Abstract
We show that Neurospora crassa has a single histone H1 gene, hH1, which encodes a typical linker histone with highly basic N- and C-terminal tails and a central globular domain. A green fluorescent protein-tagged histone H1 chimeric protein was localized exclusively to nuclei. Mutation of hH1 by repeat-induced point mutation (RIP) did not result in detectable defects in morphology, DNA methylation, mutagen sensitivity, DNA repair, fertility, RIP, chromosome pairing, or chromosome segregation. Nevertheless, hH1 mutants had mycelial elongation rates that were lower than normal on all tested carbon sources. This slow linear growth phenotype, however, was less evident on medium containing ethanol. The pyruvate decarboxylase gene, cfp, was abnormally derepressed in hH1 mutants on ethanol-containing medium. This derepression was also found when an ectopically integrated fusion of the cfp gene promoter to the reporter gene hph was analyzed. Thus, Neurospora histone H1 is required for the proper regulation of cfp, a gene with a key role in the respiratory-fermentative pathway.
Eukaryotic DNA is compacted into chromatin, a dynamic nucleoprotein complex organized into nucleosomes (31). Each nucleosome contains an octameric core of four conserved histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, around which ∼146 bp of DNA are wrapped (35). The N-terminal tails of core histones are thought to interact with nuclear proteins and to be involved in internucleosomal interactions that can lead to chromatin condensation (36, 71). Posttranslational modifications of histone tails have been shown to be involved in various aspects of gene regulation, suggesting the existence of a “histone code” specifying gene silencing, activation, and other processes (6, 26). Chromatin of most eukaryotes includes less conserved “linker histones,” most notably, histone H1 (28, 29, 63). Histone H1 has been proposed to play a role in creating and/or maintaining the higher-order structure of chromatin (52). In contrast to core histones, linker histones appear rather mobile and in fact are not permanently associated with chromatin (33, 44). The results of in vitro studies have suggested that H1 participates in the organization of nucleosomes (62), restricts the translational mobility of nucleosomes (48, 66), and can inhibit transcription (70). Interestingly, H1 is enriched in nuclease-resistant and inactive chromatin (69) and in regions of DNA that are methylated (3). Additional clues to the possible functions of H1 have come from in vivo studies. In higher eukaryotes, which have multiple linker histone genes subject to developmental regulation (30), some H1 variants seem to be dispensable (13, 60). In tobacco, H1 plays roles in development and male meiosis (49). An H1 variant is essential for the development of the germ line in Caenorhabditis elegans (25). Changes in H1 stoichiometry modulate core histone acetylation in cultured mammalian cells (18).
The functions of H1 have been studied most extensively for Tetrahymena and fungi. Both Tetrahymena thermophila and Saccharomyces cerevisiae have single genes for linker histones with unconventional structures (5, 72). The Tetrahymena gene encodes a lysine- and alanine-rich protein that lacks the globular domain, whereas the yeast protein consists almost entirely of two globular domains without a long C-terminal tail. Deletion of the linker histone gene did not lead to gross phenotypic changes in either organism. Nevertheless, the Tetrahymena linker histone mutant showed increased nuclear size (57) as well as abnormal activation of some genes and repression of others (58). Disruption of the yeast H1-like gene caused decreases in the steady-state levels of a substantial number of unrelated mRNAs (22).
Filamentous fungi have canonical H1 linker histones. Ascobolus immersus contains a single H1 gene encoding a typical tripartite H1 protein with a charged amino-terminal domain, a globular winged helix domain, and a charged alanine- and lysine-rich carboxy-terminal domain (4). Ascobolus strains in which the H1 gene was silenced by methylation showed increased sensitivity of chromatin to micrococcal nuclease (MNase), global DNA hypermethylation, and a shortened “life span” (4). These phenotypes are consistent with important roles of H1 in global chromatin function and gene regulation (2). The dispensability of the equivalent gene in Aspergillus nidulans (hhoA) (53), however, challenged the idea that canonical H1 proteins are essential in eukaryotes. We chose Neurospora crassa to further define the functions of linker histones. This fungus exhibits DNA methylation (32, 61), repeat-induced point mutation (RIP) (55), and a fully characterized set of core histones (21); in addition, as in A. immersus, nucleosomal repeats are slightly longer than in Aspergillus and yeast cells (53).
Here we report the cloning and characterization of the hH1 gene of N. crassa. This gene encodes a typical histone H1 protein. We constructed viable hH1 null mutants, demonstrating that hH1 is not essential in Neurospora. We found, however, that H1 mutants grew more slowly than wild-type strains on the various tested carbon sources, and we observed misregulation of the cfp (cellular filament polypeptide) gene (1), which encodes Neurospora pyruvate decarboxylase. Our results indicate that histone H1 is required for the proper regulation of cfp expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and genetic methods.
Standard Neurospora methods were used (10). The N. crassa strains used in this work are described in Table 1. Strain N228 carries a duplication of the al-1 gene and was kindly provided by C. Staben (University of Kentucky). Strains N1445 and N1264 were described previously (32, 43). Strains HH3 (hH1RIP his-3) and HH28 (his-3) were obtained by a cross between DF3 (mat a hH1RIP) and a his-3 mutant (FGSC 6103). Strains used to measure RIP and linear growth were constructed for this study as detailed in Tables 2 and 3, respectively.
TABLE 1.
N. crassa strains used in this study
| Strain | Genotypea | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 74-OR23-1A | mat A | FGSC 987 |
| 74-OR8-1a | mat a | FGSC 988 |
| N228 | mat a; al-1+; al-1::hph | This study |
| N623 | mat A his-3 | FGSC 6103 |
| N1264 | mat A; nic-3 wc-1 arg-10 | Reference 32 |
| N1445 | mat a his-3; am132 inl | Reference 43 |
| N1815 | mat A; hH1RIP1 | This study |
| N1817 | mat A; hH1RIP2 | This study |
| DF3 | mat a; hH1RIP1 | This study |
| HH3 | mat A his-3; hH1RIP1 | This study |
| HH28 | mat A; his-3 | This study |
RIP designations indicate that the hH1 gene contained RIP mutations.
TABLE 2.
Lack of effect of disruption of hH1 on RIP mutations
| Type | Crossa | Relevant genotype | % RIP frequency (mean ± SD)b | No. of progeny analyzed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FGSC 987 × N228 | (+) × al-1+/al-1+ | 47 ± 9 | 1,786 |
| 2 | N1815 × N228 | hH1RIP × al-1+/al-1+ | 77 ± 6 | 2,023 |
| 3 | s-wt × N228 | (+) × al-1+/al-1+ | 66 ± 6 | 6,348 |
| 4 | s-hH1 × N228 | hH1RIP × al-1+/al-1+ | 57 ± 6 | 4,045 |
| 5 | d-hH1 × FGSC 987 | hH1RIP; al-1+/al-1+ × (+) | 69 ± 14 | 3,067 |
| 6 | d-hH1 × N1815 | hH1RIP; al-1+/al-1+ × hH1RIP | 73 ± 11 | 2,870 |
| 7 | d-wt × FGSC 987 | al-1+/al-1+ × (+) | 73 ± 6 | 4,823 |
| 8 | d-wt × N1815 | al-1+/al-1+ × hH1RIP | 74 ± 7 | 4,288 |
Strain N228 has an ectopic duplication of the wild-type al-1+ gene, and FGSC 987 is a wild-type (+) strain. A total of 11 wild-type (s-wt) and 7 hH1RIP (s-hH1) progeny were isolated from a cross between N1815 and FGSC 988. Crosses of s-wt and s-hH1 strains with N228 (type 3 and 4 crosses) were designed to test linkage of the hH1RIP allele with increased RIP frequencies observed in crosses of N1815 and N228 (compare type 1 and 2 crosses). Duplications of al-1+ in wild-type (d-wt) or hH1RIP (d-hH1) progeny were obtained by crossing N1815 and N228 and selecting progeny whose al-1+ copies had survived RIP. Eight d-hH1 and seven d-wt strains were crossed with wild-type or hH1RIP strains (type 5 to 8 crosses).
