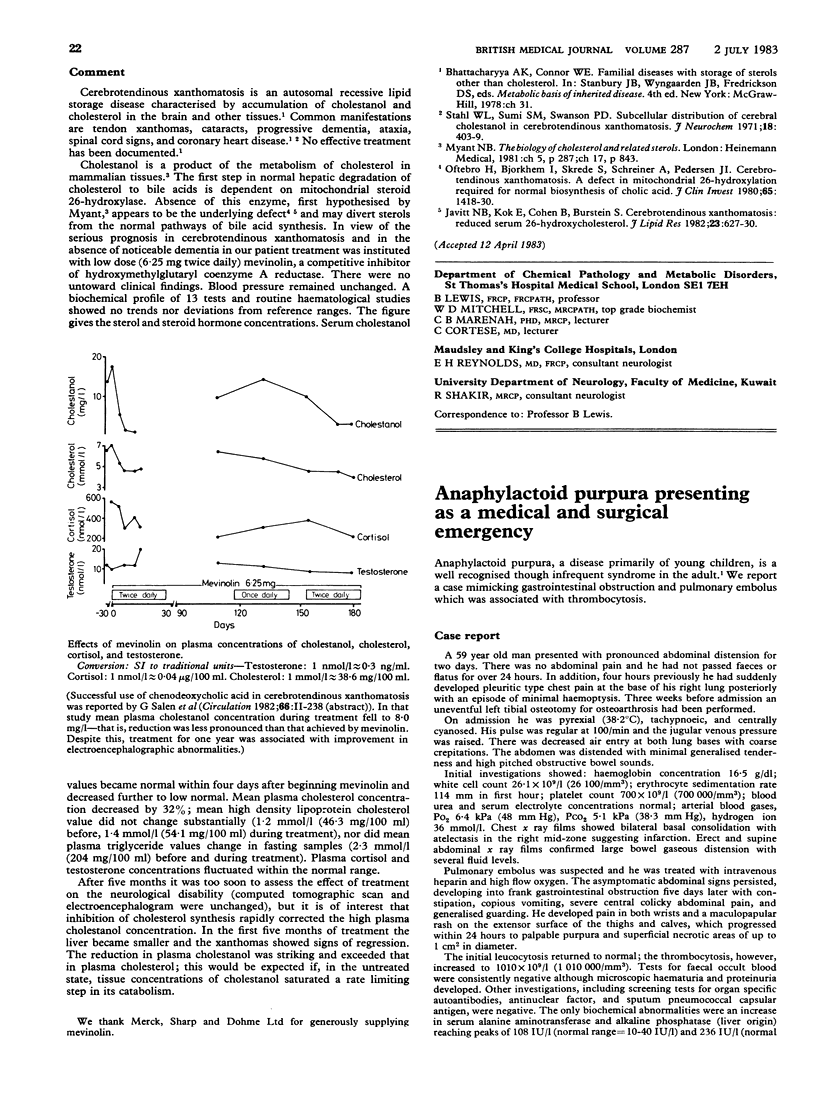
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Javitt N. B., Kok E., Cohen B., Burstein S. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: reduced serum 26-hydroxycholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):627–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftebro H., Björkhem I., Skrede S., Schreiner A., Pederson J. I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: a defect in mitochondrial 26-hydroxylation required for normal biosynthesis of cholic acid. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1418–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI109806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl W. L., Sumi S. M., Swanson P. D. Subcellular distribution of cerebral cholestanol in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



