Abstract
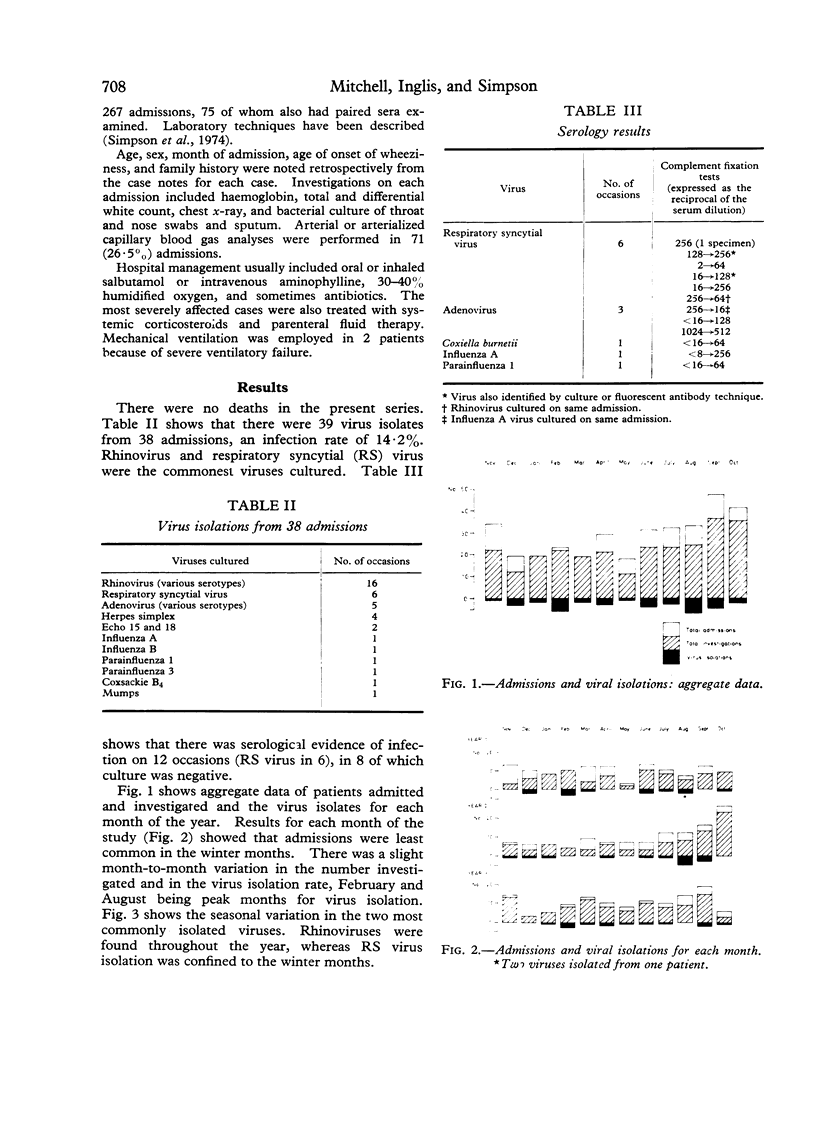
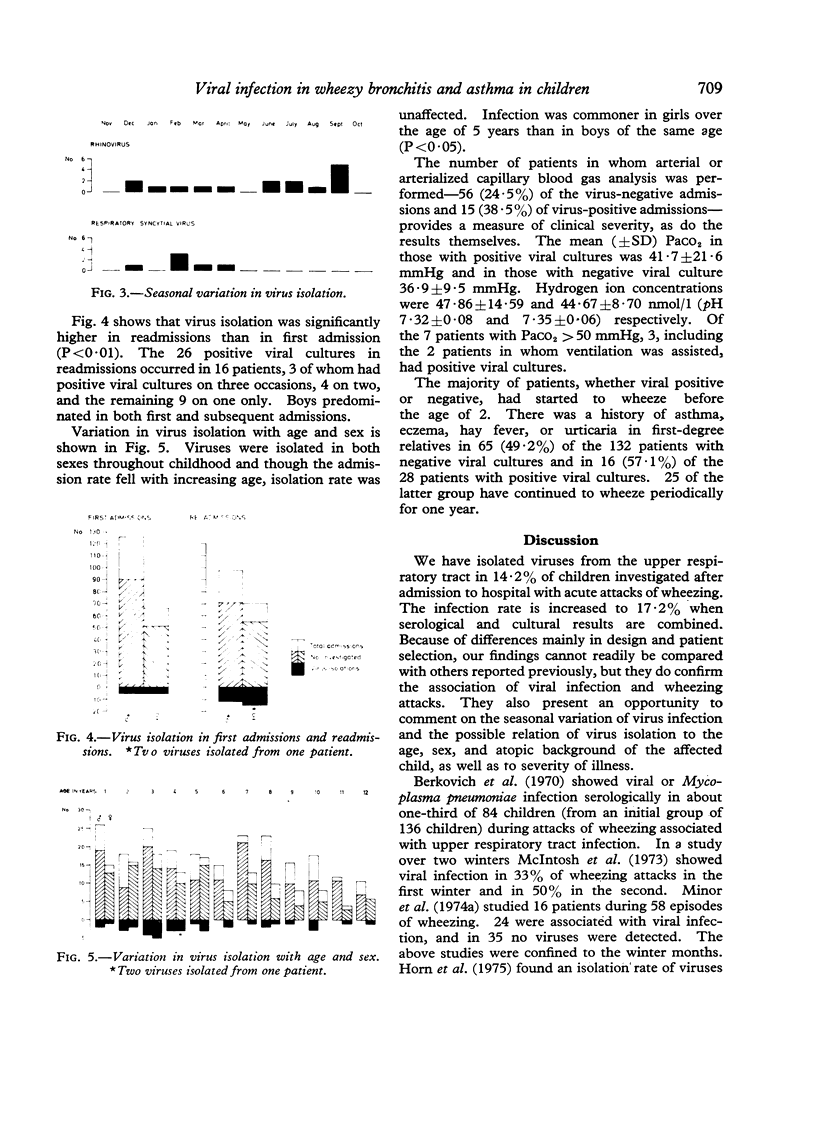
Virus isolation was attempted on 267 out of 360 patients with wheezy bronchitis or asthma admitted to hospital during a 3-year period. Viruses were isolated on 39 occasions, the most common being respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus. The peak months for virus isolation were February and August. Virus isolation was significantly more common in readmissions than in first admissions (P less than 0-01). Viruses were isolated in both sexes throughout childhood and though the admission rate fell with increasing age, the isolation rate was unaffected. The possible significance of viral infection as a cause of acute attacks of wheezing in children is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkovich S., Millian S. J., Snyder R. D. The association of viral and mycoplasma infections with recurrence of wheezing in the asthmatic child. Ann Allergy. 1970 Feb;28(2):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney M. E., Matthews R., Williams J. D. The role of infection in the morbidity of asthmatic children admitted to hospital. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):399–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. H. The role of infection in allergic disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1969 Feb;16(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN G. L., TODD R. H. The role of allergy in viral respiratory tract infections. Am J Dis Child. 1962 Oct;104:330–334. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1962.02080030332002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. E., Brain E., Gregg I., Yealland S. J., Inglis J. M. Respiratory viral infection in childhood. A survey in general practice, Roehampton 1967-1972. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Apr;74(2):157–168. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Ellis E. F., Hoffman L. S., Lybass T. G., Eller J. J., Fulginiti V. A. The association of viral and bacterial respiratory infections with exacerbations of wheezing in young asthmatic children. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):578–590. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(73)80582-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Baker J. W., Dick E. C., DeMeo A. N., Ouellette J. J., Cohen M., Reed C. E. Greater frequency of viral respiratory infections in asthmatic children as compared with their nonasthmatic siblings. J Pediatr. 1974 Oct;85(4):472–477. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(74)80447-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Dick E. C., DeMeo A. N., Ouellette J. J., Cohen M., Reed C. E. Viruses as precipitants of asthmatic attacks in children. JAMA. 1974 Jan 21;227(3):292–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney J. C., Williams H. E. The relationship between proved viral bronchiolitis and subsequent wheezing. J Pediatr. 1971 Nov;79(5):744–747. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S., Norman A. P. The bacterial flora of the upper respiratory tract in children with severe asthma. J Allergy. 1968 Jun;41(6):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson H., Matthew D. J., Inglis J. M., George E. L. Virological findings and blood gas tensions in acute lower respiratory tract infections in children. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 22;2(5920):629–632. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5920.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H., McNicol K. N. Prevalence, natural history, and relationship of wheezy bronchitis and asthma in children. An epidemiological study. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 8;4(5679):321–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5679.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



