Abstract
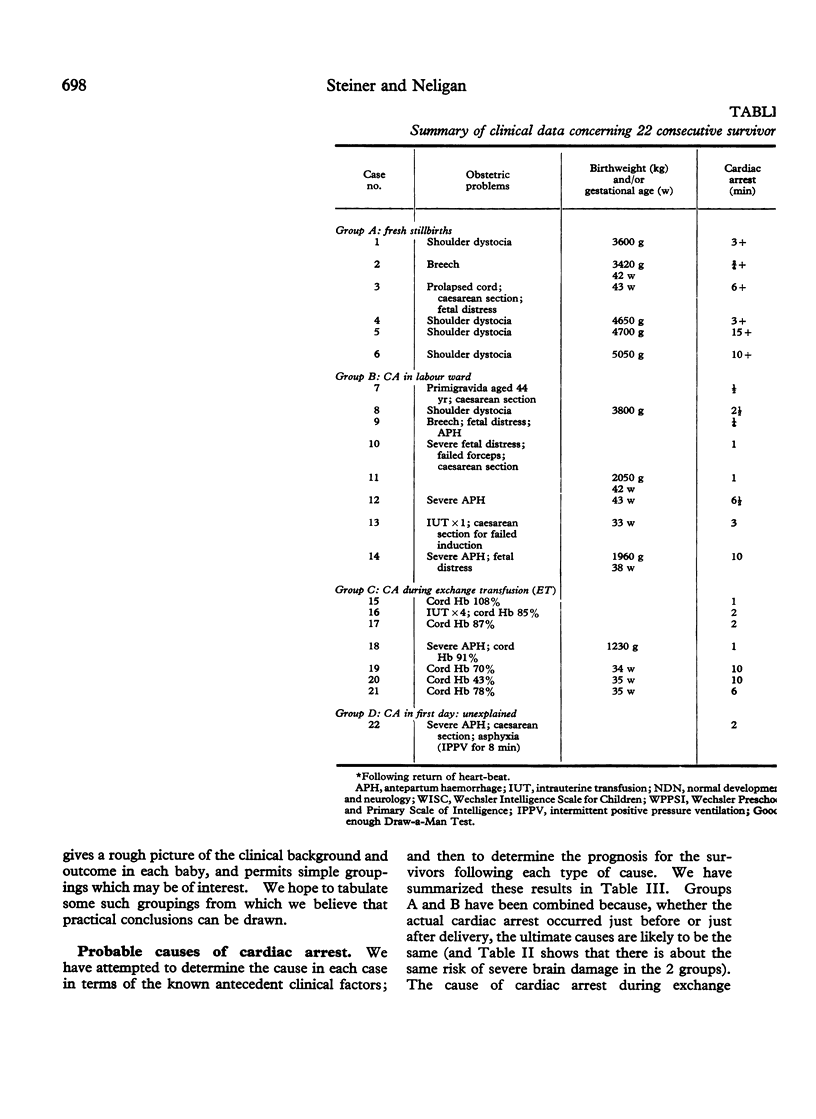
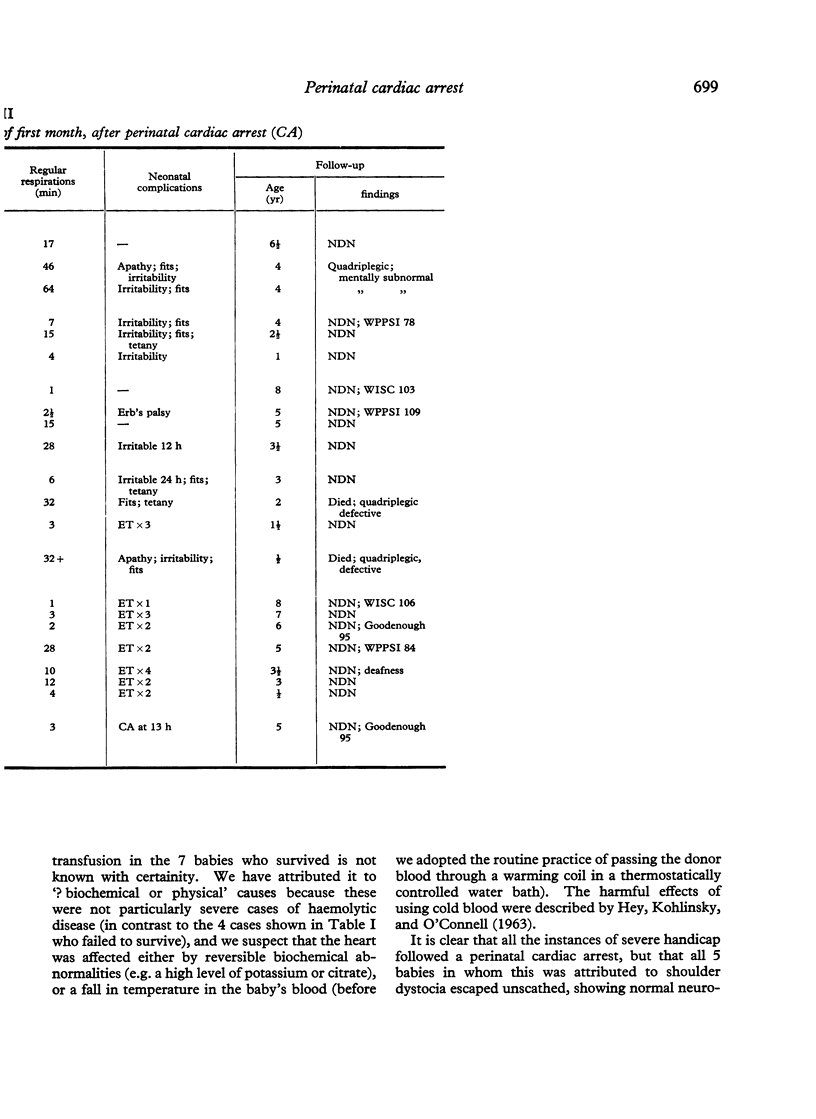
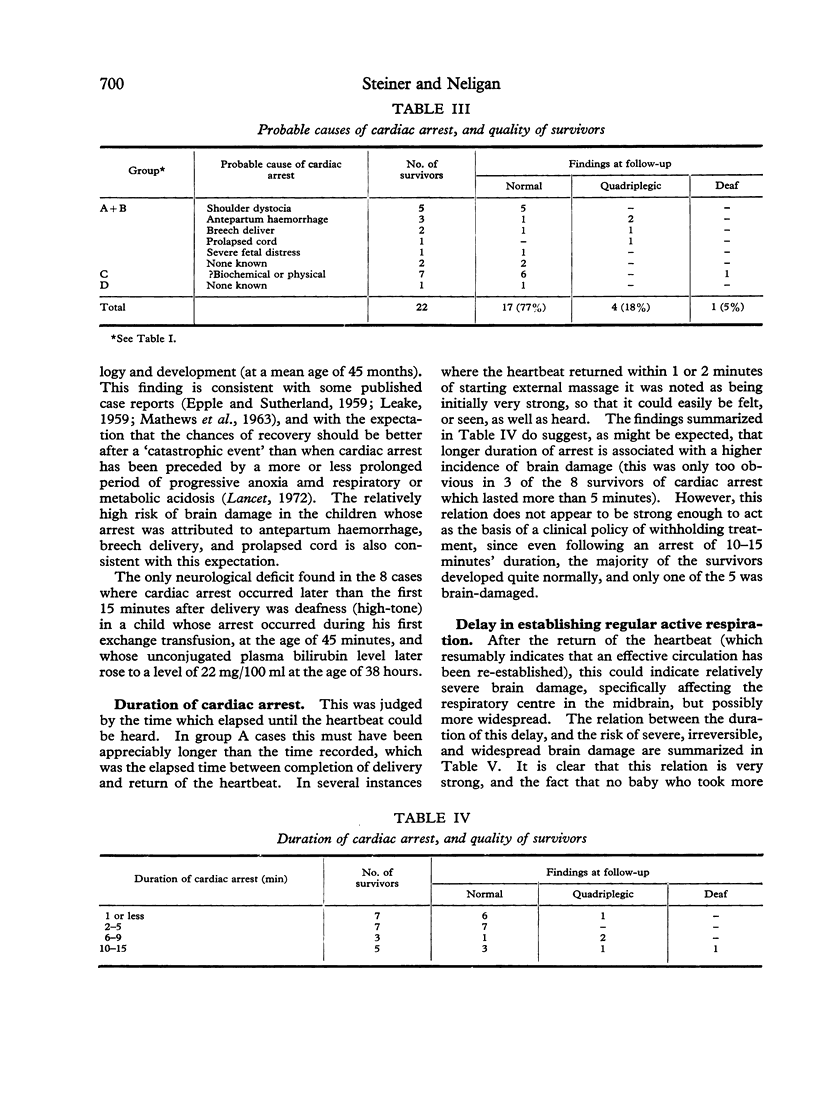
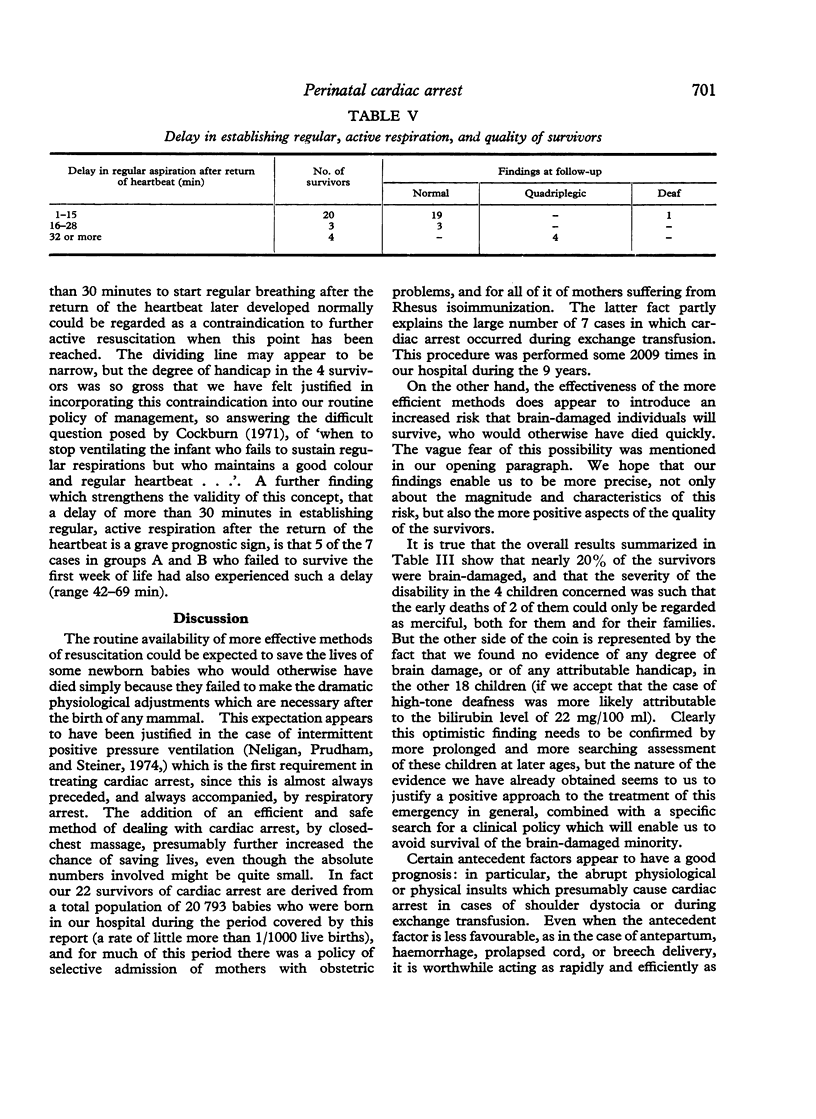
Steiner, H., and Neligan, G. (1975). Archives of Disease in Childhood, 50, 696. Perinatal cardiac arrest: quality of the survivors. Twenty-two consecutive survivors of perinatal cardiac arrest have been followed to a mean age of 4 1/4 years, using methods of neurological and developmental assessment appropriate to their ages. 4 showed evidence of gross, diffuse brain-damage (2 of these died before the age of 3 years). These were the only 4 survivors of the first month of life who took more than 30 minutes to establish regular, active respiration after their heartbeat had been restored. The arrest in these cases had occurred during or within 15 minutes of delivery, and followed antepartum haemorrhage, breech delivery, or prolapsed cord. The remaining 18 were free of any evidence of brain damage. In the majority of these the arrest had occurred during shoulder dystocia or exchange transfusion, or was unexplained; the