Abstract
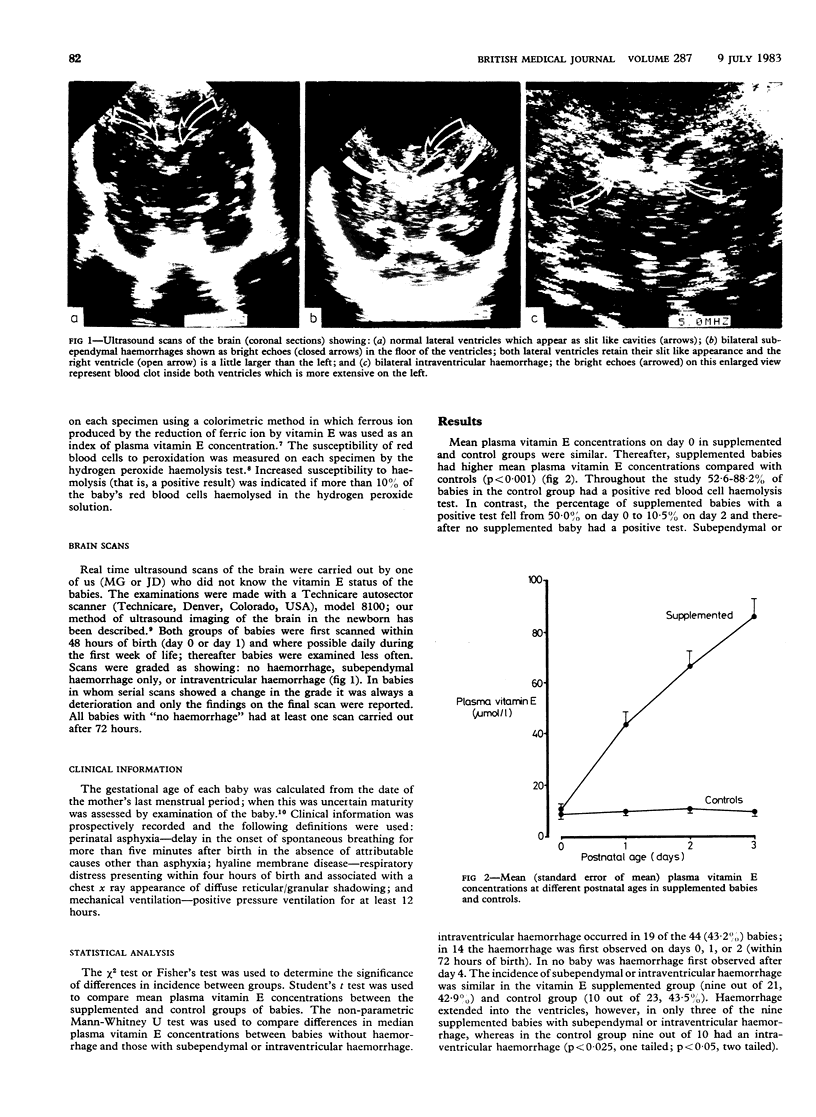
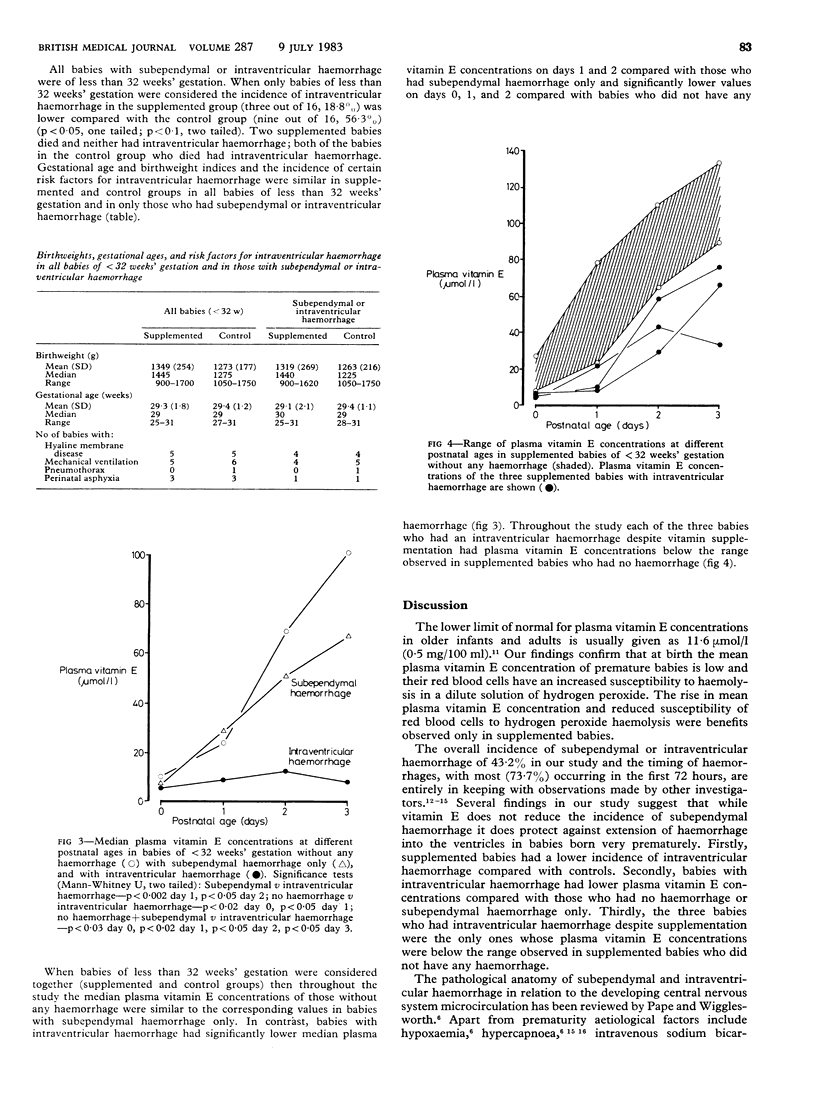
Forty four babies, of less than 32 weeks' gestation, were either randomly given 25 mg/kg vitamin E (DL-alpha-tocopherol acetate) intramuscularly after birth (day 0) and on days 1, 2, and 3 or served as controls. Frequent real time ultrasound examinations of the brain were made in each baby during the first week and less frequently thereafter. In babies under 32 weeks' gestation the incidence of intraventricular haemorrhage was lower in supplemented babies (18.8%) compared with the controls (56.3%). On days 0, 1, 2, and 3 median plasma vitamin E concentrations in babies without haemorrhage and in those with subependymal haemorrhage only were similar. Babies with intraventricular haemorrhage had lower median concentrations on day 1 (p less than 0.002) and day 2 (p less than 0.05) compared with those with subependymal haemorrhage and lower concentrations on day 0 (p less than 0.02) and day 1 (p less than 0.05) compared with those without haemorrhage. These findings suggest that in premature babies vitamin E, an antioxidant, protects endothelial cell membranes from oxidative damage and disruption and limits the magnitude of haemorrhage and its spread from the subependyma into the ventricles.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmann P. A., Lazzara A., Dykes F. D., Brann A. W., Jr, Schwartz J. F. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the high-risk preterm infant: incidence and outcome. Ann Neurol. 1980 Feb;7(2):118–124. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiswick M. L., Wynn J., Toner N. Vitamin E and intraventricular hemorrhage in the newborn. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;393:109–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. W. Factors associated with periventricular haemorrhage in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jun;56(6):425–431. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.6.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T. The clinical effects of vitamin E on purpuras due to vascular defects. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1972 Sep 10;18(3):125–130. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.18.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON H. H., NITOWSKY H. M., CORNBLATH M. Studies of tocopherol deficiency in infants and children. I. Hemolysis of erythrocytes in hydrogen peroxide. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1955 Dec;90(6):669–681. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1955.04030010671002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlóczy F., Láncos F., Szabó J. Wirkung des Vitamin E auf die Kapillarresistenz bei Purpura im Kindesalter. Acta Paediatr Acad Sci Hung. 1966;7(4):363–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcke H. T., Jr, Naeye R. L., Storch A., Blanc W. A. Perinatal cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr. 1972 Jan;80(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Perlman J. M., Volpe J. J. Relationship of pneumothorax to occurrence of intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature newborn. Pediatrics. 