Abstract
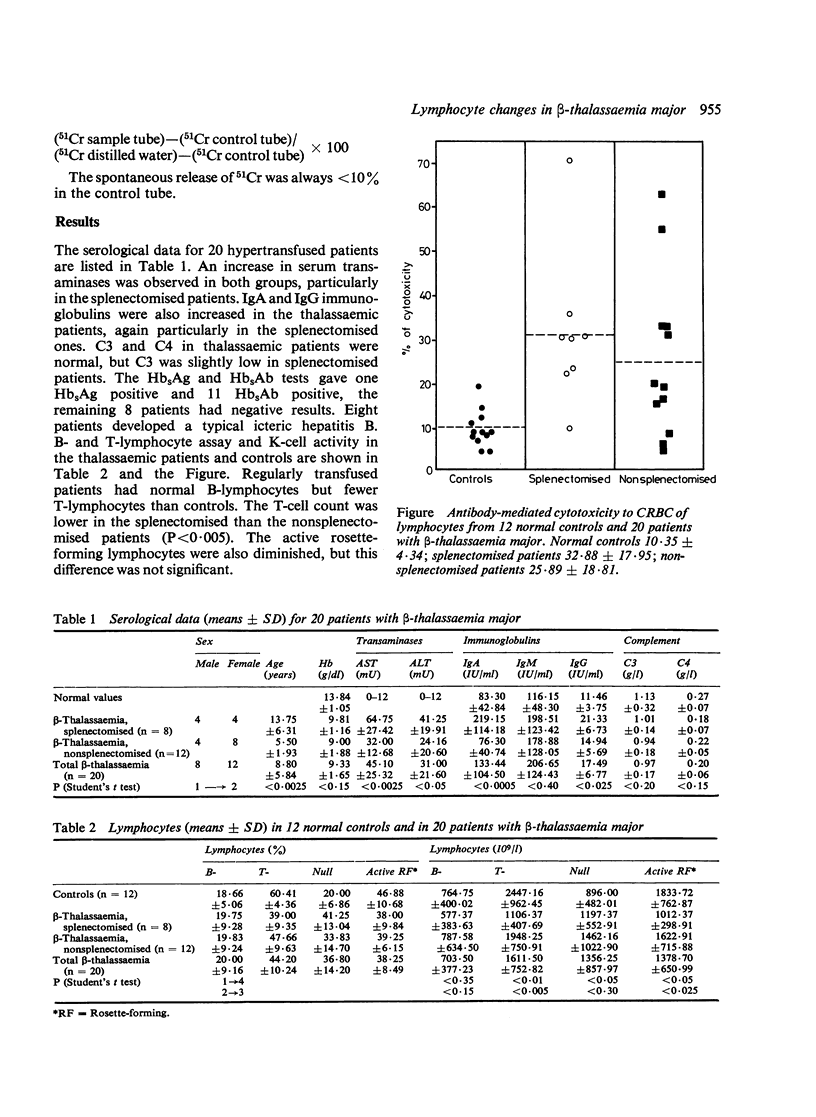
Lymphocyte subpopulations were studied in 20 hypertransfused patients with beta-thalassaemia major, some of whom had been splenectomised. B-lymphocytes were normal but T-lymphocytes were decreased in all patients. The T-cell count was lower in the splenectomised patients than in the nonsplenectomised ones. In the former, the active rosette-forming lymphocytes were also diminished, but the difference was not significant. In all patients the percentage of null cells was greater and the activity of K-cells increased compared with controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beltrami C. A., Nenci I. Per una patogenesi epatitica della sclerosi e della cirrosi epatica dei Cooleyani. Riv Patol Clin Sper. 1969 Jul-Dec;10(3):165–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Borzini P., Vergani D., Mieli-Vergani G., Masera G., Zanussi C. Occurrence of circulating immune complexes in beta-thalassaemia major. Arch Dis Child. 1978 Feb;53(2):141–143. doi: 10.1136/adc.53.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Thomsom A. D., Eddleston A. L., Wiiliams R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated (K cell) cytotoxicity against isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):441–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS J. T., SCHULMAN I., SMITH C. H. Generalized siderosis with fibrosis of liver and pancreas in Cooley's (Mediterranean) anemia; with observations on the pathogenesis of the siderosis and fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1954 Mar-Apr;30(2):287–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Groshong T., Albrecht R., Hong R. The "active" rosette test in immunodeficiency diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Sep;4(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudi-Tsakalidis F., Spyroglou K., Tzafi R., Cassimos C. Effect of blood transfusion on the immune response of children with thalassaemia. Acta Haematol. 1977;57(2):65–73. doi: 10.1159/000207861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masera G., Jean G., Gazzola G., Novakova M. Role of chronic hepatitis in development of thalassaemic liver disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Sep;51(9):680–685. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.9.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., O'Brien R. T. The management of thalassemia major. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jul;12(3):255–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Forni L., Amante L. Immunoglobulin spots on the surface of rabbit lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):1001–1018. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Cochran A. M., Mowat A. P., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cytotoxicity to isolated rabbit hepatocytes by lymphocytes from children with liver disease. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):584–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80507-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J. Peripheral lymphocyte subpopulations in human falciparum malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):471–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