Because all crosses included a parent with a single al-1 gene, the RIP frequency was calculated as (number of white colonies/total number of colonies) × 200.
TABLE 3.
Linear growth rates for wild-type and hH1RIP mutant strains
| Carbon source | Growth rate (mm/h) for the following straina:
|
hH1RIP/wild-type ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | hH1RIP | ||
| Sucrose | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 4.1 ± 0.1 | 0.85 |
| Glucose | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 0.85 |
| Ethanol | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 0.91 |
| Agar | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 0.80 |
Nine wild-type and seven hH1RIP progeny from a cross of N1815 (hH1RIP) and FGSC 988 (wild type) were selected at random. Linear growth rates were determined at 30°C by using Race tubes and Vogel's minimal medium (1.5% agar) supplemented with sucrose, glucose, or ethanol, each at 2%. Duplicate data were obtained for strains grown under the various growth conditions and were pooled for statistical analyses.
Nucleic acid manipulations.
N. crassa genomic DNA was prepared and analyzed as previously described (20, 37). For Southern blot analyses, 0.5 to 1.0 μg of DNA was used. Total mycelial RNA was purified by a method used for plant tissues (68). Northern analyses were performed as described previously (37). The following probes were used for Southern and Northern hybridizations: a 1.2-kb EcoRI hH1fragment from pDF2 (see below), a 1.7-kb BamHI-EcoRI hH1 fragment from pMF233 (see below), 0.6-kb HindIII and 0.2-kb HindIII-EcoRI hH1 fragments from pDF1 (see below), a 537-bp PCR fragment (positions +460 to +997) and a 338-bp PCR fragment (positions −348 to −10) from cfp, a 0.9-kb BanII-EcoO109I Ψ63 (Fsr-63; 5S RNA pseudogene) fragment from pPG22 (43), an 0.8-kb BamHI ζ-η (Fsr-33; 5S RNA pseudogene) fragment from pVM152 (43), a 2.7-kb HindIII his-3 fragment from pBM60 (38), and a 1.1-kb BamHI-ClaI hph fragment from pCSN44. For methylation analyses, genomic DNA was digested with methylation-insensitive DpnII or its methylation-sensitive isoschizomer Sau3AI. The his-3 probe was used as a control probe to verify that digestions were complete.
Protein purification and electrophoresis.
Protein purification and electrophoresis were carried out as described previously (53).
Cloning of the hH1 gene.
Genomic DNA (N. crassa FGSC 987) and DNA purified from plate stocks of phage λZAPII from a mycelial cDNA N. crassa library (47) were used as templates in PCR experiments with oligonucleotides NC1 (5′-ACCTTTTGCACGCCCCTT-3′) and HDF1 (5′-AGTGGTATCGTTCCAAGACGG-3′). PCR products of 1.7 kb (genomic DNA) and 1.2 kb (cDNA) were obtained, cloned into the p-GEM T Easy vector (Promega) (plasmids pDF1 and pDF2, respectively), and sequenced.
Because the hH1 gene is not available in Neurospora cosmid libraries, a genomic library of wild-type N. crassa strain FGSC 987 was constructed in the λDASHII vector by using genomic DNA partially digested with Sau3AI (10 to 18 kb) and an in vitro packaging kit (Gigapack II Gold; Stratagene). A positive clone containing the whole hH1 gene was isolated by screening with the 0.2-kb HindIII-EcoRI genomic fragment from pDF1. Oligonucleotide primer H1rt (5′-GGATGTGGTTGTGGTTTTAGG-3′) was used to sequence a 250-bp region upstream of the ATG start translation codon. 5′ Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) was carried out with a 5′/3′ Race kit (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany) and oligonucleotides NC2 (5′-TTCTTGGCAAGCTTGGTGC-3′) and NC4 (5′-CTTGTTGAAGAGCGAGTC-3′). The hH1 gene was mapped by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis (42) with the 0.6-kb HindIII genomic fragment from pDF1 as a probe.
EGFP fusion constructs.
To generate histone H1 fusions to enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), the BamHI-BglII fragment from plasmid pFA6a-GFP(S65T)-kanMX6 (34) was inserted into BamHI-digested pBM60 (38) to yield pMF255. The GFP (S65T) gene was replaced by a PCR-amplified EGFP gene (19), and the fragment was inserted into BamHI-EcoRI-digested pMF255, yielding pMF267. The Neurospora ccg-1 promoter (Pccg-1) and 5′ untranslated region of the transcript directly preceding the ccg-1 ATG (nucleotides 738 to 1659) were PCR amplified and inserted into NotI-XbaI-digested pMF267, yielding pMF272. PCR-amplified Neurospora hH1 was inserted into BamHI-PacI-digested pMF272 to yield pMF280. Both pMF272 and pMF280 were targeted to the his-3 locus of N623 (38), yielding strains N2261 and N2276, respectively. EGFP imaging was performed as previously described (15).
Generating hH1 mutants by RIP
A 1.7-kb BamHI-EcoRI PCR fragment from hH1 DNA cloned into pBM61 (pMF233) was targeted to the his-3 locus (38). Transformants were crossed to strain N1264, and random ascospores were isolated 28 days after fertilization. Strain N1264 is mat A and carries nic-3, which was determined by RFLP analysis (see above) to map closely to hH1 on LG VIIL. Therefore, selection for growth on minimal medium and screening for mat A increased the likelihood of isolating strains with a single mutated hH1 copy at the native locus. We isolated 43 prototrophs, 27 of which were mat A and 22 of which showed evidence of RIP mutations. The mutated alleles of strains N1815 (hH1RIP1), N1817 (hH1RIP2), N1816 (hH1RIP3), and N1819 (hH1RIP4) were amplified by PCR with Pfu DNA polymerase. Products from at least five reactions per strain were pooled prior to sequencing.
Construction of the ectopic cfp-hph reporter locus.
Plasmid pDF12 was generated by ligation of the 2.7-kb ApaI-SacI fragment from pA3, which carries hph under the control of the cfp promoter and the Aspergillus nidulans trpC terminator (E. D. Temporini and A. L. Rosa, unpublished data), into ApaI-SmaI-digested pBM61 (38). Control plasmid pDF85, with a trpC promoter instead of the cfp promoter, was constructed by ligating a 2.4-kb ApaI-NotI fragment from pCSN44 into ApaI-NotI-digested pBM61. These constructs were targeted to his-3 of strains HH3 and HH28, and correct integrations were confirmed by Southern analysis.
MNase digestion of chromatin.
