Abstract
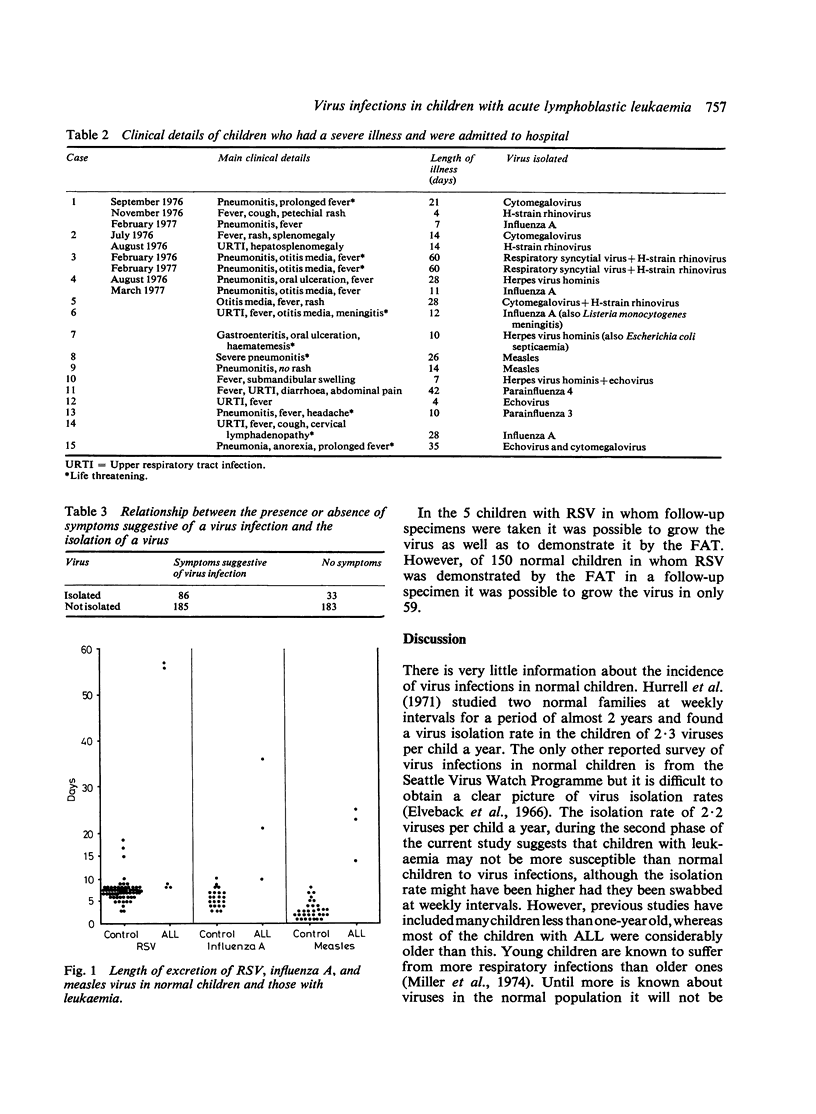
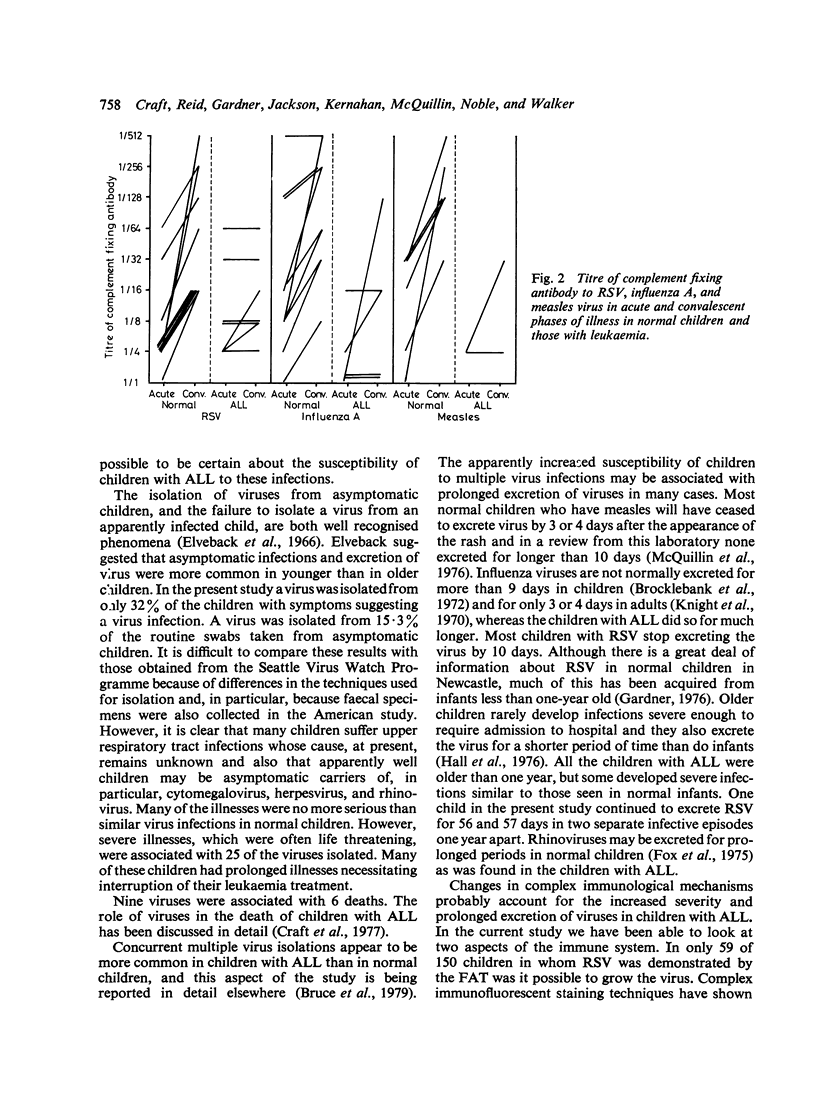
The pattern of virus isolation and illness was studied in 64 children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) during periods of apparent infection and when the children were well. The virus isolation rate of 2.2 viruses per child a year is similar to that previously found in normal children. In only 32% of children with symptoms were viruses found and 14.5% had viruses isolated when asymptomatic. The children with ALL appear to be more vulnerable to multiple virus infections and to excrete the virus for longer periods. This may be due to failure of production of both local and systemic antibodies. The failure in the past to recognise the true importance of virus infections in ALL may have been due to inadequate diagnostic techniques.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borella L., Webster R. G. The immunosuppressive effects of long-term combination chemotherapy in children with acute leukemia in remission. Cancer Res. 1971 Apr;31(4):420–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosu S. K., Ciudad H., Sinks L. F., Ogra P. I. Antibody response to poliovirus immunization in childhood leukemia. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1975;1(3):217–225. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklebank J. T., Court S. D., McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. Influenza-A infection in children. Lancet. 1972 Sep 9;2(7776):497–500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91902-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft A. W., Reid M. M., Bruce E., Kernahan J., Gardner P. S. Role of infection in the death of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Oct;52(10):752–757. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.10.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elveback L. R., Fox J. P., Ketler A., Brandt C. D., Wassermann F. E., Hall C. E. The Virus Watch program: a continuing surveillance of viral infections in metropolitan New York families. 3. Preliminary report on association of infections with disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 May;83(3):436–454. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S., Cox F. Viral infections and haematological malignancies. Clin Haematol. 