Abstract
A method is described for the simultaneous measurement of flow rate, mean transit time, and volume of the intestine during the transport of fluid through a segment of the small intestine of the dog.
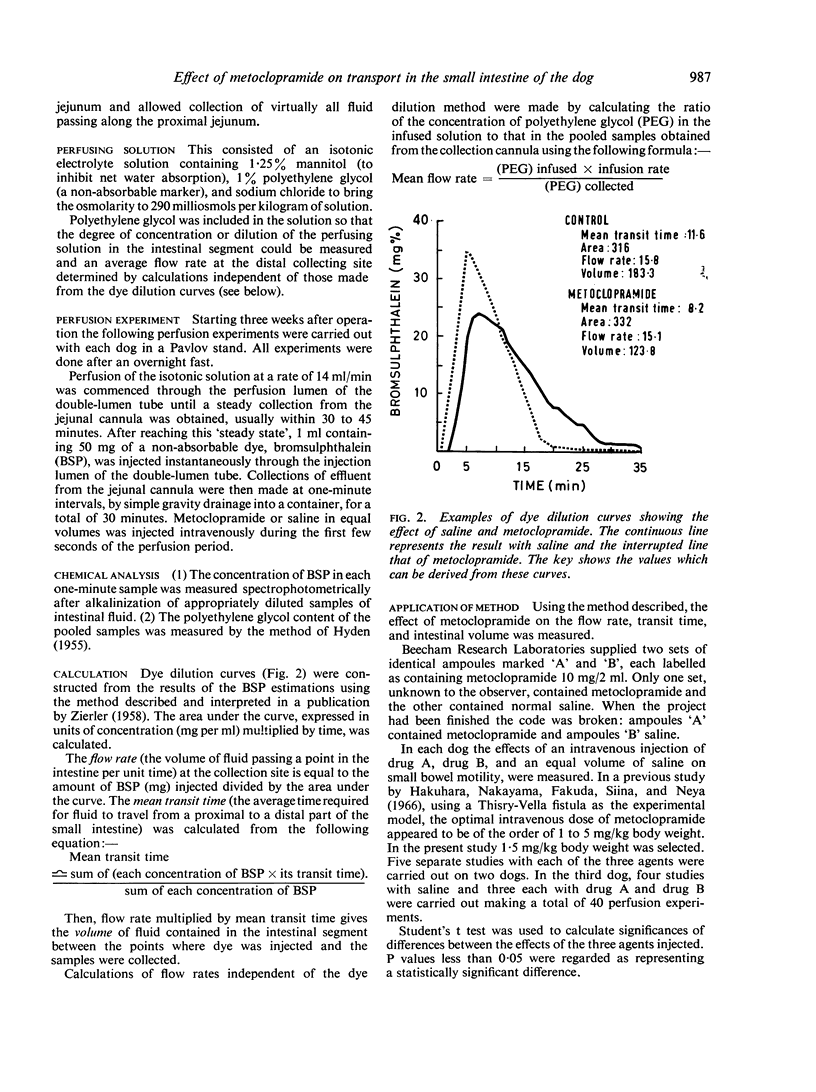
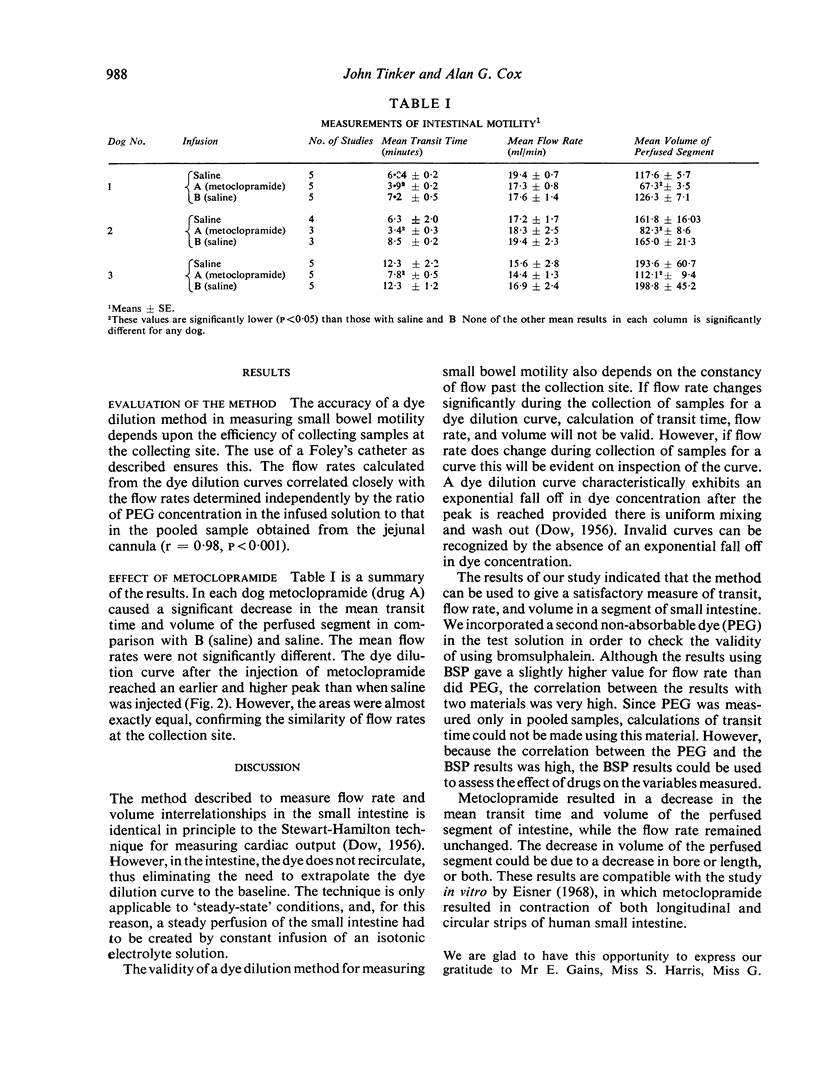
Using this method, the effect of metoclopramide on motility of the small bowel was assessed. The drug resulted in a decrease in transit time and volume in the test segment of bowel while the flow rate remained constant. This finding suggests that metoclopramide-stimulated contraction of intestinal smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOW P. Estimations of cardiac output and central blood volume by dye dilution. Physiol Rev. 1956 Jan;36(1):77–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner M. Gastrointestinal effects of metoclopramide in man. In vitro experiments with human smooth muscle preparations. Br Med J. 1968 Dec 14;4(5632):679–680. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5632.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUSTIN-BESANCON L., LAVILLE C. ACTION ANTI'EM'ETIQUE DU M'ETOCLOPRAMIDE VIS-'A-VIS DE L'APOMORPHINE ET DE L'HYDERGINE. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1964;158:723–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUSTIN-BESANCON L., LAVILLE C., THOMINET M. LE M'ETOCLOPRAMIDE ET SES HOMOLOGUES. INTRODUCTION 'A LEUR 'ETUDE BIOLOGIQUE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Apr 27;258:4384–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby H. I., Brodie D. A. Gastrointestinal actions of metoclopramide. An experimental study. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):676–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. B., Hume R. Action of metoclopramide on gastric emptying and small bowel transit time. Gut. 1968 Apr;9(2):203–205. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. A simplified explanation of the theory of indicator-dilution for measurement of fluid flow and volume and other distributive phenomena. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1958 Oct;103(4):199–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



