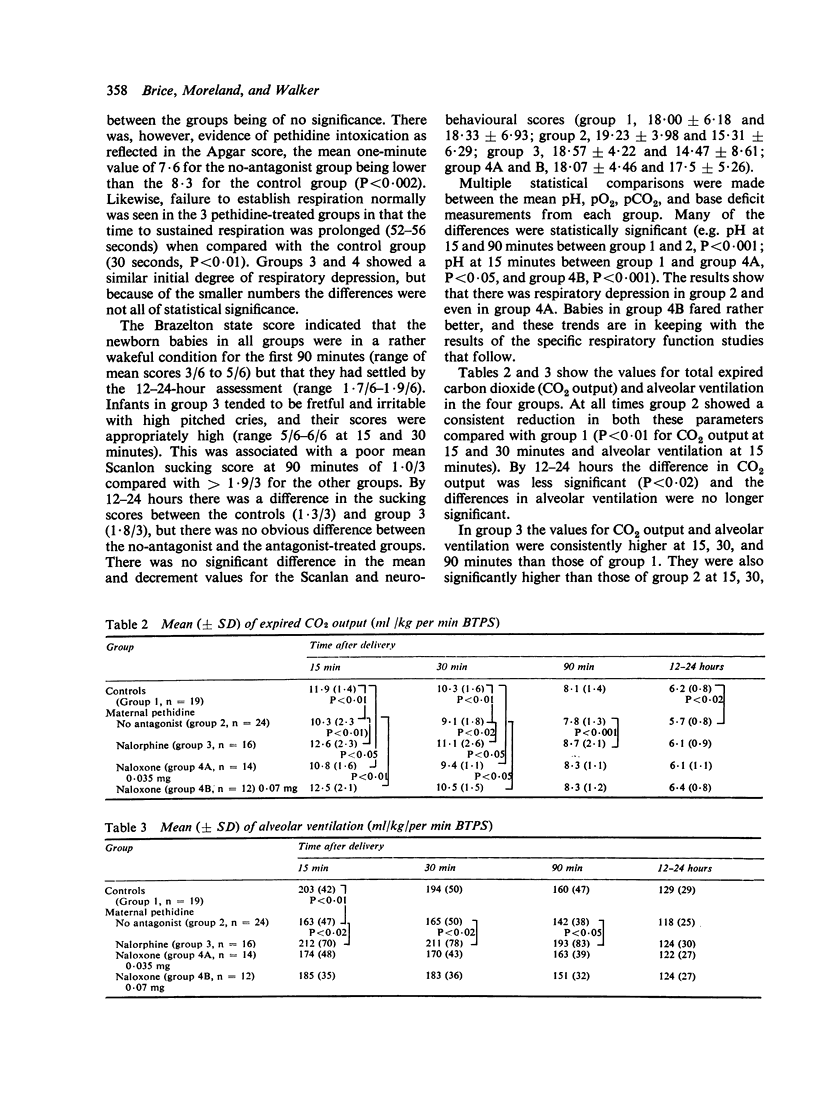
Nalorphine and naloxone were compared as to their effectiveness as pethidine antagonists. 85 infants were divided into a control group containing 19 newborn babies whose mothers did not receive pethidine and the babies received no antagonist, and three groups in which the mothers all received pethidine and the babies had either no antagonist (24), nalorphine IV (16), or naloxone IV (26). All the babies were assessed by measuring their neurobehavioural states and respiratory functions. A further 12 newborn babies had naloxone plasma levels measured by radioimmunoassay. Although standard doses of nalorphine effectively antagonised the depressive effect on respiration induced by pethidine, there was a pronounced and undesirable excitatory agonist action. Naloxone was not observed to have any agonist activity, but the recommended IV dose (0.01 mg/kg) had only a slight and delayed antagonist action as measured by respiratory function tests. A more rapid and improved antagonism was noted after this dose was doubled (0.02 mg/kg). The plasma elimination-phase half-life of naloxone after intravenous cord injection was about 3 hours.20
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz B. A., Ngai S. H., Hempstead J., Spector S. Disposition of naloxone: use of a new radioimmunoassay. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Dec;195(3):499–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackbill Y., Kane J., Manniello R. L., Abramson D. Obstetric meperidine usage and assessment of neonatal status. Anesthesiology. 1974 Feb;40(2):116–120. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197402000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramwell G. J., Bradley P. B. Actions and interactions of narcotic agonists and antagonists on brain stem neurones. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. V., Stephen G. W., Aggett P. J. Elimination of pethidine and bupivacaine in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Aug;52(8):638–641. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.8.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. M., Hogg M. I., Rosen M. Measurement of carbon dioxide output, alveolar carbon dioxide concentration and alveolar ventilation in the neonate. Br J Anaesth. 1977 May;49(5):453–456. doi: 10.1093/bja/49.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. M., Hogg M. I., Rosen M. Reversal of narcotic depression in the neonate by nalozone. Br Med J. 1976 Nov 6;2(6044):1098–1100. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6044.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt T., Bancalari E., Cohen H., Rocha L. F. Use of nalotone to to reverse narcotic respiratory depression in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1977 Jun;90(6):1009–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappagoda C. T., Stoker J. B., Linden R. J. A method for the continuous measurement of oxygen comsumption. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Oct;37(4):604–607. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.4.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON N. M., PROD'HOM L. S., CHERRY R. B., LIPSITZ P. J., SMITH C. A. Pulmonary function in the newborn infant. II. Perfusion--estimation by analysis of the arterial-alveolar carbon dioxide difference. Pediatrics. 1962 Dec;30:975–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell J. P., Kappagoda C. T., Linden R. J. Method for continuous measurement of carbon dioxide output. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Nov;41(5 Pt 1):810–813. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.5.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai S. H., Berkowitz B. A., Yang J. C., Hempstead J., Spector S. Pharmacokinetics of naloxone in rats and in man: basis for its potency and short duration of action. Anesthesiology. 1976 May;44(5):398–401. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197605000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon J. W., Brown W. U., Jr, Weiss J. B., Alper M. H. Neurobehavioral responses of newborn infants after maternal epidural anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1974 Feb;40(2):121–128. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197402000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener P. C., Hogg M. I., Rosen M. Effects of naloxone on pethidine-induced neonatal depression. Part I--Intravenous naloxone. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 23;2(6081):228–229. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6081.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