1982 Feb;69(2):144–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler R. F., Young S. Role of vitamin E in the etiology of spontaneous hemorrhagic necrosis of the central nervous system of fetal hamsters. Teratology. 1979 Aug;20(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420200116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard P. J., Doyle E., Harrington W. Levels of vitamin E in the plasma of newborn infants and of the mothers. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 May;25(5):480–484. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.5.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Fawer C. L., Lamont R. F. Risk factors in the development of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Jun;57(6):410–417. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.6.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Wigglesworth J. S., Dubowitz V. Cerebral structure and intraventricular haemorrhage in the neonate: a real-time ultrasound study. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jun;56(6):416–424. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.6.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb A. P., Thorburn R. J., Reynolds E. O., Stewart A. L., Blackwell R. J., Cusick G., Whitehead M. D. Pneumothorax and cerebral haemorrhage in preterm infants. Lancet. 1981 Feb 21;1(8217):414–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91794-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEK R. G. METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF VITAMIN E (TOTAL TOCOPHEROLS) IN SERUM. Clin Chem. 1964 Dec;10:1078–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER W. T. Vitamin E levels in term and premature newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1950 Dec;6(6):893–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A., Barness L. A. Vitamin E deficiency: a previously unrecognized cause of hemolytic anemia in the premature infant. J Pediatr. 1967 Feb;70(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H., Koops B. Relationship of intravenous sodium bicarbonate infusions and cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr. 1978 Nov;93(5):834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. A., Adcock E. W., 3rd, Bard H., Battaglia F. C. Hypernatremia and intracranial hemorrhage in neonates. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 4;291(1):6–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407042910102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT S. W., FILER L. J., Jr, MASON K. E. Vitamin E blood levels in premature and full term infants. Pediatrics. 1951 Mar;7(3):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W. A., Yu M. C., Young P. A. Ultrastructural changes in the cerebrovascular endothelium induced by a diet high in linoleic acid and deficient in vitamin E. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Dec;21(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