heartbeat had been restored within 5 minutes in most cases, and regular, active respiration had been established within 30 minutes thereafter in all cases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrman R. E. Alkali therapy in the delivery room. J Pediatr. 1966 Jul;69(1):173–174. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn F. Resuscitation of the newborn. Br J Anaesth. 1971 Sep;43(9):886–902. doi: 10.1093/bja/43.9.886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPPLE H. H., SUTHERLAND J. M. Resuscitation of stillborn infants. Obstet Gynecol. 1959 Mar;13(3):259–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Dodds J. B. The Denver developmental screening test. J Pediatr. 1967 Aug;71(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey E. N., Kohlinsky S., O'Connell B. Heat-losses from babies during exchange transfusion. Lancet. 1969 Feb 15;1(7590):335–338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey E., Kelly J. Gaseous exchange during endotracheal ventilation for asphyxia at birth. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Apr;75(4):414–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS D. H., AVERY M. E., JUDE J. R. Closed-chest cardiac massage in the newborn infant. JAMA. 1963 Mar 16;183:964–966. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63700110024020a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYA F., JAMES L. S., BURNARD E. D., HANKS E. C. Cardiac massage in the newborn infant through the intact chest. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1962 Sep 15;84:798–803. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(62)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani-Comparetti A., Gidoni E. A. Routine developmental examination in normal and retarded children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1967 Oct;9(5):631–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1967.tb02335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SURKS S. N., LADNER W. Closed-chest cardiac massage in the stillborn. JAMA. 1962 Apr 28;180:328–329. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050170060016a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