Chromatin structure was analyzed by a modification of a method described for A. nidulans (17). Briefly, N. crassa was grown at 30°C in Vogel's minimal medium with 2% sucrose for 16 h. Ethanol (2%) or glucose (2%) was added, and mycelia were harvested 4 h later and used immediately or freeze-dried. Frozen and powdered mycelia were suspended (100 mg/ml) in a buffer containing 250 mM sucrose, 60 mM KCl, 15 mM NaCl, 0.05 mM CaCl2, 3.0 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, and 15 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), and aliquots were treated with various amounts of MNase for 5 min at 30°C. DNA was purified by phenol extraction and ethanol precipitation, digested with either EcoRI or BglII, and subjected to Southern blot analysis and probing with the 537-bp PCR fragment (+460 to +997) or the 338-bp PCR fragment (−348 to −10) from cfp, respectively.
Sensitivity to MMS, UV, and DMSO.
Neurospora conidia were plated at a density of 500 conidia/plate on Vogel's minimal medium containing 1.5% sorbose, 0.1% glucose, and 0.1% fructose and supplemented with methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) at 0.005, 0.015, or 0.030% (vol/vol). Colonies were counted at 48 and 72 h (24). UV sensitivity was tested as described previously (23). The UV dose was 25 J min−1, and exposure times were 0, 8, 16, 20, and 24 min. For dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) assays, equal numbers of conidia (∼500) were plated on petri dishes containing Vogel's minimal medium with 4.5% DMSO. Colonies were counted after 72 h at 30°C, and morphology was noted.
Measurement of linear growth rates with Race tubes
Linear growth rates were determined at 30°C with glass Race tubes (40 cm long, 12 mm in diameter) (10). Ten microliters of a conidial suspension (∼104/ml) was inoculated at one end, and growth was monitored for 4 days at intervals of 8 to 12 h.
Measurement of RIP frequencies.
Crosses were carried out on Westergaard-Mitchell medium (10) after the “female” strain had grown for 5 days at 25°C in the dark. Random ascospores were harvested, heat activated, and plated on Vogel's minimal medium containing 2% sucrose and 0.0075% Tergitol (Sigma) (59). White (RIP-mutated) and orange (wild-type) colonies were scored by visual inspection.
Microscopic examination of vegetative and sexual tissues.
Asci and chromosomes were visualized by staining with hematoxylin-ferric acetate or acriflavine (50). The number, size, and shape of nuclei (i.e., mycelia and conidia) were determined after staining (Hoechst 33258 or 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI] dyes) and visualization under a fluorescence microscope. Imaging of EGFP was carried out as described previously (15). Strains were grown overnight at room temperature in a thin layer of Vogel's minimal medium without a carbon source on microscope slides to induce the ccg-1 promoter.
Nucleotide sequence accession number.
The GenBank accession number for the sequence reported in this article is AY124883.
RESULTS
Isolation of the hH1 gene from N. crassa.
We identified a histone H1 cDNA clone in a Neurospora expressed sequence tag (EST) database (b7 h12ne; http://www.genome.ou.edu) and used it to design specific primers to isolate the hH1 gene from Neurospora genomic DNA and from a mycelial cDNA library (47) by PCR. We isolated and sequenced a 1.7-kb genomic fragment as well as a 1.2-kb cDNA fragment. Because of uncertainties regarding the N-terminal region of the predicted protein and the promoter region, the entire hH1 gene was cloned from a λDASH N. crassa genomic library (Fig. 1A). We mapped hH1 to the left arm of LG VII between 5:5A and 00003 by RFLP analysis (42) and confirmed by additional Southern analyses that hH1 is the only histone H1 gene in N. crassa (data not shown). This conclusion was further supported by BLAST searches of the >98% completed Neurospora genome sequence (http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/annotation/fungi/neurospora/; release 3: 02.12.2002).
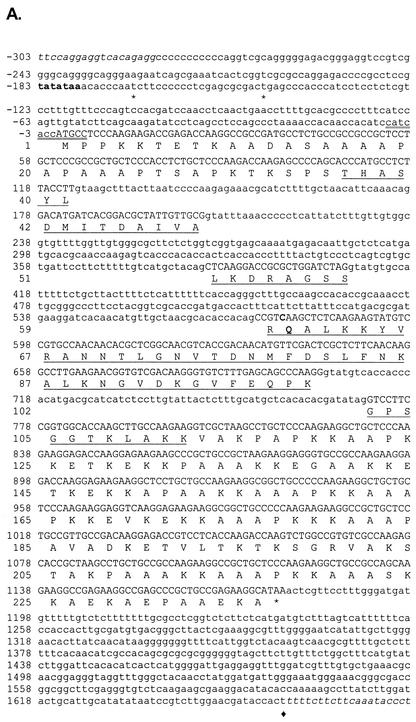
FIG. 1.
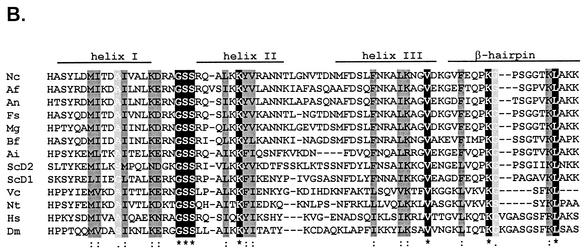
hH1 gene of N. crassa. (A) Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences for the N. crassa hH1 gene. Coding regions are shown in uppercase letters, and noncoding sequences are shown in lowercase letters. Transcription start sites (asterisks) and the 3′ end of the longest available EST sequence (black diamond) are indicated. The putative TATA box is shown in bold type. The sequence around the most likely ATG start codon is doubly underlined. The central globular domain of the protein is underlined. Genomic sequences flanking the hH1 gene, from contig 3.396 (http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/annotation/fungi/neurospora), are shown in italic type. The cytosine at +577 and Q60, mutated in hH1RIP strains, are indicated in bold type. (B) Comparison of the highly conserved globular domains of histone H1 proteins from N. crassa (Nc); A. fumigatus (Af; sequence deduced from data available at http://tigrblast.tigr.org/ufmg/); A. nidulans (An; CAB72936); Fusarium sporotrichioides (Fs), Magnaporthe grisea (Mg), and Botrytis fuckeliana (Bf) (these three sequences deduced from ESTs availables at http://www.cogeme.ex.ac.uk); A. immersus (Ai; AAF16011); S. cerevisiae (ScD1 and ScD2; NP_015198); Volvox carterii (Vc; H1-1; Q08864); tobacco (Nt; S53502); human (Hs; H10; XP_009973); and Drosophila melanogaster (Dm; P02255). Yeast H1 is unconventional because it does not contain N- or C-terminal tails but rather contains two fused globular domains (ScD1 and ScD2). The globular domains were aligned with CLUSTAL W (64). Identical residues (black) are indicated by asterisks, conservative substitutions of major groups (dark gray) are indicated by colons, and conservative substitutions of minor groups (light gray) are indicated by periods. Regions identified as α helices or β sheets in the histone H5 crystal structure are indicated.
Alignment of genomic and cDNA sequences allowed us to determine the positiond of four introns. The G+C content of the hH1 open reading frame (61.2%) is significantly higher than that of the introns (46.4%), consistent with the previously described codon bias for constitutively expressed genes of N. crassa (12). We determined the major transcription start sites by RACE experiments (Fig. 1A) and identified a consensus TATA box (8). Northern blot analyses of total RNA extracted from vegetative mycelium revealed a single 1.4-kb hH1 transcript. RNA levels were similar when mycelia were grown on sucrose, glucose, ethanol, or ethanol-glucose media (data not shown).
