Abstract
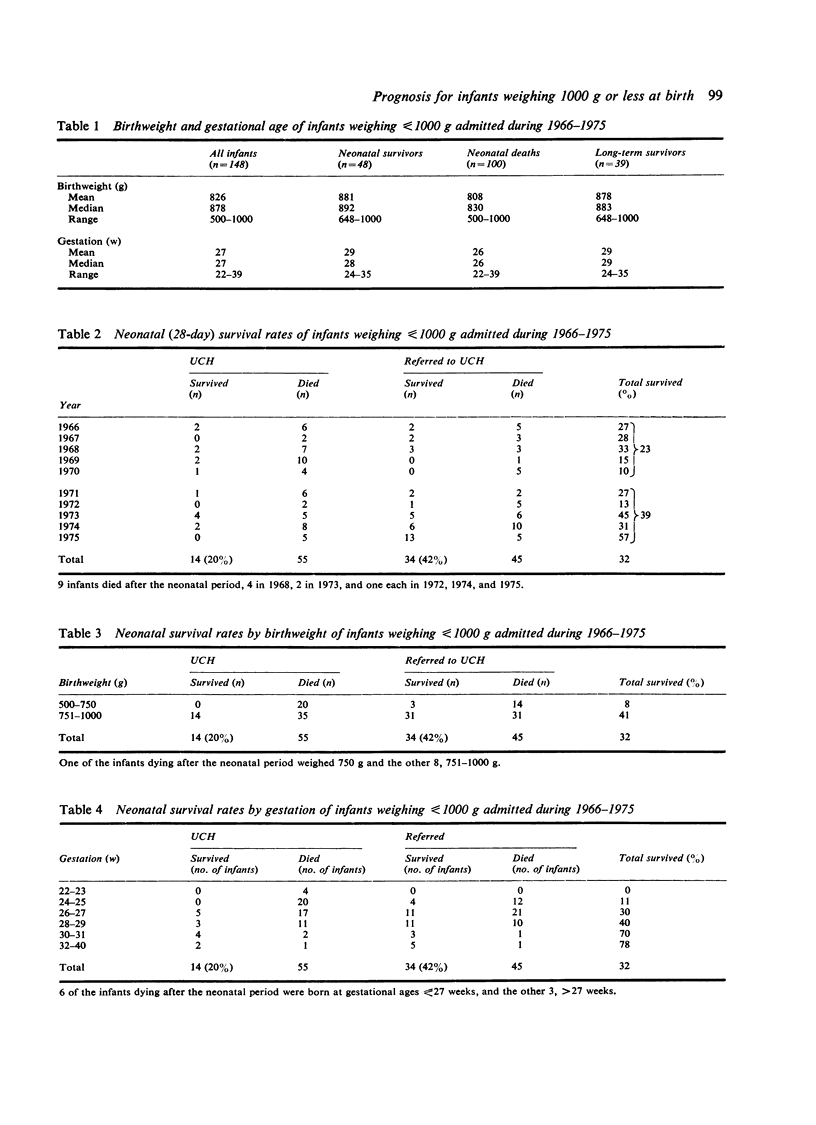
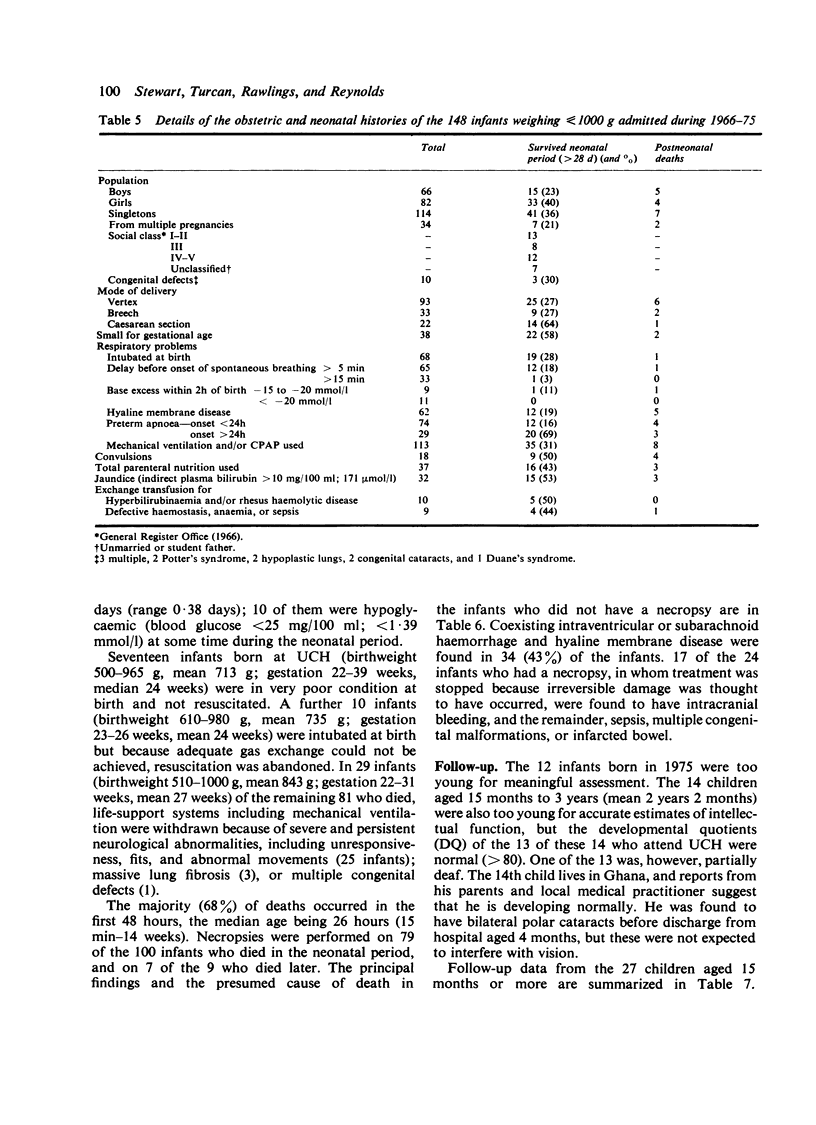
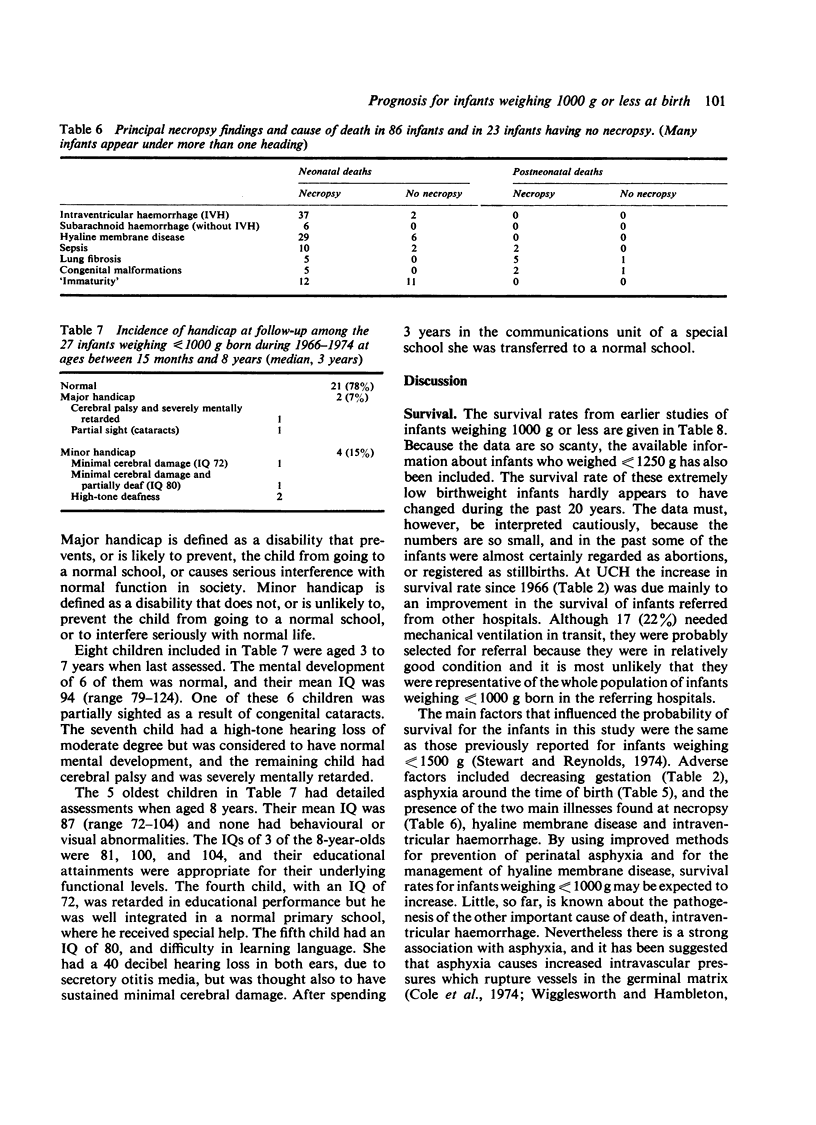
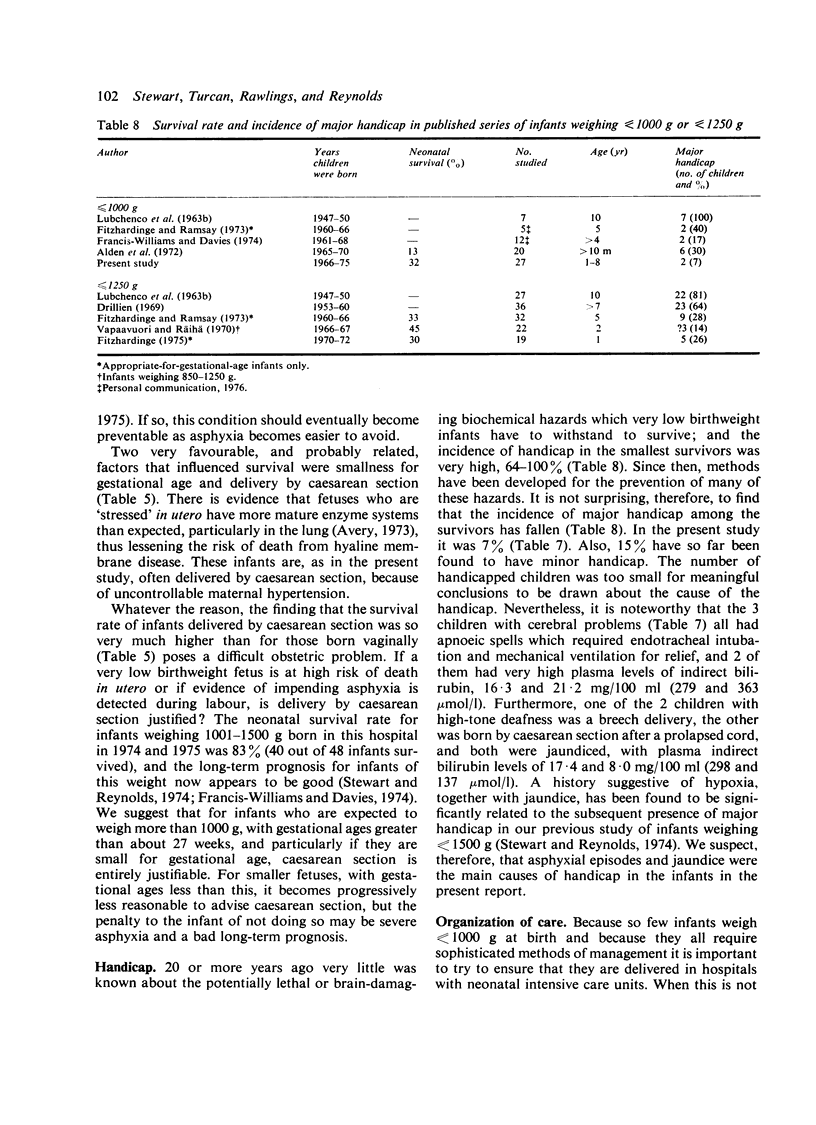
During the 10 years 1966-1975, 148 infants weighing less than or equal to 1000 g were admitted to the Neonatal Unit of University College Hospital. 48 (32%) survived the neonatal period. The neonatal survival rate for infants weighing less than or equal to 750 g was 8% and for infants weighing 751-1000 g, 41% 9 infants died later, leaving 39 (26%) long-term survivors, all of whom are being followed-up. The progress of the 27 older children, born in 1966-74 (median birthweight 899 g, range 648-998 g; median gestational age 28 weeks, range 24-35 weeks), was assessed at ages between 15 months and 8 years (median 3 years). No abnormalities were detected in 21 infants (78%): 2 (7%) had major handicaps and 4 (15%) minor handicaps. We conclude that provided intensive care methods are available, the prognosis for infants weighing less than or equal to 1000 g is now better than in the past.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden E. R., Mandelkorn T., Woodrum D. E., Wennberg R. P., Parks C. R., Hodson W. A. Morbidity and mortality of infants weighing less than 1,000 grams in an intensive care nursery. Pediatrics. 1972 Jul;50(1):40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen L. P., Blake A. M., Durbin G. M., Ingram D., Reynolds E. O., Wimberley P. D. Continuous positive airway pressure and mechanical ventilation by facemask in newborn infants. Br Med J. 1975 Oct 18;4(5989):137–139. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5989.