Abstract
To determine the importance of the presence of serological markers of hepatitis B virus infection in patients with alcohol related liver disease we compared cumulative alcohol intake and clinical and histological features in patients with markers of hepatitis B virus infection and in those without. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was detected in five (2%) out of 285 patients studied and antibody to HBsAg (anti-HBs) in 41 (14%); one patient had antibody to hepatitis B core antigen alone. The combined prevalence of markers of hepatitis B virus infection was similar in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (18%) and precirrhotic liver disease (13%). Two patients positive for HBsAg had histological features of both alcoholic liver disease and chronic active hepatitis, with stainable HBsAg. Patients with anti-HBs were, however, histologically indistinguishable from patients without markers, and the mean cumulative alcohol intake of patients with anti-HBs was similar to or even higher than that of patients with liver disease of comparable severity who had no evidence of previous infection. The presence of markers of hepatitis B virus infection was related to former residence in countries with a high prevalence of the infection and to previous parenteral treatment and blood transfusions. Infection with hepatitis B virus does not enhance the development of chronic liver disease in heavy drinkers, except in the small number who remain positive for HBsAg.
Full text
PDF
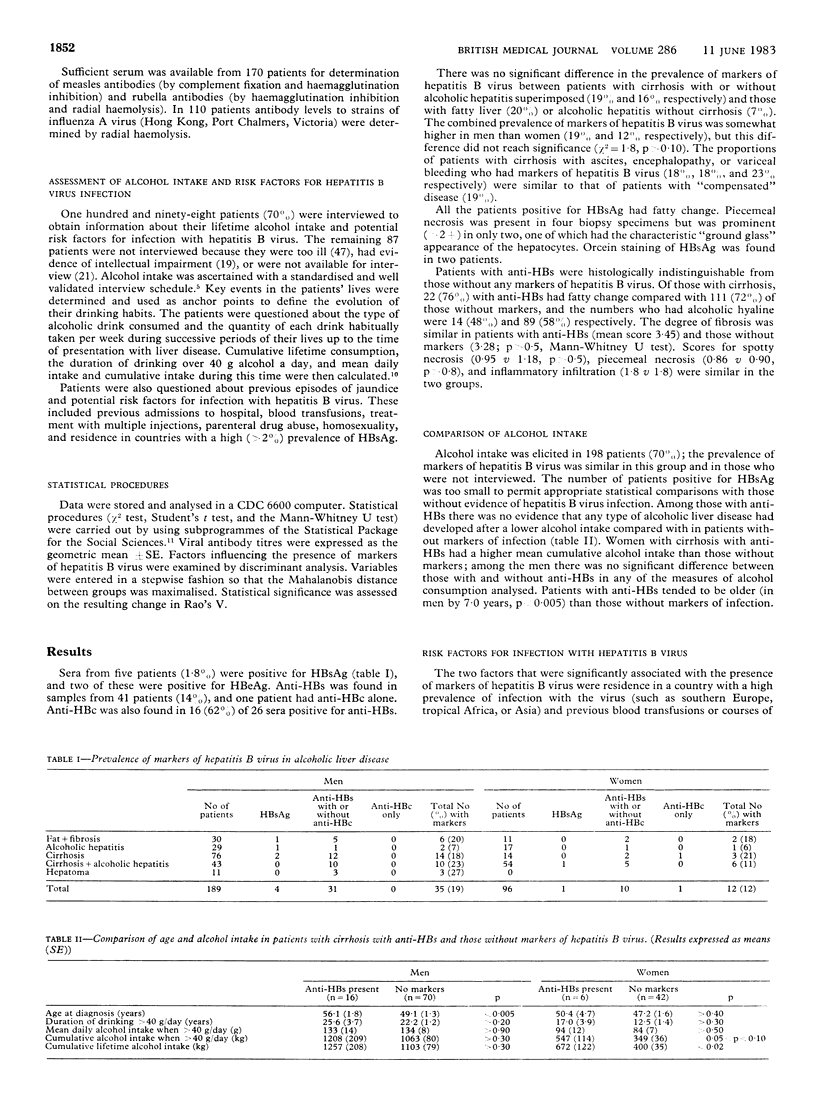
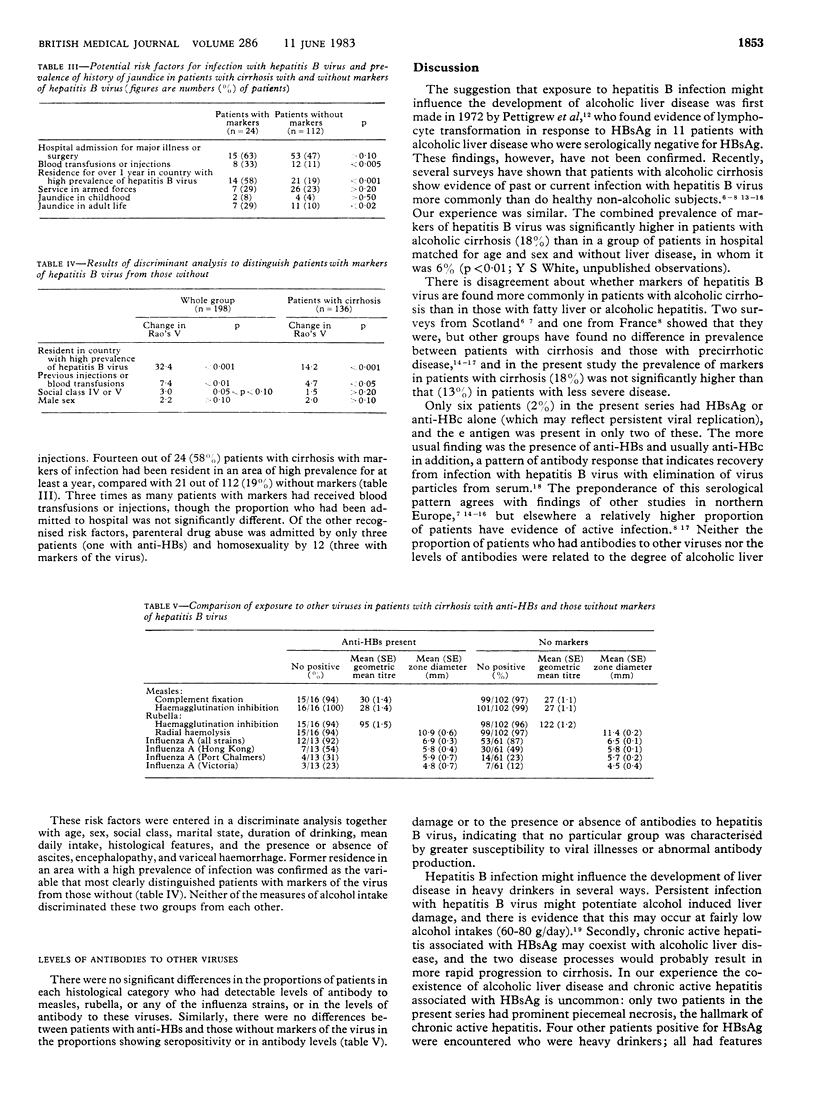

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcoholic liver disease: morphological manifestations. Review by an international group. Lancet. 1981 Mar 28;1(8222):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. J., Krasner N., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Tee D. E., Doniach D., Kennedy L. A., Batchelor J. R. Histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies, and immunoglobulins in alcoholic liver disease. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 25;2(6038):727–729. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6038.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassendine M. F., Della Seta L., Salmeron J., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Incidence of hepatitis B virus infection in alcoholic liver disease, HBsAg negative chronic active liver disease and primary liver cell cancer in Britain. Liver. 1983 Apr;3(2):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1983.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell H., Nordhagen R. HLA antigens in alcoholics, with special reference to alcoholic cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(4):453–456. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréchot C., Nalpas B., Couroucé A. M., Duhamel G., Callard P., Carnot F., Tiollais P., Berthelot P. Evidence that hepatitis B virus has a role in liver-cell carcinoma in alcoholic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 10;306(23):1384–1387. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206103062302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers D. M., Bullen A. W., Levi A. J. Evidence for previous hepatitis B virus infection in alcoholic cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 7;282(6266):819–819. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6266.819-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudeau A., Maupas P., Dubois F., Coursaget P., Bougnoux P. Hepatitis B infection in alcoholic liver disease and primary hepatocellular carcinoma in France. Prog Med Virol. 1981;27:26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop W. S., Follett E. A., Bouchier I. A., MacSween R. N. Serological markers of hepatitis B in patients with alcoholic liver disease: a multi-centre survey. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):1017–1019. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K. The clinicopathological features of the alcoholic liver injury in Japan and its etiological relationship to hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1977;12(3):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02781768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills P. R., Follett E. A., Urquhart G. E., Clements G., Watkinson G., Macsween R. N. Evidence for previous hepatitis B virus infection in alcoholic cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 7;282(6262):437–438. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6262.437-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. Y., Ross M. G., Ng C. M., Adams D. M., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. HLA-B8, immunoglobulins, and antibody responses in alcohol-related liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;33(5):488–492. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.5.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orholm M., Aldershvile J., Tage-Jensen U., Schlichting P., Nielsen J. O., Hardt F., Christoffersen P. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among alcoholic patients with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1378–1380. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew N. M., Goudie R. B., Russell R. I., Chaudhuri A. K. Evidence for a role of hepatitis virus B in chronic alcoholic liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Oct 7;2(7780):724–725. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. B., Davis M., Williams R. Do women develop alcoholic liver disease more readily than men? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Apr 4;282(6270):1140–1143. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6270.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. B., Wodak A. D., Haines A., Powell-Jackson P. R., Portmann B., Davis M., Williams R. Accelerated development of alcoholic cirrhosis in patients with HLA-B8. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1381–1384. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodossi A., Wilkinson S. P., Portmann B., White Y., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J. De novo acute infection and reactivation of hepatitis B virus in established cirrhosis. Br Med J. 1979 Oct 13;2(6195):893–895. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6195.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa E., Rubbiani L., Barchi T., Ferretti I., Grisendi A., De Palma M., Bellentani S., Manenti F. Susceptibility of chronic symptomless HBsAg carriers to ethanol-induced hepatic damage. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