The sequence surrounding the most likely initiation codon of hH1, CCATCACCATGCC (initiation codon in italic type), fits the consensus translation start site sequence for Neurospora (7, 12) (Fig. 1A). Conceptual translation of the hH1 open reading frame yields a protein of 236 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 24.2 kDa and high contents of alanine (26.3%) and lysine (23.3%). This predicted protein shows strong similarity to H1 from various organisms, suggesting that hH1 encodes a bona fide histone H1. Sequence alignments revealed that residues 36 to 112 of Neurospora H1 correspond to the globular winged helix domain, the most conserved region of linker histones (Fig. 1B). Moreover, the Neurospora H1 protein shows the characteristic three-domain structure of metazoan histone H1 proteins: (i) an N-terminal region of 35 amino acids, (ii) a globular region of 77 amino acids, and (iii) a positively charged C-terminal region of 124 amino acids. The predicted isoelectric point (10.2) may account for our observation that H1 migrates as a protein of 32 kDa (see below), a behavior shared by its homologs from A. nidulans (53) and A. immersus (4).
An H1-EGFP fusion protein is localized in nuclei.
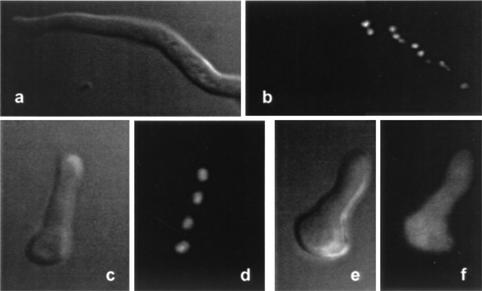
To confirm that Neurospora histone H1 is localized in nuclei, we constructed translational fusions of the H1 and EGFP genes (19) and targeted these fusion constructs to the his-3 locus. Fusion constructs with the native hH1 promoter or the inducible qa-2 promoter did not yield sufficient H1-EGFP for visualization. We therefore made use of the Neurospora ccg-1 (grg-1) promoter (Pccg-1) (41) to drive the overexpression of EGFP fusion genes (see Materials and Methods). Expression patterns observed were typical for normal ccg-1 induction; i.e., on sucrose medium, little or no expression was observed in hyphae growing on or through agar. Fusions of Pccg-1-H1-EGFP genes produced high levels of H1-EGFP fusion protein, localized exclusively in the nucleus (Fig. 2a to d). Control fusions of Pccg-1-EGFP genes produced cytoplasmic EGFP (Fig. 2e and f).
FIG. 2.
EGFP-tagged H1 is localized in nuclei. Overexpressed H1-EGFP fusion protein is exclusively localized in nuclei of fully developed hyphae (a and b) and germinating conidia (c and d) of strain N2276. The nuclear localization of H1-EGFP was confirmed by staining with DAPI (data not shown). Nonfused EGFP expressed under the control of the Pccg-1 promoter is localized in the cytoplasm (e and f) of a germinating conidium of strain N2261. a, c, and e, phase-contrast microscopy; b, d, and f, fluorescence microscopy. EGFP imaging was carried out as described previously (15).
Construction of hH1 mutants.
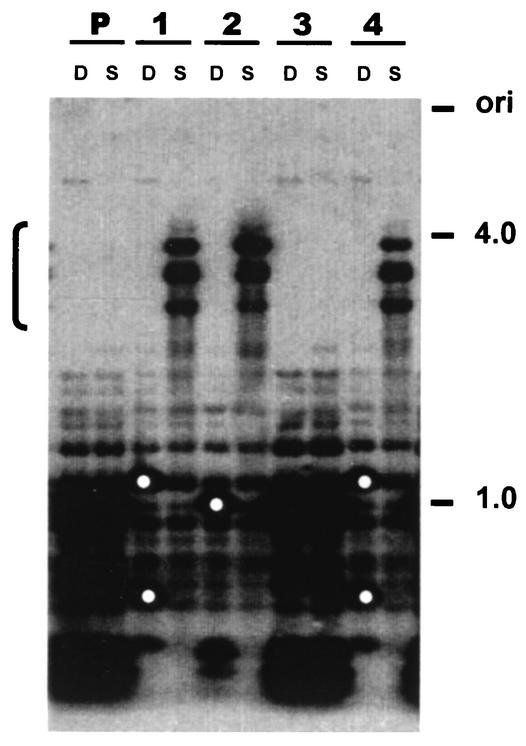
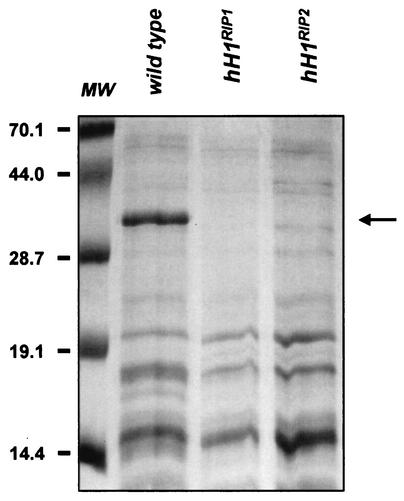
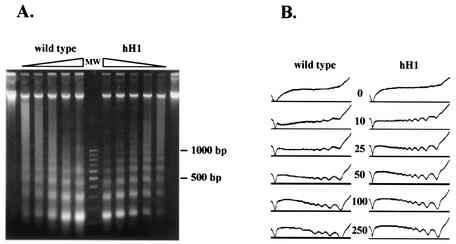
We made use of the RIP process (55) to create hH1 mutants. A 1.7-kb fragment of hH1 was introduced at the his-3 locus (LG IR) by gene replacement (38). Single-copy transformants of mating type mat a (LG IL) were crossed with a mat A strain marked on LG VII (nic-3 wc-1 arg-10). Progeny carrying RIP-mutated alleles at the endogenous hH1 locus were recovered as mat A prototrophs. Southern analysis of genomic DNAs from these strains showed evidence of DNA methylation and C:G to T:A transition mutations, both indicators of RIP (Fig. 3). Four heavily mutated hH1RIP strains were characterized in detail. A 700-bp genomic fragment from the 5′ region of the hH1 gene was amplified by PCR and sequenced. Strains N1815 (hH1RIP1) and N1817 (hH1RIP2) showed the most mutations (85 and 92, respectively) and were therefore selected for further characterization. In addition to missense mutations, both strains have a CAA-to-TAA nonsense mutation at residue Q60 (Fig. 1A). Histone H1 was absent from perchloric acid (PCA) extracts obtained from vegetative tissue of strains N1815 and N1817, confirming that the hH1 gene was disrupted (Fig. 4). No hH1 transcript was detectable by Northern blot analyses of total RNAs isolated from these strains (data not shown). These observations support the conclusion that N. crassa has a single active histone H1 gene.
FIG. 3.