1976 Jun;5(2):311–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Cooney M. K., Hall C. E. The Seattle virus watch. V. Epidemiologic observations of rhinovirus infections, 1965-1969, in families with young children. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Feb;101(2):122–143. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J. The coating of respiratory syncytial (RS) virus-infected cells in the respiratory tract by immunoglobulins. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):165–173. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. Viruses and respiratory infection in childhood. Proc R Soc Med. 1976 Sep;69(9):687–693. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Geiman J. M., Biggar R., Kotok D. I., Hogan P. M., Douglas G. R., Jr Respiratory syncytial virus infections within families. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 19;294(8):414–419. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602192940803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurrell G. D., Sturdy P. M., Frood J. D., Gardner P. S. Viruses in families. Lancet. 1971 Apr 17;1(7703):769–774. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight V., Fedson D., Baldini J., Douglas R. G., Couch R. B. Amantadine therapy of epidemic influenza a(2) (Hong Kong). Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):200–204. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.200-204.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. S., Schimpff S. C., Graw R. G., Jr, Young R. C. Hematologic malignancies and other marrow failure states: progress in the management of complicating infections. Semin Hematol. 1974 Apr;11(2):141–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillin J., Gardner P. S., McGuckin R. Rapid diagnosis of influenza by immunofluorescent techniques. Lancet. 1970 Oct 3;2(7675):690–695. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91961-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcquillin J., Bell T. M., Gardner P. S., Downham P. S. Application of immunofluorescence to a study of measles. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Jun;51(6):411–419. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.6.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M. M., Craft A. W., Todd J. A. Serial studies of numbers of circulating T and B lymphocytes in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Mar;52(3):245–247. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