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery M. E. What is new in our understanding of perinatal pulmonary problems? Presidential address to the Society for Pediatric Research, May 19, 1973. Pediatr Res. 1973 Oct;7(10):842–845. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197310000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake A. M., McIntosh N., Reynolds E. O., Andrew D. S. Transport of newborn infants for intensive care. Br Med J. 1975 Oct 4;4(5987):13–17. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5987.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame A., Prod'hom L. S. Pronostic vital et qualité de survie des prématurés peasant 1500 g et moins à la naissance, soignés en 1966-1968. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1972 Jan 22;102(3):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole V. A., Durbin G. M., Olaffson A., Reynolds E. O., Rivers R. P., Smith J. F. Pathogenesis of intraventricular haemorrhage in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Sep;49(9):722–728. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.9.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway M., Durbin G. M., Ingram D., McIntosh N., Parker D., Reynolds E. O., Soutter L. P. Continuous monitoring of arterial oxygen tension using a catheter-tip polarographic electrode in infants. Pediatrics. 1976 Feb;57(2):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRILLIEN C. M. Growth and development in a group of children of very low birth weight. Arch Dis Child. 1958 Feb;33(167):10–18. doi: 10.1136/adc.33.167.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. A., Tizard J. P. Very low birthweight and subsequent neurological defect (with special reference to spastic diplegia). Dev Med Child Neurol. 1975 Feb;17(1):3–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1975.tb04951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhardinge P. M. Early growth and development in low-birthweight infants following treatment in an intensive care nursery. Pediatrics. 1975 Aug;56(2):162–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhardinge P. M., Ramsay M. The improving outlook for the small prematurely born infant. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1973 Aug;15(4):447–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1973.tb05066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis-Williams J., Davies P. A. Very low birthweight and later intelligence. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1974 Dec;16(6):709–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1974.tb03392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck L., Kulovich M. V., Borer R. C., Jr, Brenner P. H., Anderson G. G., Spellacy W. N. Diagnosis of the respiratory distress syndrome by amniocentesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Feb 1;109(3):440–445. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huch R., Lübbers W., Huch A. Reliability of transcutaneous monitoring of arterial PO2 in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):213–218. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOBLOCH H., RIDER R., HARPER P., PASAMANICK B. Neuropsychiatric sequelae of prematurity; a longitudinal study. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Jun 16;161(7):581–585. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02970070013004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch H., Pasamanick B., Sherard E. S., Jr A developmental screening inventory for infants. Pediatrics. 1966 Dec;38(6 Suppl):1095–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBCHENCO L. O., HANSMAN C., DRESSLER M., BOYD E. INTRAUTERINE GROWTH AS ESTIMATED FROM LIVEBORN BIRTH-WEIGHT DATA AT 24 TO 42 WEEKS OF GESTATION. Pediatrics. 1963 Nov;32:793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBCHENCO L. O., HORNER F. A., REED L. H., HIX I. E., Jr, METCALF D., COHIG R., ELLIOTT H. C., BOURG M. Sequelae of premature birth. Evaluation of premature infants of low birth weights at ten years of age. Am J Dis Child. 1963 Jul;106:101–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings G., Stewart A., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Changing prognosis for infants of very low birth weight. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):516–519. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Reynolds E. O. Improved prognosis for infants of very low birthweight. Pediatrics. 1974 Dec;54(6):724–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vapaavuori E. K., Räihä N. C. Intensive care of small premature infants. I. Clinical findings and results of treatment. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1970 Jul;59(4):353–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1970.tb15528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