Generation of hH1 mutants by RIP. RFLPs and DNA methylation at the hH1 locus of four RIP-mutated strains are revealed by Southern analysis. Genomic DNA from the parental strain (lanes P) with the hH1 duplication and four prototrophic mat A progeny (lanes 1 to 4) were digested with either DpnII (D; 5-methylcytosine insensitive) or Sau3AI (S; 5-methylcytosine sensitive). Isolates 1, 2, and 4 carry mutated hH1 alleles, as indicated by RFLPs in the DpnII lanes (white dots), and exhibit methylation, as indicated by high-molecular-weight fragments (bracket on the left) in the Sau3AI lanes. Isolate 3 carries two copies of hH1 and may be free of mutations or only sparsely mutated. A 1.7-kb hH1 fragment was used as a probe. Molecular size markers (in kilobases) are shown on the right.
FIG. 4.
Histone H1 is absent from hH1RIP mutants. PCA-soluble protein extracts from N. crassa wild-type and hH1RIP1 and hH1RIP2 mutant strains were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Coomassie blue staining. N. crassa H1 (arrow) is readily identifiable in protein extracts from total mycelium of the wild-type strain. H1 is absent from extracts from total mycelium of the hH1RIP mutant strains. Molecular weight (MW) markers (in thousands) are shown on the left.
Absence of histone H1 does not affect DNA methylation but results in subtle changes in chromatin accessibility to MNase.
Conflicting reports on the association of linker histones with methylated DNA in vivo (3, 27) and in vitro (9, 40) led us to examine effects of the hH1RIP mutants on DNA methylation. Gross global DNA methylation was not affected, as indicated by digestion of total DNA with a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme and staining of gels with ethidium bromide (data not shown). No localized changes in the DNA methylation levels of several known methylated regions tested (ψ63, ζ-η, and ribosomal DNA) (39, 56) were detected in hH1RIP mutants (Fig. 5). These findings are in stark contrast to those of studies with silenced H1 in A. immersus, in which the lack of H1 resulted in global hypermethylation (4).
FIG. 5.
Absence of histone H1 does not affect DNA methylation. For Southern blot analysis, genomic DNAs from a wild-type strain (wt) and two strains with hH1RIP alleles were digested with DpnII (D) or Sau3AI (S) and probed with a 32P-labeled ribosomal DNA repeat. Methylation patterns and relative intensities of bands were identical when wild-type and mutant strains were compared. Molecular size standards (in kilobases) are shown on the right.
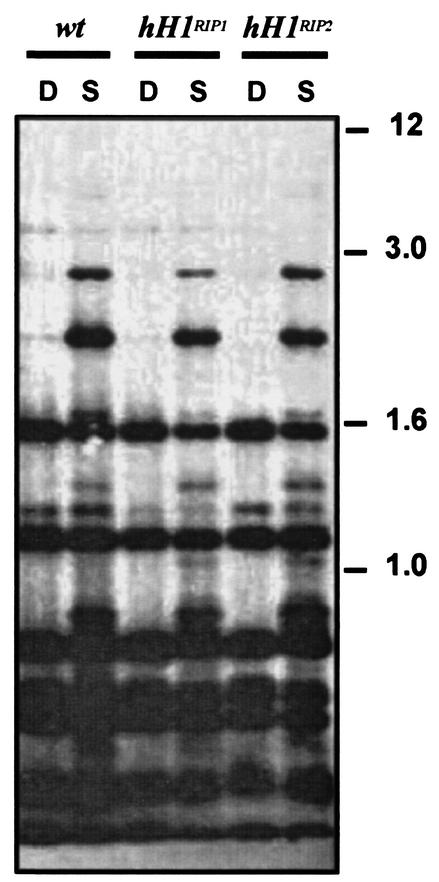
Global chromatin structure was investigated with MNase (17). A subtle alteration in the pattern of nucleosomal DNA digestion was reproducibly found with chromatin from the Neurospora hH1RIP mutants (Fig. 6A). Although the size of the nucleosomal repeat was similar to that in the wild type, a sharper banding pattern was observed in hH1 chromatin. Densitometry confirmed that wild-type chromatin yielded more diffuse bands after nuclease digestion (Fig. 6B). Similar differences were observed with chromatin purified from nuclei (data not shown). These observations are consistent with the idea that in H1-depleted chromatin, linker DNA is abnormally accessible to MNase.
FIG. 6.
Chromatin of hH1RIP mutants is more accessible to MNase. (A) Chromatin from the wild-type strain and a strain carrying an hH1RIP null allele (hH1) was obtained from mycelia and treated with various amounts of MNase (250, 100, 50, 25, 10, and 0 U/g of mycelium, indicated by the ramps). Molecular weight markers are indicated in lane MW. (B) Densitometric analysis of a gel similar to that shown in panel A. Plots were made with the program Scion Image (http://www.scioncorp.com/). A sharper profile of peaks and valleys was observed for hH1 chromatin than for wild-type chromatin. Amounts of MNase in units per gram are indicated between the plots.
Histone H1 is not required during the sexual cycle.
In both heterozygous and homozygous crosses, hH1RIP mutants were fertile when used as either male or female. The development of asci and ascospores was normal, and ascospores exhibited normal morphology, viability, and germination rates. Meiotic chromosomes were stained with hematoxylin-ferric acetate and acriflavine and observed from 3 days postfertilization until the end of ascus development. Compared to controls examined in parallel and also in comparison to the results of previous studies (51), no changes in chromatin condensation or chromosome behavior were observed (data not shown).
To study the effect of histone H1 on RIP mutations, we generated hH1RIP strains carrying a duplication of the al-1 gene (54) by crossing the hH1RIP1 strain (N1815) to an al-1 duplication strain (N228). RIP frequencies in either homozygous or heterozygous crosses were equivalent to those in wild-type control crosses (Table 2).
H1 mutants exhibit a slow linear growth phenotype.
Both hH1RIP null mutants studied (N1815 and N1817) retained normal morphology in liquid or on solid minimal media (Vogel's minimal medium, PPC, and Westergaard-Mitchell medium) (10) at all temperatures tested (10 to 39°C) (data not shown). The size, shape, and distribution of nuclei in mycelia were normal. Mutants produced normal quantities of conidia (asexual spores), with the expected number of nuclei per conidium, and conidia showed normal viability. The mutants also showed normal sensitivity to MMS, UV irradiation, and DMSO. Measurements of linear growth rates, however, revealed that hH1RIP mutants had lower mycelial elongation rates on all carbon sources tested (P < 0.005) (Table 3). This slow linear growth phenotype segregated with the hH1RIP allele (data not shown). Interestingly, hH1 mutants showed better linear growth rates on ethanol (91%) than on sucrose (85%), glucose (85%), or agar (80%) (P < 0.001). Based on these selective responses to different carbon sources, we hypothesized that H1 is required for the expression of one or more specific genes involved in carbon metabolism.
cfp is misregulated in hH1 mutants.
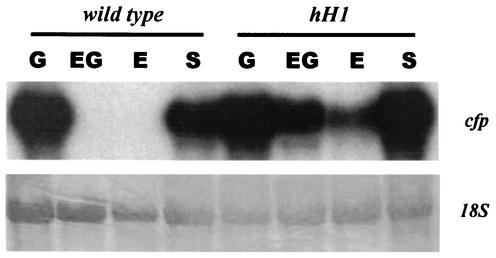
The possibility that H1 plays a regulatory role in carbon metabolism was explored by studying cfp, the Neurospora gene encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (1, 20). Pyruvate decarboxylase is a key postglycolytic enzyme and converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde (65). The expression of the cfp gene is strongly induced by glucose and repressed by ethanol (1). Northern analyses showed that cfp mRNA levels were similar when wild-type and hH1RIP mutants were grown on media containing either sucrose or glucose (Fig. 7). In contrast, no cfp mRNA was detected when the wild-type strain was grown under repressing conditions on media containing ethanol (1) or ethanol-glucose, but cfp mRNA was readily detected when hH1RIP mutants were grown under these conditions (Fig. 7). These results suggested that histone H1 is required for the proper regulation of cfp.
