Abstract
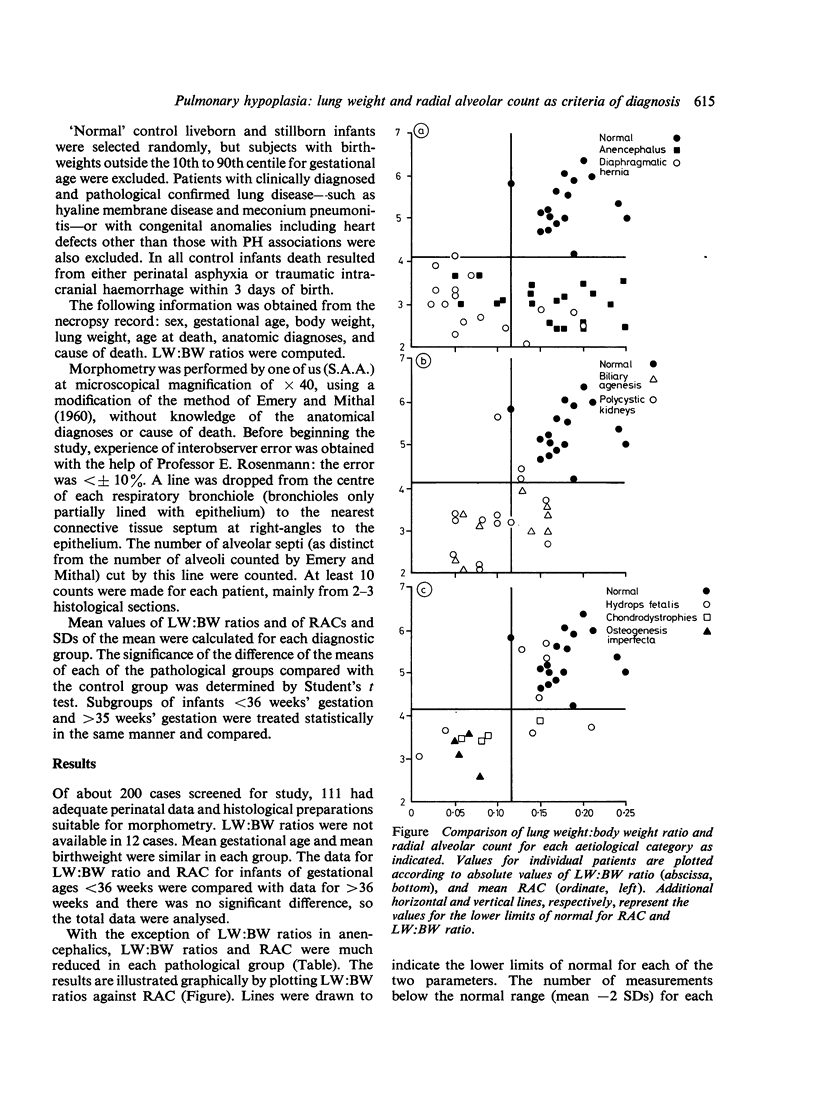
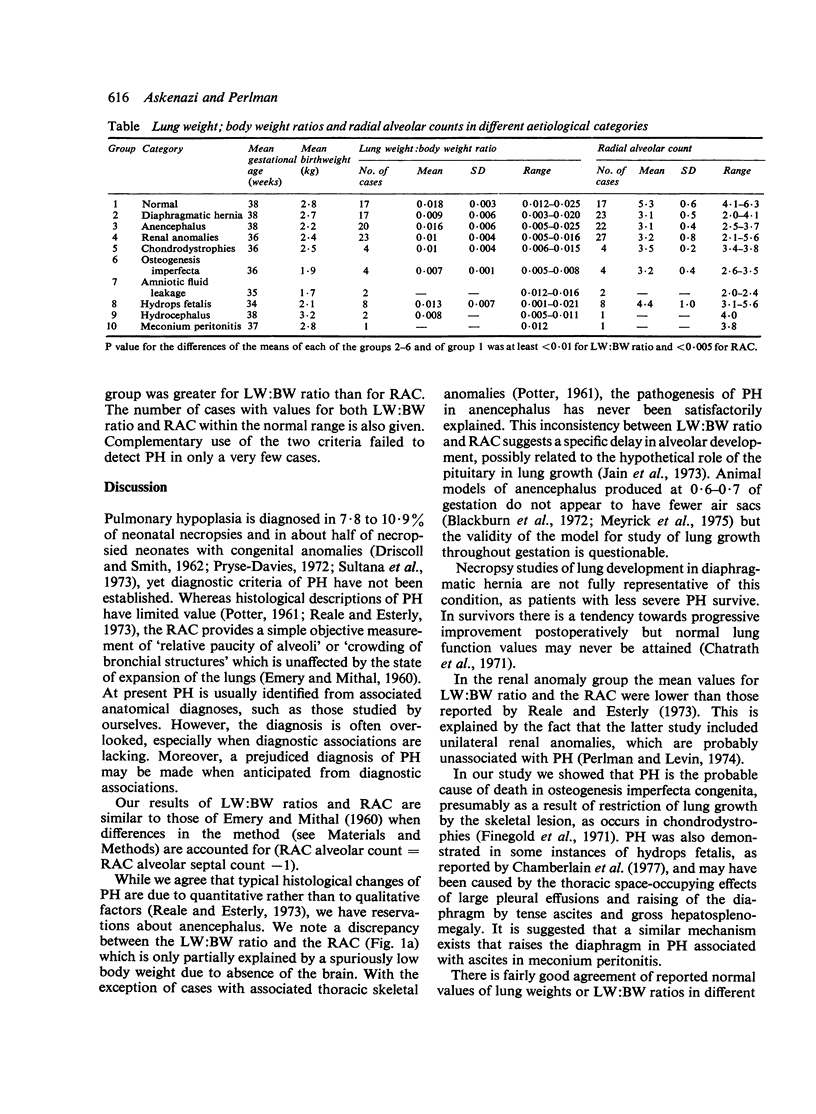
A working definition of pulmonary hypoplasia (PH) was established by retrospective assessment of lung growth both in recognised and hypothetical PH-associated conditions. Lung weight: body weight ratios (LW:BW) were calculated, and morphometry was determined by the radial alveolar count (RAC) (Emery and Mithal, 1960). Both parameters were reduced compared with those of normal controls in diaphragmatic hernia, anencephalus, anuric renal anomalies, chondrodystrophies, and osteogenesis inperfecta. Comparison of LW:BW ratio and RAC indicated that the RAC was the more reliable criterion of PH, LW:BW ratio of less than or equal to 0.12 (67%) of mean normal ratio) and/or RAC of less than or equal to 4.1 (75% of mean normal count) are suggested as diagnostic criteria of PH. Evidence of PH was incidentally discovered in a number of clinically unsuspected cases and retrospectively clarified the clinical and radiological findings. Routine assessment of lung growth should be an essential part of the neonatal necropsy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHERNE W., DAWKINS M. J. THE REMOVAL OF FLUID FROM THE PULMONARY AIRWAYS AFTER BIRTH IN THE RABBIT, AND THE EFFECT ON THIS OF PREMATURITY AND PRE-NATAL HYPOXIA. Biol Neonat. 1964;7:214–229. doi: 10.1159/000239925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn W. R., Travers H., Potter D. M. The role of the pituitary-adrenal-thyroid axes in lung differentiation. I. Studies of the cytology and physical properties of anencephalic fetal rat lung. Lab Invest. 1972 Mar;26(3):306–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkle F. M., Jr, Bravo A. J. Asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy. Malformation of the newborn. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1969 Mar;8(3):165–170. doi: 10.1177/000992286900800309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain D., Hislop A., Hey E., Reid L. Pulmonary hypoplasia in babies with severe rhesus isoimmunisation: a quantitative study. J Pathol. 1977 May;122(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/path.1711220108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatrath R. R., el-Shafie M., Jones R. S. Fate of hypoplastic lungs after repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Oct;46(249):633–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.249.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRISCOLL S. G., SMITH C. A. Neonatal pulmonary disorders. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1962 May;9:325–352. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERY J. L., MITHAL A. The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:544–547. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold M. J., Katzew H., Genieser N. B., Becker M. H. Lung structure in thoracic dystrophy. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Aug;122(2):153–159. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02110020087013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain B. P., Brody J. S., Fisher A. B. The small lung of hypopituitarism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):49–55. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Hislop A., Boyden E. A., Reid L. Lung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. A quantitative study of airway, artery, and alveolar development. Br J Surg. 1971 May;58(5):342–346. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E., Babbitt D. P. Dystrophic thoraces and infantile asphyxia. Radiology. 1970 Jan;94(1):55–62. doi: 10.1148/10.1148/94.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonidas J. C., Fellows R. A., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Beatty E. C. Value of chest radiography in the diagnosis of Potter's syndrome at birth. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975 Apr;123(4):716–723. doi: 10.2214/ajr.123.4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Bearn J. G., Cobb A. G., Monkhouse C. R., Reid L. The effect of in utero decapitation on the morphological and physiological development of the fetal rabbit lung. J Anat. 1975 Jul;119(Pt 3):517–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Blanc W. A. Organ and body growth in anencephaly. A quantitative, morphological study. Arch Pathol. 1971 Feb;91(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Levin M. Fetal pulmonary hypoplasia, anuria, and oligohydramnios: clinicopathologic observations and review of the literature. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Apr 15;118(8):1119–1123. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90692-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Williams J., Hirsch M. Neonatal pulmonary hypoplasia after prolonged leakage of amniotic fluid. Arch Dis Child. 1976 May;51(5):349–353. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.5.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryse-Davies J. Pathology of the perinatal lung. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Oct;65(10):823–824. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale F. R., Esterly J. R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: a morphometric study of the lungs of infants with diaphragmatic hernia, anencephaly, and renal malformations. Pediatrics. 1973 Jan;51(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renert W. A., Berdon W. E., Baker D. H., Rose J. S. Obstructive urologic malformations of the fetus and infant--relation to neonatal pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax (air-block). Radiology. 1972 Oct;105(1):97–105. doi: 10.1148/105.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULZ D. M., GIORDANO D. A., SCHULZ D. H. Weights of organs of fetuses and infants. Arch Pathol. 1962 Sep;74:244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultana Z., Talib V. H., Patil S. D., Deshpande M. S., Sharma K. D. Hypoplasia of the lung in the newborn. An autopsy study. Indian J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;40(311):419–421. doi: 10.1007/BF02760296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas I. T., Smith D. W. Oligohydramnios, cause of the nonrenal features of Potter's syndrome, including pulmonary hypoplasia. J Pediatr. 1974 Jun;84(6):811–815. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80753-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