FIG. 7.
The cfp gene is misregulated in N. crassa hH1 mutants. Northern blot analyses of cfp mRNAs were performed with wild-type N. crassa and H1 mutant N1815 (hH1) of N. crassa. Strains were grown for 16 h at 30°C in Vogel's minimal medium containing 2% sucrose. Fresh carbon sources (G, glucose; EG, ethanol plus glucose; E, ethanol; and S, sucrose), each at 2%, were added, and mycelia were harvested 4 h later. The 18S rRNA (stained with methylene blue) is shown as a loading control.
Based on this possibility, we examined the chromatin structure of the cfp promoter region in the wild type and the hH1RIP mutants under inducing and repressing conditions. Chromatin was digested with MNase, treated with EcoRI or BglII, and analyzed by Southern blotting with a cfp probe. Identical MNase patterns were found with chromatin from wild-type and hH1RIP mutant strains grown under inducing conditions (i.e., glucose). The same pattern was observed with hH1RIP mutant strains grown under repressing conditions, while wild-type chromatin from mycelia grown under repressing conditions (i.e., ethanol) showed subtle differences in the MNase pattern (data not shown). These results are consistent with the possibility that cfp is constitutively expressed in hH1RIP mutants, as suggested by the analyses described above (Fig. 7).
We investigated whether the misregulation of cfp in hH1RIP mutants was dependent on the chromosomal position and/or the integrity of the cfp transcriptional unit. A cfp promoter (Pcfp) (positions −847 to −26) was fused to the coding region of the bacterial hph gene, which confers resistance to hygromycin; the fusion was integrated at the Neurospora his-3 locus. Wild-type or hH1RIP mutant strains with a single copy of the reporter Pcfp-hph fusion gene were selected. The expression of the Pcfp-hph gene was examined in strains grown on minimal media with various carbon sources and hygromycin. As a control, we tested a fusion of the constitutive A. nidulans trpC promoter to hph (PtrpC-hph). Both wild-type and hH1RIP cells transformed with the Pcfp-hph fusion were highly resistant to hygromycin under inducing conditions. On ethanol-containing media, however, wild-type cells with the Pcfp-hph fusion were hygromycin-sensitive, whereas hH1RIP mutants with the Pcfp-hph fusion were hygromycin resistant. As expected, wild-type and hH1RIP mutant strains carrying the control PtrpC-hph gene fusion were resistant to hygromycin on media containing either glucose or ethanol as a carbon source (data not shown). These results show that the cfp promoter is misregulated in hH1RIP mutants regardless of whether it is driving the expression of the endogenous cfp gene or expression of a reporter gene at an ectopic location, indicating that the cfp promoter per se is sensitive to negative regulation by H1.
DISCUSSION
The hH1 gene of N. crassa encodes a typical eukaryotic histone H1 composed of a central globular domain flanked by alanine- and lysine-rich regions. Southern blot studies, as well as analyses of available genome sequence data, indicated that hH1 is the only gene encoding a linker histone in N. crassa. Linker histones from filamentous fungi are well conserved (Fig. 1B). The N-terminal tails of Neurospora H1 and Ascobolus H1 are longer (35 and 25 amino acids, respectively) than that of A. nidulans H1 (17 amino acids). These data are consistent with the longer nucleosomal repeats in Neurospora (170 ± 5 bp) (46) and Ascobolus (174 ± 6 bp) (53) than in A. nidulans (159 ± 7 bp) (17). In both A. nidulans and N. crassa, histone H1 tagged with EGFP was localized exclusively in the nucleus, consistent with an association with chromatin.
Based on intron number and distribution, N. crassa hH1 seems to be more closely related to A. nidulans hhoA and a putative H1 gene from Aspergillus fumigatus than to the H1 gene from A. immersus. The positions of the first four introns of the H1 genes from N. crassa, A. nidulans, and A. fumigatus are identical. The position of the first intron of the A. immersus H1 gene is the same as that of the third intron of the Neurospora and Aspergillus H1 genes, suggesting that this is the most ancient intron in the H1 genes of filamentous fungi.
It is now clear that histone H1 and closely related linker histones are not essential in several model organisms—N. crassa, T. thermophila, S. cerevisiae, A. nidulans, and A. immersus—all organisms with single genes for unusual or bona fide linker histones (4, 53, 57, 67). Interestingly, H1 mutants of these organisms exhibited different phenotypes. In T. thermophila, deletion of H1 genes resulted in increases in the volume of nuclei and in alterations in gene expression (57, 58). The function of the atypical H1 in Tetrahymena is regulated by phosphorylation (11). In A. immersus, silencing of the single H1 gene by MIP results in global DNA hypermethylation, a shortened life span, and hypersensitivity of chromatin to digestion with MNase (4). In the yeast S. cerevisiae, deletion of the atypical single HHO1 gene has no dramatic effect on vegetative or sexual phenotypes. Freidkin and Katcoff (14) determined that S. cerevisiae has only approximately one HHO1p molecule per 37 nucleosomes, showing that HHO1p cannot be associated with linker DNA at all nucleosomes. Interestingly, deletion of HHO1 in S. cerevisiae results in a reduction in the steady-state levels of many mRNAs, as shown by microarray analyses (22).
Mycelia from N. crassa hH1 mutants have normal nuclei, and the gross structure of meiotic chromosomes does not appear to be affected during meiosis. It remains possible that the loss of H1 is compensated for by other chromatin proteins, e.g., HMG1-class proteins (45, 73), for which there are at least eight homologs in the Neurospora predicted proteome (M. Freitag and E. U. Selker, unpublished data). Chromatin from hH1 mutants showed somewhat sharper bands in MNase digests, similar to what was seen for A. immersus H1-silenced strains (4). Perhaps linker histones from Ascobolus and Neurospora protect linker DNA from protein access, as expected from in vitro studies with chromatin from higher eukaryotes. No change in MNase digestion behavior was observed for A. nidulans chromatin depleted of H1 (53), consistent with the possibility that the protein encoded by hhoA represents an evolutionary variant with a more specific function. RIP was not affected in Neurospora hH1 mutants. We did not observe global or localized changes in DNA methylation, in contrast to the situation for A. immersus (4).
The slow linear growth phenotype of N. crassa hH1 mutants was dependent on the carbon source, suggesting that histone H1 may play a role in pathways associated with carbohydrate metabolism. Based on the linear growth of hH1 mutants in media containing ethanol versus sucrose or glucose, we expected a change in the balance between respiratory and fermentative pathways. Indeed, in hH1 mutants grown under repressing conditions, the expression of cfp, the gene encoding pyruvate decarboxylase, was misregulated and abnormally high cfp mRNA levels were detected. Moreover, the chromatin structures at the cfp promoter appeared to be identical under either inducing or repressing conditions in hH1 mutants. Perhaps Neurospora chromatin lacking H1 fails to generate the alternative promoter structures associated with normal regulation of the cfp gene.
H1 may affect the expression of certain genes according to their positions in a specific chromosome “neighborhood,” rather than by acting on specific regulatory sequences (16). Nevertheless, an hph reporter gene fused to the cfp promoter and introduced into an ectopic position in the Neurospora genome showed normal H1 dependence for gene expression. This observation suggests that histone H1 specifically modulates cfp expression in N. crassa and that cfp expression is not position dependent.
Our suggestion that histone H1 participates in the expression of specific genes in Neurospora is consistent with previous studies showing that the depletion of H1 resulted in the induction of some genes but in the repression of others (58, 60, 67). Linker histones traditionally have been considered “stabilizers” of higher-order chromatin structure by rendering a condensed chromatin state, but it is also conceivable that histone H1 destabilizes chromatin and thus facilitates interactions of DNA with transcription factors. A recent global analysis of S. cerevisiae showed that several mRNAs exhibit abnormally low steady-state levels in a mutant linker histone background (22). This result indicates that histone H1 can act as a direct or an indirect “facilitator” of gene expression. In this model, the multiple modifications of core histone tails in single nucleosomes, as predicted by the “histone code” (26), may represent various states of a chromatin stabilizer. We propose that histone H1 plays a role in fine-tuning of the expression of a subset of genes involved in primary metabolism. Further studies with Neurospora hH1 mutants and DNA microarrays will explore this hypothesis.
Acknowledgments
H. Diego Folco and Michael Freitag contributed equally to this work. Claudio Scazzocchio is affiliated with Institut Universitaire de France.
We thank Chuck Staben for providing strain N228. We are grateful to D. Perkins, N. Raju, and R. Metzenberg for support, discussions, and suggestions during the study of vegetative and sexual phenotypes of hH1RIP mutants.
This work was supported by grants from CONICET, SETCIP, Fundacion Antorchas (Argentina), and the International Program of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (to A.L.R.); SETCIP-ECOS Sud Action (to A.L.R. and C.S.); the NSF (grant INT-9820195 to E.U.S.); the National Institutes of Health (grant GM35690 to E.U.S. and grant CA73123 to M.F.); and Université Paris-Sud, CNRS, Institut Universitaire de France, and Association pour la Recherche sur la Cancer (to C.S.). Irene García was supported by a Marie Curie Fellowship of the European Union. Ana Ramón was supported by the Fondation de la Recherche Medicale.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alvarez, M. E., A. L. Rosa, E. D. Temporini, A. Wolstenholme, G. Panzetta, L. Patrito, and H. J. Maccioni. 1993. The 59-kDa polypeptide constituent of 8-10-nm cytoplasmic filaments in Neurospora crassa is a pyruvate decarboxylase. Gene 130:253-258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ausio, J. 2000. Are linker histones (histone H1) dispensable for survival? Bioessays 22:873-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ball, D. J., D. S. Gross, and W. T. Garrard. 1983. 5-methylcytosine is localized in nucleosomes that contain histone H1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:5490-5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barra, J. L., L. Rhounim, J. L. Rossignol, and G. Faugeron. 2000. Histone H1 is dispensable for methylation-associated gene silencing in Ascobolus inmersus and essential for long life span. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:61-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baxevanis, A. D., and D. Landsman. 1998. Homology model building of Hho1p supports its role as a yeast histone H1 protein. In Silico Biol. 1:5-11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berger, S. L. 2002. Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12:142-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bruchez, J., J. Eberle, and V. Russo. 1993. Regulatory sequences involved in the translation of Neurospora crassa mRNA: Kozak sequences and stop codons. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 40:85-88. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bruchez, J., J. Eberle, and V. Russo. 1993. Regulatory sequences involved in the transcription of Neurospora crassa genes: CAAT box, TATA box, introns, poly(A) tail formation sequences. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 40:89-96. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Campoy, F. J., R. R. Meehan, S. McKay, J. Nixon, and A. P. Bird. 1995. Binding of histone H1 to DNA is indifferent to methylation at CpG sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 270:26473-26481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Davis, R. H. 2000. Neurospora: contributions of a model organism. Oxford University Press, New York, N.Y.
- 11.Dou, Y., and M. A. Gorovsky. 2000. Phosphorylation of linker histone H1 regulates gene expression in vivo by creating a charge patch. Mol. Cell 6:225-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Edelmann, S. E., and C. Staben. 1994. A statistical analysis of sequence features within genes from Neurospora crassa. Exp. Mycol. 18:70-81. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fan, Y., A. Sirotkin, R. G. Russell, J. Ayala, and A. I. Skoultchi. 2001. Individual somatic H1 subtypes are dispensable for mouse development even in mice lacking the H1(0) replacement subtype. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21:7933-7943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Freidkin, I., and D. J. Katcoff. 2001. Specific distribution of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae linker histone homolog HHO1p in the chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:4043-4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Freitag, M., L. M. Ciuffetti, and E. U. Selker. 2001. Expression and visualization of green fluorescent protein (GFP) in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 48:15-19. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Georgel, P. T., and J. C. Hansen. 2001. Linker histone function in chromatin: dual mechanisms of action. Biochem. Cell Biol. 79:313-316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gonzalez, R., and C. Scazzocchio. 1997. A rapid method for chromatin structure analysis in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3955-3956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gunjan, A., D. B. Sittman, and D. T. Brown. 2001. Core histone acetylation is regulated by linker histone stoichiometry in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 276:3635-3640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haas, J., E. C. Park, and B. Seed. 1996. Codon usage limitation in the expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr. Biol. 6:315-324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haedo, S. D., E. D. Temporini, M. E. Alvarez, H. J. Maccioni, and A. L. Rosa. 1992. Molecular cloning of a gene (cfp) encoding the cytoplasmic filament protein P59Nc and its genetic relationship to the snowflake locus of Neurospora crassa. Genetics 131:575-580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hays, S. M., J. Swanson, and E. U. Selker. 2002. Identification and characterization of the genes encoding the core histones and histone variants of Neurospora crassa. Genetics 160:961-973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hellauer, K., E. Sirard, and B. Turcotte. 2001. Decreased expression of specific genes in yeast cells lacking histone H1. J. Biol. Chem. 276:13587-13592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Inoue, H., R. C. Harvey, D. F. Callen, and F. J. De Serres. 1981. Mutagenesis at the ad-3A and ad-3B loci in haploid UV-sensitive strains of Neurospora crassa. V. Comparison of dose-response curves of single- and double-mutant strains with wild-type. Mutat. Res. 84:49-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Inoue, H., and C. Ishii. 1984. Isolation and characterization of MMS-sensitive mutants of Neurospora crassa. Mutat. Res. 125:185-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jedrusik, M. A., and E. Schulze. 2001. A single histone H1 isoform (H1.1) is essential for chromatin silencing and germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 128:1069-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jenuwein, T., and C. D. Allis. 2001. Translating the histone code. Science 293:1074-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jost, J.-P., and J. Hofsteenge. 1992. The repressor MDBP-2 is a member of the histone H1 family that binds preferentially in vitro and in vivo to methylated nonspecific DNA sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:9499-9503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kasinsky, H. E., J. D. Lewis, J. B. Dacks, and J. Ausio. 2001. Origin of H1 linker histones. FASEB J. 15:34-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khochbin, S. 2001. Histone H1 diversity: bridging regulatory signals to linker histone function. Gene 271:1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khochbin, S., and A. P. Wolffe. 1994. Developmentally regulated expression of linker-histone variants in vertebrates. Eur. J. Biochem. 225:501-510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kornberg, R. D., and Y. Lorch. 1999. Twenty-five years of the nucleosome, fundamental particle of the eukaryote chromosome. Cell 98:285-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kouzminova, E., and E. U. Selker. 2001. dim-2 encodes a DNA methyltransferase responsible for all known cytosine methylation in Neurospora. EMBO J. 20:4309-4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lever, M. A., J. P. Th'ng, X. Sun, and M. J. Hendzel. 2000. Rapid exchange of histone H1.1 on chromatin in living human cells. Nature 408:873-876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Longtine, M. S., A. McKenzie, D. J. Demarini, N. G. Shah, A. Wach, A. Brachat, P. Philippsen, and J. R. Pringle. 1998. Additional modules for versatile ands economical PCR-based gene deletion and modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14:953-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Luger, K., A. W. Mader, R. K. Richmond, D. F. Sargent, and T. J. Richmond. 1997. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 389:251-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luger, K., and T. J. Richmond. 1998. The histone tails of the nucleosome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8:140-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luo, Z., M. Freitag, and M. S. Sachs. 1995. Translational regulation in response to changes in amino acid availability in Neurospora crassa. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:5235-5245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Margolin, B. S., M. Freitag, and E. U. Selker. 1997. Improved plasmids for gene targeting at the his-3 locus of Neurospora crassa by electroporation. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 44:34-36. (Author's correction, 47:112, 2000.)
- 39.Margolin, B. S., P. W. Garrett-Engele, J. N. Stevens, D. Yen-Fritz, C. Garrett-Engele, R. L. Metzenberg, and E. U. Selker. 1998. A methylated Neurospora 5S rRNA pseudogene contains a transposable element inactivated by RIP. Genetics 149:1787-1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McArthur, M., and J. O. Thomas. 1996. A preference of histone H1 for methylated DNA. EMBO J. 15:1705-1714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.McNally, M. T., and S. J. Free. 1988. Isolation and characterization of a Neurospora glucose-repressible gene. Curr. Genet. 14:545-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Metzenberg, R. L., J. N. Stevens, E. U. Selker, and E. Morzycka-Wroblewska. 1985. Identification and chromosomal distribution of 5S rRNA genes in Neurospora crassa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:2067-2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Miao, V., M. Freitag, and E. U. Selker. 2000. Short TpA-rich segments of the zeta-eta region induce DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. J. Mol. Biol. 300:249-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Misteli, T., A. Gunjan, R. Hock, M. Bustin, and D. T. Brown. 2000. Dynamic binding of histone H1 to chromatin in living cells. Nature 408:877-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nightingale, K., S. Dimitrov, R. Reeves, and A. P. Wolffe. 1996. Evidence for a shared structural role for HMG1 and linker histones B4 and H1 in organizing chromatin. EMBO J. 15:548-561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Noll, M. 1976. Differences and similarities in chromatin structures of Neurospora crassa and higher eukaryotes. Cell 8:349-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Orbach, M. J., M. S. Sachs, and C. Yanofsky. 1990. The Neurospora crassa arg-2 locus. J. Biol. Chem. 111:543-551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pennings, S., G. Meersseman, and E. M. Bradbury. 1994. Linker histones H1 and H5 prevent the mobility of positioned nucleosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:10275-10279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Prymakowska-Bosak, M., M. R. Przewloka, J. Slusarczyk, M. Kuras, J. Lichota, B. Kilianczyk, and A. Jerzmanowski. 1999. Linker histones play a role in male meiosis and the development of pollen grains in tobacco. Plant Cell 11:2317-2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Raju, N. B. 1986. A simple fluorescent staining method for meiotic chromosomes of Neurospora. Mycologia 78:901-906. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Raju, N. B. 1992. Genetic control of the sexual cycle in Neurospora. Mycol. Res. 96:241-262. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ramakrishnan, V. 1997. Histone H1 and chromatin higher-order structure. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 7:215-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ramón, A., M. I. Muro-Pastor, C. Scazzocchio, and R. Gonzalez. 2000. Deletion of the unique gene encoding a typical histone H1 has no apparent phenotype in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 35:223-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schmidhauser, T. J., F. R. Lauter, V. E. Russo, and C. Yanofsky. 1990. Cloning, sequence, and photoregulation of al-1, a carotenoid biosynthetic gene of Neurospora crassa. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:5064-5070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Selker, E. U. 2002. Repeat-induced gene silencing in fungi. Adv. Genet. 46:439-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Selker, E. U., and J. N. Stevens. 1985. DNA methylation at asymmetric sites is associated with numerous transition mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8114-8118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shen, X., L. Yu, J. W. Weir, and M. A. Gorovsky. 1995. Linker histones are not essential and affect chromatin condensation in vivo. Cell 82:47-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Shen, X., and M. A. Gorovsky. 1996. Linker histone H1 regulates specific gene expression but not global transcription in vivo. Cell 86:475-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Springer, M. L. 1991. Tergitol-induced colonial growth without inhibition of conidiation. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 38:92. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takami, Y., and T. Nakayama. 1997. A single copy of linker H1 genes is enough for proliferation of the DT40 chicken B cell line, and linker H1 variants participate in regulation of gene expression. Genes Cells 2:711-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tamaru, H., and E. U. Selker. 2001. Histone H3 methyltransferase controls DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. Nature 414:277-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Thoma, F. T., T. Koller, and A. Klug. 1979. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J. Cell Biol. 83:403-427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Thomas, J. O. 1999. Histone H1: location and role. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11:312-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Thompson, J. D., D. G. Higgins, and T. J. Gibson. 1994. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignement through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choices. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:4673-4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ullrich, J. 1982. Structure-function relationships in pyruvate decarboxylase of yeast and wheat germ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 378:287-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ura, K., J. J. Hayes, and A. P. Wolffe. 1995. A positive role for nucleosome mobility in the transcriptional activity of chromatin templates: restriction by linker histones. EMBO J. 14:3752-3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ushinsky, S. C., H. Bussey, A. A. Ahmed, Y. Wang, J. Friesen, B. A. Williams, and R. K. Storms. 1997. Histone H1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 13:151-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wadsworth, G. H., M. H. Redinbaugh, and J. G. Scandalios. 1988. A procedure for the small-scale isolation of plant RNA suitable for RNA blot analysis. Anal. Biochem. 172:279-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Weintraub, H. 1984. Histone H1-dependent chromatin superstructures and the suppression of gene activity. Cell 38:17-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wolffe, A. P. 1989. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 8:527-537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Woodcock, C. L., and S. Dimitrov. 2001. Higher-order structure of chromatin and chromosomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:130-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wu, M., C. D. Allis, R. Richman, R. G. Cook, and M. A. Gorovsky. 1986. An intervening sequence in an unusual histone H1 gene of Tetrahymena thermophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:8674-8678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zlatanova, J., and K. Van Holde. 1998. Linker histones versus HMG1/2: a struggle for dominance? Bioessays 20:584-588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]